![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Marketing Channel (channel of distribution)
|
A set of interdependent organizations that ease the transfer of ownership as products move from producer to business user or consumer.
|
|
|
Channel Members
|
All parties in the marketing channel that negotiate with one another, buy and sell products, and facilitate the change of ownership between buyer and seller in the course of moving the product from the manufacturer into the hands of the final consumer.
|
|
|
Supply Chain
|
The connected chaning of all of the business entities, both internal and external to the company, that perfom or support the logistics function.
|
|
|
Discrepancy of Quantity
|
The difference between the amount of product produced and the amount an end user wants to buy.
|
|
|
Discrepancy of Assortment
|
the lack of all the items a customer needs to receive full satisfaction from a products or products.
|
|
|
Temporal Discrepancy
|
A situation that occurs when a product is produced but a customer is not ready to buy it.
|
|
|
Spatial Discrepancy
|
The difference between the location of a producer and the location of widely scattered markets.
|
|
|
Retailer
|
A channel intermediary that sells mainly to consumers.
|
|
|
Merchant Wholesaler
|
An institution that busy goods from manufactuers and resells them to bussinesses, government agencies, and other wholesalers or retailers and that receives and takes titles to goods, stores them in its own warehousees, and later ships them.
|
|
|
what allows for rapid acquisition of antibiotic resitance genes in bacteria?
|
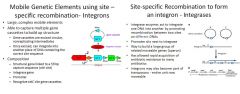
site-specific recombination involving intergrases
|
|
|
Logistics
|
The process of strategically managing the efficient flow and storage of raw materials, in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
|
|
|
Direct Channel
|
A distribution channel in which producers sell directly to consumers.
|
|
|
Dual Distribution (multiple distribution)
|
The use of two (or more) channels to distribute the same product to target markets.
|
|
|
Strategic Channel Allisance
|
A cooperative agreements between business firms to use the other's already established distribution channel.
|
|
|
Supply Chain Management
|
A management system that coordinates and integrates all of the activities performed by supply chain members in to a seemless process, from the source to the point of consumption, resulting in enhanced customer and economic value.
|
|
|
Intensive Distribution
|
A form of distribution aimed at having a product available in every outlet where target customers might want to buy it.
|
|
|
Selective Distribution
|
A form of distribution achieved by screening dealers t oeliminate all but a few in any single area.
|
|
|
Exclusive Distribution
|
A form of distribution that establisehd on or a few dealers within a given area.
|
|
|
Channel Power
|
The cpacity of a particular marketing channel member to control or influence the behavior of other channel members.
|
|
|
the state of F factor, F+ means what?
|
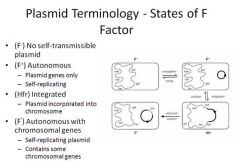
autonomous plasmid with plasmid genes only that is capable of self-replication
|
|
|
Channel Leader (channel captain)
|
A member of a marketing channel that exercises authority and power over the activities of other channel members.
|
|
|
Channel Conflict
|
A clash of goals and mthods between distribution channel members.
|
|
|
Horizontal Conflict
|
A channel conflict that occurs among channel members on the same level.
|
|
|
Verticle Conflict
|
A channel conflict that occurs between different levels in a marketing channel, most typically between the manufacturere and wholesaler or between the manufacturer and retailer.
|
|
|
Channel Partnering (channel cooperation)
|
The joing effort of all channel members to create a supply chain that serves customers and creates a competitve advantage.
|
|
|
Logistics Information System
|
The link that connects all of the logistics components of the supply chain.
|
|
|
Supply Chain Team
|
An entire group of individuals who orchestrate the movement of goods, services, and information from the source to the consumer.
|
|
|
Mass Customization (build-to-order)
|
A production method wherby products are nor made until an order in placed by the customer, products are made according to customer specifications.
|
|
|
Just-in-Time Production (JIT)
|
A process that redefines and simplifies manufacturing by reducing inventory levels and delivering raw materials just when they are needed on the production line.
|
|
|
which bacteria is a colonizer of nares, skin, GI tract, GU tract with a sixty year history of antibiotic resistance?
|
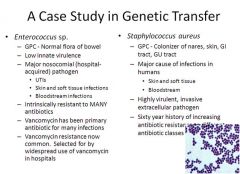
staphylococcus aureus - highly virulent and invasive extracellular pathogen
|
|
|
Electronice data Interchange (EDI)
|
Information technology that replaces the paper documents that usually accompany business transactions, such as purchase orders and invoices, with electronic transmission of the needed information to reduce inventory levels, improve cash flow, streamline operations, and increase the speed and accuracy of information transimission.
|
|
|
Inventory Control System
|
A method of dveloping and maintaining an adequate assortment of materials or products or products to meet a manufacturer's or customer's demand.
|
|
|
Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) (materials management)
|
An inventory control systme that manages the replenishment of raw materials, supplies, and components from the supplier to the manufacturer.
|
|
|
Distribution Resource Planning (DRP)
|
AN inventory control system that manages the replenishment of goods from the manufacture to the final consumer.
|
|
|
Materials-Handling System
|
A method of moving inventory into, within, and out of the warehouse.
|
|
|
Outsourcing (Contract Logistics)
|
A manufacturer's or supplier's use of an independent third party to manage an entire function of the logistics system such as transportation, warehousing, or order processing.
|
|
|
Electronic Distribution
|
A distribution technique that includes any kind of product or service that can be distributed electronicall, whether over traditional forms such as fiber-optic cable or through satelite transmissino of elctronic signals.
|
|
|
Retailing
|
All the activities directly related to the sale of goods and services to the ultimate consumer for personal, nonbusiness use.
|
|
|
Independent Retailers
|
Retailers owned by a single person or partnership and not operated as part of a larger retail institution.
|
|
|
Chain Stores
|
Stores owned and operated as a group by a single organization.
|
|
|
Franchise
|
The right to operate a business or to sell a product.
|
|
|
Gross Margin
|
The amount of money the retailer makes as a percentage of sales after the cost of goods sold is subtracted.
|
|
|
Department Store
|
A store housing several departments under one roof.
|
|
|
Buyer
|
A department head who selects the merchandise for his or her department and may also be responsible for promotion and personnel.
|
|
|
Specialty Store
|
A retail store specializing in a given type of merchandise.
|
|
|
Supermarket
|
A large, departmentalized, self-service retailer that specializes in food and some nonfood items.
|
|
|
Scrambled Merchandising
|
The tendency to offer a wider variety of nontraditional goods and services under one roof.
|
|
|
Drugstore
|
A retail sstore that stocks pharmacy-related products and services as its main draw.
|
|
|
Convenience Store
|
A miniature supermarket, carrying only a limited line of high-turnover convenience goods.
|
|
|
Discound Store
|
A retailer that competes on the basis of low prices, high turnover, and high volume.
|
|
|
Full-Line Discount Stores
|
A retailer that offers consumers very limited service and carries a broad assortment of well-known, nationally branded "hard goods".
|
|
|
Mass Merchandising
|
A retailing strategy using moderate to low prices on large quantities of merchandise and lower service to stimulate high turnover of products.
|
|
|
Supercenter
|
A retail store that combines groceries and general merchandise goods with a wide range of services.
|
|
|
Specialty Discount Store
|
A retail store that offers a nearly complete selections of single-line merchandise and usese self-service , discount prices, high volume, and high turnover.
|
|
|
Category Killers
|
Specialty discount stores that heavily dominate their narrow merchandise segment.
|
|
|
Warehouse Membership Clubs
|
Limited-service merchant wholesalers that sell a limited selection of brand name appliances, household items, and groceries on a cash-and-carry basis to members,usually small business and groups.
|
|
|
Off-Price Retailer
|
A retailer that sells at prices 25 percent or more below traditional department store prices because it pasy cahs for its stock and usually doesn't ask for return privileges.
|
|
|
Factory Outlet
|
An off-price retailer that is owned and operated by a manufacturer.
|
|
|
Nonstore Retailing
|
Shopping without visiting a store.
|
|
|
Automatic Vending
|
The use of machine to offer goods for sale.
|
|
|
Direct Retailing
|
The selling of products by representatives who work door-to-door, office-to-office, or at home parties.
|
|
|
Direct Marketing (direct-response marketing)
|
Techniques used to get consumers to make a purchase from their home, office, or another nonretail setting.
|
|
|
Telemarketing
|
The use of the telephone to sell directly to consumers.
|
|
|
Online Retailing
|
A type of shopping available to constumer with acess to the internet.
|
|
|
Franchisor
|
The originator of a trade name, product, methods of operations, and so on, that grants operating rights to another party to sell its product.
|
|
|
Franchisee
|
An individual or business that is granted the right to sell another party's product.
|
|
|
Retailing Mix
|
A combination of the six P's to sell goods and services to the ultimate consumer.
|
|
|
Product Offering
|
The mix of products offered to the consumer by the retailer; also called the product assortment or merchandise mix.
|
|
|
Destination Stores
|
Stores that consumers purposely plan to visit.
|
|
|
Atmosphere
|
The overall impression conveyed by a store's physical layout, decor, and surroundings.
|

