![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Marine biology |
The study of organisms that live in the ocean. |
|
|
What are the four types of oceanography? |
Physical, chemical, biological, geological. |
|
|
Physical oceanography |
The movement of water; waves, currents, tsunamis. |
|
|
Chemical oceanography |
Chemistry of the ocean; salinity, pH, temperature. |
|
|
biological oceanography |
Where organisms are found. |
|
|
Geological oceanography |
Plate tectonics, volcanoes |
|
|
Who is considered to be the first real marine biologist? |
Aristotle - first to really look at the ocean. |
|
|
Why is James Cook important to the field of marine biology? |
First captain to have a full-time naturalist on board his ship. |
|
|
Why is Charles Darwin important to marine biology? |
Describe how atolls were formed. |
|
|
What does sonar stand for? |
Sound navigation ranging |
|
|
What does ROV stand for? |
Remote operated vehicles |
|
|
Where does an ROV operate from and what is it used for? |
Operates from a distance on the surface. Used for rescue scuba divers collect samples. |
|
|
What does AUV stand for? |
Autonomic operated vehicle |
|
|
Where does an AUV operate from and what is it used for? |
It is controlled by itself (computer program). Used for taking chemistry data. |
|
|
What is an Aquarius? |
Underwater lab |
|
|
What are the steps of scientific method? |
Observation > question > hypothesis > prediction > experiments > results. The scientific method is circular. |
|
|
What was the first voyage done for scientific purposes? |
Challenger expedition |
|
|
What did the invention Marine Laboratories allow? |
Allowed us to study marine organisms alive |
|
|
What did the invention of scuba allow us to do? |
Allowed us to look at organisms in natural habitat |
|
|
Covalent bond |
Sharing of electrons. Strongest bond. |
|
|
Ionic bond |
Taking of electrons. Weaker than covalent bonds. |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
No movement of electrons. Opposites attract with positive hydrogen. Both strong and weak depends on temperature. |
|
|
Molecules |
Combination of two or more atoms. |
|
|
Elements |
Substance composed of a single type of atom. |
|
|
What is the basic unit of matter? |
Atoms |
|
|
Why is water polar? |
It shares electrons unequally. |
|
|
The three states of water? |
Ice, liquid, gas |
|
|
Which state has a strong hydrogen bond? |
Ice - less dense |
|
|
Which state has the weakest hydrogen bonds? |
Gas |
|
|
Which state has fluid hydrogen bonds? |
Liquid - denser than ice |
|
|
Ice state occurs at what degree? |
0 degrees and below |
|
|
At what degree does liquid state occur? |
0 degrees to 100 degrees |
|
|
At what degree does the gas state occur? |
100 degrees and over |
|
|
What is the number of protons and electrons in an element? |
Its atomic number |
|
|
What are two interesting things about water? |
High heat capacity, great solvent. |
|
|
What is the amount of heat that must be added to a substance to raise the temperature by a certain degree? |
Heat capacity |
|
|
Why is water a great solvent? |
Because its polar |
|
|
What is a solvent? |
The thing that's doing the dissolving |
|
|
What is the solute? |
The thing that is being dissolved |
|
|
Ions created form ionic bonds are called? |
Salts |
|
|
What are the most common types of salts that make up salinity in the ocean? |
Sodium, chloride |
|
|
What is the salinity of the ocean? |
35 parts per thousand (0/00) |
|
|
What happens to salt when water freezes or evaporates? |
It leaves the salt behind |
|
|
Is the temperature of the water the same everywhere? |
Deep down yes. Up and around the surface no. |
|
|
Is the salinity of the ocean the same everywhere? |
No |
|
|
Where is the warmest water located? |
Near or on the equator |
|
|
Where is the coldest water located? |
In the poles |
|
|
The temperature changes from surface temperature to colder deeper water temperatures is called? |
Thermocline |
|
|
How do positive ions that make up salt get into the ocean? |
Positive ions get in through litogenous sediment brought from rivers and streams |
|
|
How do negative ions that make up salt get into the ocean? |
Negative ions get in through volcanic eruptions and hydrothermal vents. |
|
|
What are the four major building blocks of life? |
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids. |
|
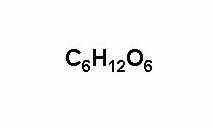
|
Glucose |
|
|
List three functions of proteins? |
Enzymes, hormones, toxins. |
|
|
What is DNA? |
deoxyribonucleic acid- double stranded |
|
|
What is RNA? |
Ribonucleic acid - single-stranded |
|
|
what nucleotide bases are found in DNA? |
AGTC |
|
|
What nucleotide bases are found in RNA? |
AGUC |
|
|
What is the purpose of an enzyme? |
Quicken chemical reactions (catalyst) |
|
|
In DNA G matches to? And aA matches to? |
C and T |
|
|
In RNA A matches to? And G matches to? |
U and C |
|
|
What is the function of cellulose and what is it found in? |
Makes up fiber, support cell walls (structure) . Found in plants and algae |
|
|
what is the function of chitin and what is it found in? |
Support of cell wall (structure) . Found in fungi and arthropods. |
|
|
What is the function of glycogen and what is it found in? |
Used for energy storage. Found in animals. |
|
|
What is the function of peptidoglycan and what is it found in? |
Support of cell wall (structure) . Found in bacteria. |
|
|
What is the function of starch and what is it found? |
Used as a form of energy storage. Found in plants and algae. |
|
|
What is ATP? |
(Adenosine tri-phosphate) an energy source (eating food makes ATP) |
|
|
What types of organisms do photosynthesis, what are they called? |
Plants, algae, and bacteria. Autotrophs |
|
|
What organelle in eukaryotes does photosynthesis? |
Chloroplasts |
|
|
Other organisms that produce energy not using the Sun are called? |
Chemoautotrophs |
|
|
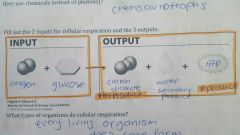
What types of organisms to cellular respiration? |
Every living organism does some form |
|
|
What types of organisms only do cellular respiration what are they called? |
Heterotroph |
|
|
What organelle in eukaryotes does cellular respiration? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
What are the two types of cellular respiration? |
Anaerobic, aerobic |
|
|
Anaerobic cellular respiration uses... |
Oxygen and is very efficient |
|
|
Aerobic cellular respiration uses... |
Something other than oxygen and is not as efficient |
|
|
What organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? |
Vacuole, chloroplast, & a cell wall |
|
|
What is the characteristics of a prokaryote cell and who has this type of cell? |
Simple, small, non nucleus, circular DNA. Bacteria and archaea. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a eukaryote cell and who has this type of cell? |
Complex, large nucleus, linear DNA, membrane bound organelles. Everything besides bacteria and archaea |
|
|
what is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What is the movement of water over a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower concentration of solutes to an higher concentration of solutes? |
Osmosis |
|
|
What does not use energy to move molecules in and out of the cell? |
Passive transport (Moves with diffusion) |
|
|
What uses energy, ATP, to move molecules in and out of cell? |
Active transport (Moves against diffusion) |
|
|
What are the two types of osmoregulation found in animals? |
Osmoconformer, osmoregulators |
|
|
Osmoconformers... |
Salinity in the body is the same as outside |
|
|
Osmoregulators... |
Control internal salinity concentrations to be different than outside |
|
|
Ways organisms thermoregulate: ectothermic |
Can't maintain metabolic heat body temperature imitates external temperature. Body heat generated leaves |
|
|
Ways organisms thermoregulate: endothermic |
Maintain metabolic heat internal temperature stays warmer than external temperature. Body heat generated stays. |
|
|
Ways organisms thermoregulate: polikilotherm |
Temperature varies with external temperature |
|
|
Ways organisms thermoregulate: homeotherm |
Regulate body temperature, does not vary as much as external temperature. |
|

|
Know |
|
|
Two types of cell division? |
Mitosis, meiosis. |
|
|
Two equal daughter cells. Identical to each other and parent cells. Happens everywhere except testes and ovaries. |
Mitosis |
|
|
4 daughter cells that are not the same genetically. Have genetic info from parent cell. Happens in testes and ovaries. |
Meiosis |
|

|
Know |
|
|
Know |
|
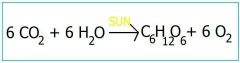
|
Photosynthesis formula |
|

Know how to draw |
Atomic number, symbol, name, mass. |
|
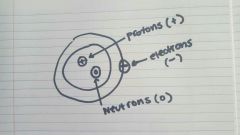
Know how to draw |
An atom |
|
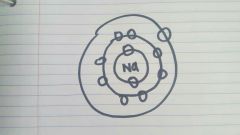
Know how to draw an |
Electron configuration |

