![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Efficiency |
How productively recourses are used to achieve goal |
|
|
Effectiveness |
The degree in which the organization achieves the goals and the appropriateness of the goals |
|
|
Functions of management |
1. Individuals learn through personal experience |
|
|
Functions of management |
2. Economic benefit 3. Help make good decisions |
|
|
Controlling |
Establish accurate measuring and monitoring systems to evaluate how well the organization has achieved its goals |
|
|
Planning |
Choose appropriate organizational goals of the courses of action to best achieve those goals |
|
|
Leading |
Motivate corded night and energize individuals and groups to work together to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
Organizing |
Astablish task and authority relationships that allow people to work together to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
Decisional role |
Entrepreneur Disturbance handler Resource allocator Negotiator |
|
|
Interpersonal |
Figurehead Leader Laison |
|
|
Interpersonal |
Figurehead Leader Laison |
|
|
Informational role |
Monitor Disseminator Spokesperson |
|
|
First line managers |
Lowest: responsible for the daily supervision of the nonmanagerial employees |
|
|
First line managers |
Lowest: responsible for the daily supervision of the nonmanagerial employees |
|
|
Middle managers |
Supervises first-line managers Responsible for finding the best way to use resources to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
First line managers |
Lowest: responsible for the daily supervision of the nonmanagerial employees |
|
|
Middle managers |
Supervises first-line managers Responsible for finding the best way to use resources to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
Top managers |
Responsible for the performance of all departments -decide how different department should interact -CEO |
|
|
First line managers |
Lowest: responsible for the daily supervision of the nonmanagerial employees |
|
|
Middle managers |
Supervises first-line managers Responsible for finding the best way to use resources to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
Top managers |
Responsible for the performance of all departments -decide how different department should interact -CEO |
|
|
Building blocks of competitive advantage |
Increasing efficiency -reduce the quantity of resources used to produce goods or services |
|
|
First line managers |
Lowest: responsible for the daily supervision of the nonmanagerial employees |
|
|
Middle managers |
Supervises first-line managers Responsible for finding the best way to use resources to achieve organizational goals |
|
|
Top managers |
Responsible for the performance of all departments -decide how different department should interact -CEO |
|
|
Building blocks of competitive advantage |
Increasing efficiency -reduce the quantity of resources used to produce goods or services |
|
|
Building blocks of competitive advantage |
Increase quality - improve the skills and abilities of the workforce |
|
|
Competitive advantage |
Innervation - process of creating new or improved goods and services that customers want |
|
|
Competitive advantage |
Innervation - process of creating new or improved goods and services that customers want |
|
|
Competitive advantage |
Responsiveness to customers |
|
|
Principles of management 1. |
Study the way workers perform their task gather all the informal job knowledge that workers process an experiment with way of improving how tasks are performed |
|
|
Principles of management 1. |
Study the way workers perform their task gather all the informal job knowledge that workers process an experiment with way of improving how tasks are performed |
|
|
2. |
Codify the new methods of performing task into written rules and standard operating procedure's |
|
|
Principles of management 1. |
Study the way workers perform their task gather all the informal job knowledge that workers process an experiment with way of improving how tasks are performed |
|
|
2. |
Codify the new methods of performing task into written rules and standard operating procedure's |
|
|
3. |
Carefully select workers who process skills and abilities that match the needs of the task |
|
|
Principles of management 1. |
Study the way workers perform their task gather all the informal job knowledge that workers process an experiment with way of improving how tasks are performed |
|
|
2. |
Codify the new methods of performing task into written rules and standard operating procedure's |
|
|
3. |
Carefully select workers who process skills and abilities that match the needs of the task |
|
|
4. |
Develop a pay system that provides a reward for performance above the acceptable level |
|
|
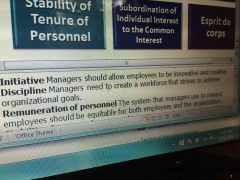
Bureaucracy principle 1 |
A managers formal authority derives from the position he holds in the organization |
|
|
Bureaucracy principle 1 |
A managers formal authority derives from the position he holds in the organization |
|
|
Buracraucy 2 |
Individuals occupy positions because of their performance |
|
|
Bureaucracy principle 1 |
A managers formal authority derives from the position he holds in the organization |
|
|
Buracraucy 2 |
Individuals occupy positions because of their performance |
|
|
Bureaucracy 3 |
Each individual's authority and responsibilities or specified by the organization |
|
|
Bureaucracy 4 |
Authority is exercise efectively when positions or arranged hierarchically |
|
|
Bureaucracy 5 |
Roles of the organization are followed and control individual behavior |
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
The Hawthorne studies |
Researchers found that regardless of whether the light levels were raised or lowered, worker productivity increased |
|
|
Theory x |
Negative assumptions about workers that leads to the conclusion managers task is to supervise workers closely and control their behaviors |
|
|
Theory x |
Negative assumptions about workers that leads to the conclusion managers task is to supervise workers closely and control their behaviors |
|
|
Theory y |
Positive assumptions that leads managers to create a work setting that encourages commitment to organizational goals |
|
|
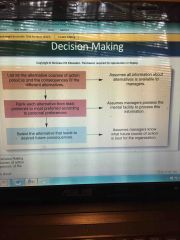
Classical model of decision making |
|
|
Steps in dm 1 |
Recognize the need for a decision |
|
|
Steps in dm 1 |
Recognize the need for a decision |
|
|
Steps in dm 2 |
Generate alternatives |
|
|
Steps in dm 1 |
Recognize the need for a decision |
|
|
Steps in dm 2 |
Generate alternatives |
|
|
Steps in dm 3 |
Access alternatives |
|
|
Steps in dm 4-6 |
-Choose among alternatives -Implement the chosen alternative -learn from feedback |
|
|
Prior hypothesis bias |
A cognitive bias resulting from the tendency to base decisions when strong prior believes even if evidence shows that those beliefs or wrong |
|
|
Representativeness |
A cognitive bias resulting from the tendency to generalize inappropriately from a small sample or from a single vivid event or episode |
|
|
Illusion of control |
The tendency to overestimate one's own ability to control activities and events |
|
|
Illusion of control |
The tendency to overestimate one's own ability to control activities and events |
|
|
Escalating commitment |
A source of cognitive bias resulting from the tendency to commit additional resources to a project even if evidence shows that the project is failing |

