![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Although not highly species-rich, mammals are considered very successful. Why? |
+They occupy a uniquely wide range of ecological niches (aerial, marine, fossorial, arboreal, desert, amphibious). |
|
|
Who created the hierarchy of taxonomic ranks? |
Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) |
|
|
What does a family name end in? What does a superfamily name end in? What does a subfamily name end in? |
-idae (ex. Canidae) |
|
|
What are the rules of binomial nomenclature? |
Species of animals are always assigned unique scientific names. A species name always consists of two parts: Genus and species. The genus name is always first and capitalized. The species name is second and not capitalized. |
|
|
What is a clade or a monophyletic group? |
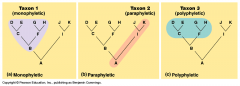
A group of species that contains a common ancestor, all of its descendents and nothing else is called a clade or monophyletic group. |
|
|
What is an outgroup and what are sister groups? |
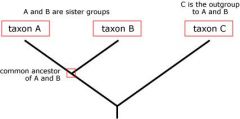
- All the members of the group of interest are more closely related to each other than they are to the outgroup. Hence, the outgroup stems from the base of the tree. An outgroup can give you a sense of where on the bigger tree of life the main group of organisms falls. It is also useful when constructing evolutionary trees. |
|
|
What is paraphyletic? What is a synapomorphy? |
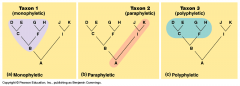
-a group having a common ancestor; but from which one or more descendent groups have been excluded; cannot be defined strictly by synapomorphies*; e.g. Class Reptilia if you don't include birds
* Synapomorphy (shared derived trait) – derived trait shared by 2 or more groups |
|
|
What is do the terms ingroup and outgroup mean? |
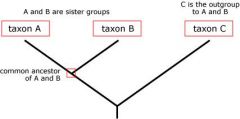
Ingroup: group of organisms being studied |
|
|
What is polyphyletic? |
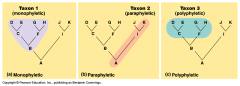
Polyphyletic: descendents of unrelated ancestors; does not include the common ancestor of at least two taxa; taxa are grouped together because of convergent evolution (or anything not covered by monophyletic or paraphyletic) |
|
|
What is a character (or trait)? |
any discrete feature or attribute that exhibits variation |
|
|
Character state |
expression of a particular character (e.g., presence, absence) |
|
|
Character polarity |
direction of evolutionary change in a character |
|
|
Primitive character (plesiomorphy) |
character state is primitive or “generalized” (shared by both the ingroup and outgroup) |
|
|
Derived character (apomorphy) |
character state is advanced or “specialized” (differs from the outgroup) |
|
|
Synapomorphy (shared derived trait) |
derived trait shared by 2 or more groups |
|
|
homologous characters |
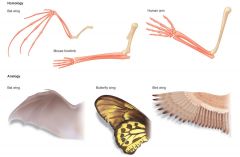
+character inherited from a common ancestor
+ homology is determined by position relative to other structures; development (embryological tissue, pattern of ontogeny), and evolution |
|
|
analogous characters |
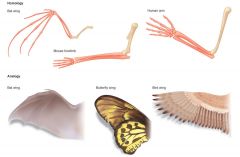
-similar function, but arose independently (insect, bat and bird wings) |
|
|
What is convergent evolution? (Homoplasy) |
+homoplasy means similarity in appearance but not in origin (convergence)
+Flying squirrels and sugar gliders both have skin flaps for gliding but the squirrels are placentals while the gliders are marsupials. Both are found in similar forest environments so the skin flaps are considered to be convergent or homoplastic.
Similarity in species of different ancestry, which is the result of convergent evolution, is called homoplasy – features or parts that look alike but do not share function or ancestry (camouflage/mimicry).
similar features from different ancestors as a result of ecological equivalence
|
|
|
What is divergent evolution? |
The opposite of convergent evolution is divergent evolution, whereby related species evolve different traits. |
|
|
What is homology? |
Means similarity in origin (implying a common ancestor). |
|
|
What is homoplasy? |
Means similarity in appearance but not in origin (convergence). |
|
|
What is analogy? |
Means similarity in function but not in origin. |
|
|
What is ecomorph? |

Another term used to describe convergence is ecomorph. Ecomorphs typically are similar in dietary preferences, feeding adaptations, and/or locomotor adapatations. |
|
|
The Order Monotremata includes which species? |
Echidnas and platypus; 5 species |
|
|
Are monotremes good at controlling their body temperature? |
-No, they cannot control body temperature as well as other mammals
|
|
|
Are monotremes oviparous mammals? |
Yes, they lay eggs which have a thin, leathery shell. Babies hatch relatively undeveloped.
|
|
|
Do monotremes nurse on milk? |
Yes they do |
|
|
Do echidnas have a placenta or do they use a pouch an abdominal pouch for the young? |

Echidnas have an abdominal pouch for the young. |
|
|
Echidnas aka spiny anteaters live where? |
They live in forests, mountains and plains of Australia / New Zealand |
|
|
Echidnas are known as spiny anteaters because they eat ants using what? |
they eat ants and termites with a long prehensile tongue. |
|
|
Do echidnas have a long snout, thick coat of hair and spines? What do they do when threatened? |
+Yes +They burrow so only their spines show |
|
|
What do duckbilled platypuses eat? |
They eat shellfish, insects, and worms in the muddy bottoms of lakes/ streams. |
|
|
What is special about a platypluses duck-bill? |
It is covered with electroreception receptors. |
|
|
What do duckbilled platypuses live in? |

They live in burrows. |
|
|
Do platypuses have a flat beaver-like tail and webbed feet? |
Yes |
|
|
What is the only marsupial found in North America? |
opossums; almost all others live in Australia |
|
|
What are the only surviving marsupials found in South America? |

Shrew opossums and Monito del Monte are the only surviving marsupials in North America. |
|
|
Before birth how does an embryonic marsupial receive nourishment? |
By absorbing nutrient secretions in the uterus. |
|
|
Marsupials are born very early in development and completes development while nursing within a maternal pouch called a __? |
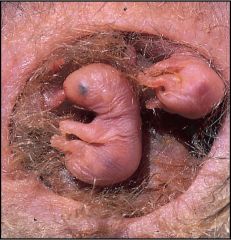
Marsupium |
|
|
What are Eutherians? |
Placental Mammals |
|
|
Are 95% of all extant mammals placental? |
Yes |
|
|
Do eutherians have higher metabolic rates than monotremes/ marsupials. |
Yes |
|
|
Order Dermoptera includes which 2 animals? |

flying lemurs or colugos; 2 species |
|
|
What kind of diet do flying lemurs or colugos eat? |
They are herbivores |
|
|
Do colugos/ flying lemurs lack opposable thumbs? Are they surprisingly clumsy climbers, hop up a tree? Are they fairly large for a tree dwelling mammal (4 lbs)? |

Yes |
|
|
Why do flying lemurs / colugos have "marsupial-like" breeding habits? |

They have very undeveloped young (35 g), spend first 6 months clinging to mothers belly. |
|
|
What 1 animal does the Order Chiroptera include? |

Order Chiroptera- bats; 925 species |
|
|
Are bats the second large order with 925 species? Do they account for 20% of all mammal species? |
Yes |
|
|
What do bats eat? |
They eat all kinds of things: insects, fruit, blood, fish |
|
|
What do night bats use to find food? |
Echolocation |
|
|
Do many bats live in colonies, sleeping together upside down with wings wrapped around their bodies? |
Yes |
|
|
The order Primates includes which 3 animals? |

Order Primates - lemurs, monkeys and apes; 362 species |
|
|
What some characteristics of primates? |
-opposable thumb; enables them to grasp branches and other objects -nails replace claws -omnivores -most developed cerebrum and the most complicated behaviors -often live in organized social groups |
|
|
The order Tubulidentata includes which 1 animal? |

-aardvarks or "Earth pig" |
|
|
What are some characteristics of aardvarks? |

-Solitary, shy, nocturnal burrowing animal native to Africa that feeds on ants and termites. -aardvarks are 5 to 6 feet long, including a 2 foot long tail. They weigh about 140 pounds. |
|
|
The order Cingulata includes which 1 animal? |

-Armadillos; 21 species
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of armadillos? |

-timid, armored mammals -can jump 3 ft straight up into the air -have peg-like teeth |
|
|
The order Pholidota includes which 1 animal? |

-scaly anteater or pangolin; 7 species |
|
|
What are some characteristics of scaly anteater or pangolins? |
-Covered with tough, protective scales made of keratin -the long tail is prehensile (grasping); the pangolin can even hang from its tail -when in danger, the pangolin curls into a ball, protecting its soft belly and face. It may also hit an enemy with its tail or spray urine. |
|
|
Where are scaly anteaters or pangolins found? |
Found in Africa and Southeast Asia |
|
|
The order Pilosa includes which 2 animals? |
-True anteaters and sloths; 10 species |
|
|
What are Sloths and how do they defend themselves? |

They are slow-moving, nocturnal herbivores that spend most of their lives hanging upside-down in trees.
Their main defense against a predator is to claw and nip at an attacker. |
|
|
What are anteaters good at? How do they walk? |
-Good at swimming and tree climbing -walk on knuckles; have long, hook-like claws that don't retract, but curve under the paws when walking. |
|
|
How do anteaters catch insects? |
-Catch insects using their long tongue, flicking the tongue in and out up to 160 times each minute.
|
|
|
The order Carnivora includes which 5 animals? |
-cats, dogs, bears, seals, raccoons etc.; 286 species |
|
|
What is the difference between Suborder Fissipedia and Suborder Pinnipedia carnivores? |
-Fissipedia: terrestrial carnivores (plus the sea otter) -Pinnipedia: aquatic carnivores |
|
|
The order Cetacea includes which 2 animals? |
-Whales and dolphins; 84 species |
|
|
42% of all mammals belong to which order? |
Rodentia; 2273 species |
|
|
Order Rodentia includes which 7 animals? |
-Mice, rats, squirrels, beavers, porcupines, chipmunks, and gophers |
|
|
What kind of teeth do the order Rodentia have? |
-Have two long front teeth, used for chewing, which grow continuously throughout their life (hypsodont).
|
|
|
What kind of diet does order Rodentia have? |
-herbivores, granivores (seed predators) |
|
|
Does order Rodentia have short gestation periods? |
Yes |
|
|
What 3 animals belong to the order Lagomorpha? |

-Rabbits, pikas, and hares (84 species) |
|
|
What are some characteristics of Lagomorphs? |
-Sharp front teeth -herbivores -short gestation period, produce a lot of young -pikas have rounded ears and legs of equal length |
|
|
What 2 animals are in the order Serenia? |
-manatees and dugongs; 4 species
|
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of order Serenia? |
-slow moving, low metabolic rates -herbivores -fresh water and marine
|
|
|
What 2 animals are in the order Hyracoidea? |

-Hyraxes, tree hyraxes (4 species) |
|
|
What are some characteristics of order Hyracoidea? |
-"Guinea-pig like" animals living in Africa and Middle East -30-70 cm long, weighing 2-5 kg -They have complex, multi-chambered stomachs that allow symbiotic bacteria to break down tough plant materials, and their overall ability to digest fiber is similar to that of the ungulates. |
|
|
What 1 animal belongs to the order Proboscidea? |

-elephants (2 species) |
|
|
What are some characteristics of order Proboscidea? |

-African and Indian elephants -African element is larger and taller and has larger ears than the Indian (Asian) elephant. -large head broad flat ears, thick skin with little hair -boneless trunk transfers food and water to mouth -tusks dig up plant roots or pry bark -herbivores |
|
|
What 3 animals are in the order Perissodactyla? |

-horses, tapirs, and rhinos; 16 species |
|
|
What are some characteristics of the order Perissodactyla? |
-odd toed ungulates -grazers -flat teeth for grinding food -hind-gut fermentation used to break down cellulose |
|
|
What 6 animals are in the order Artiodactyla? |
-pigs, hippos, camels, bovids, antelopes, deer; 240 species |
|
|
What are some characteristics of the order Artiodactyla? |

-grazing animals with two toes on the foot, known as even toed ungulates -some have multi-chambered stomachs used to break down cellulose. -flat teeth for grinding food |

