![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
241 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the organs of the male reproductive system
|
testes
vas deference seminal vesicles penis accessory glands: prostate & Cowper's gland |
|
|
who are the diseases of the male reproductive treated by
|
urologist
|
|
|
what is the function of the testes
|
Dual function:
spermatogenesis (production of sperm) and Secretion of Testosterone |
|
|
what is the vas deferens
|
firm tubular structure passing upward through the inguinal canal to enter the abdominal cavity behind the perioteneum and extends downward toward the base of the bladder
|
|
|
what is the seminal vesicles
|
an out pouching from the vas deferens which acts as a reservoir for testicular secretions.
|
|
|
what does the prostate gland do
|
it produces a secretion that is chemically and physiologically suitable to the needs of the spermatozoa in their passage from the testes.
|
|
|
where does the cowper's gland lie
|
below the prostate
|
|
|
what does the cowpers gland do
|
provides lubrication during ejaculation by emptying its secretions into the urethra
|
|
|
What is the function of the penis
|
Dual function:
copulation Urination |
|
|
what does the penis compose of
|
glans penis, body and the root
|
|
|
What are 8 different Gerintological considerations RT male repro changes
|
Prostate enlarges w/age and secretions decrease
Scrotum hangs lower Testes smaller and more firm Public hair sparse and stiffer decreased testosterone level decreased sexual function increased GU cancer Increased incontinence |
|
|
what does a decrease in sex hormone secretion cause
|
decrease in muscle strength and sexual energy
decrease in # of viable sperm shrinkage and loss of firmness of testes erectile dysfunction enlargement of the prostate gland what are the changes in sexual response? |
|
|
what are the changes in sexual response to age?
|
prolonged time - full erection
rapid penile detumescence (decrease swelling) proloonged refractory time decrease # viable sperm smaller testes erectile dysfunction weakening of prostatic contractions S/S of obstruction of lower urinary tract |
|
|
what cancers have increased incident in men older than 50
|
kidney, bladder, prostate and penis
|
|
|
what is the PLISSIT
|
Framework for doing the H&P on pts with sexual issues
|
|
|
What does PLISSIT stand for
|
P Permission
L limited I Information S specific S suggestions I intensive T therapy |
|
|
what re s/s of changes in urinary function and obstruction caused by an enlargd prostate
|
increased urnary freuency,
decreased force double or triple oviding dysuria hematuria hematospermia |
|
|
what are influencing factors of sexual dysfunction
|
stress, physical disease (DM MS, Stroke, Cardiac Disease), use of medications (antihypertensives & anticholesterolemic meds, psychotropics), drugs or alcohol
|
|
|
what is a DRE
|
digital Rectal Exam
|
|
|
when is a DRE recommended
|
every man over 40
|
|
|
what does the DRE do
|
asses the size, shape and consistency of the prostate
|
|
|
When the DRE deteects the tumors is it in time?
|
If large - they may have spread to surrounding tissue
|
|
|
if doctor finds something on the DRE and you have an increased PSA what does it =
|
Prostate CA
|
|
|
What is a TSE
|
Testicular Exam
|
|
|
what is a TSE for
|
the male genitalia is inspected for abnormalities
|
|
|
what does the doctor note on a TSE
|
nodules, masses or inflammation
|
|
|
What is the technique for a TSE
|
once a month after bath when scrotum is relaxed
use both hands to palpate the testis normal is smooth and uniform index and middle fingers under testes, thumb on top - roll in a horizontal plane. |
|
|
What are you looking for in a TSE
|
small lump or abnormality
|
|
|
do you check the epididymis in a TSE
|
yes, palpate the epididymis, which is a cord-like structure on the top and back of the testicle that stores and transports sperm.
|
|
|
what if you find a testis larger than the other in a TSE
|
it is normal
|
|
|
what does the DRE do
|
asses the size, shape and consistency of the prostate
|
|
|
When the DRE deteects the tumors is it in time?
|
If large - they may have spread to surrounding tissue
|
|
|
if doctor finds something on the DRE and you have an increased PSA what does it =
|
Prostate CA
|
|
|
What is a TSE
|
Testicular Exam
|
|
|
what is a TSE for
|
the male genitalia is inspected for abnormalities
|
|
|
what does the doctor note on a TSE
|
nodules, masses or inflammation
|
|
|
What is the technique for a TSE
|
once a month after bath when scrotum is relaxed
use both hands to palpate the testis normal is smooth and uniform index and middle fingers under testes, thumb on top - roll in a horizontal plane. |
|
|
What are you looking for in a TSE
|
small lump or abnormality
|
|
|
do you check the epididymis in a TSE
|
yes, palpate the epididymis, which is a cord-like structure on the top and back of the testicle that stores and transports sperm.
|
|
|
what if you find a testis larger than the other in a TSE
|
it is normal
|
|
|
what if you find a small, pea-like lump or a swollen testis during a TSE
|
consult your physician. Swollen could be an infection or tumor.
|
|
|
what if your testis is large but painless
|
Might be testicular Cancer
|
|
|
when should discussion of male reproductive system be made with pt
|
initiated during adolescence. Can reveal disorders of hydrocele, hernia or tumors of the testes
|
|
|
What is a PSA
|
PSA is Prostate Specific Antigen that is produced by the prostate gland. It increases in prostate cancer.
|
|
|
When is a PSA drawn
|
prior to a rectal exam or urinary catherization or you will get a false negative
|
|
|
What is the # for an elevated PSA
|
0ver 0.4 ng/mL
normal is 0.2 to 0.4 |
|
|
When is a PSA elevated
|
in BPH, prostate cancer, infections of prostate and urinary tract. it identifies those at risk and used as a monitor following Tx for CA
|
|
|
When is an Ultrasound used
|
used in detecting nonpalable prostate cancers
helps guide needle biopsies staging of localized prostate cancers |
|
|
which is more sensitive - a DRE or Ultrasound for detection
|
a Ultrasound is more sensitive than a DRE for detection of the prostate
|
|
|
What is a TRUS
|
Transrectal Ultrasound of the Prostate
|
|
|
when is a TRUS done
|
after the DRE
|
|
|
is a TRUS used for needle biopsies
|
Yes, it they guide the needle biopsies.
|
|
|
How is a biopsy doe for obtaining tissue for histological examination
|
doe by prostatectomy or via perineal or transrectal needle biopsy
|
|
|
What is part of pt teaching to minimize possibility of recurrence of prostate ca?
|
Have regular prostate-specific antigen PSA tests and repeat lymph node biopsies
|
|
|
What term refers to surgical removal of one testes
|
Orchiectomy.
|
|
|
What is the term for excision of the foreskin, prepuce of the glans penis?
|
Circumcision
|
|
|
What term is for the ligation and transection of part of the bas deferens to prevent passage of the sperm from the testes
|
Vasectomy
|
|
|
What term describes the surgical repair of a hydrocele
|
Hydrocelectomy
|
|
|
What is a hydrocele
|
Collection of fluid in the tunica vaginalis
|
|
|
How soon before intercourse should you take Viagra
|
One hour before intercourse
|
|
|
Will Viagra create an erection
|
No, sexual stimulation does
|
|
|
Will Viagra restore sex drive
|
No
|
|
|
What are the s/s of prostatism
|
Increased frequency of urination, nocturia, urgency, dribbling and sensation the bladder has not completely emptied.
|
|
|
What is prostatitis
|
Inflammation of the prostate gland
|
|
|
what is the term or disease associated w/buildup of fibrous plaques in the sheath of the corpus cavernosum causing curvature of the penis when erect
|
Peyronie’s Disease
|
|
|
What is Bowen’s disease
|
Form of squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the penile shaft
|
|
|
What is Phimosis
|
Condition in which the foreskin is constricted so that it cannot be retracted over the glans
|
|
|
What is Priapism
|
Uncontrolled, persistent erection of the penis occurring from either neural or vascular causes
|
|
|
What term describes the opening of the urethra on the dorsum of the penis
|
Episapdias
|
|
|
What is hypospadias
|
Congenital anomaly in which the urethral opening is on the underside of the penis
|
|
|
What is a urethral stricture
|
Condition in which a section of urethra is narrowed
|
|
|
What is urethritis
|
Inflammation of the urethra and is commonly associated with sexually transmitted disease
|
|
|
What is a complication resulting from a miss-sized implant cylinder
|
Erosion of the penile or urethral tissue
|
|
|
Does a pt need to use contracteption after a vasectomy
|
Yes until pysican ensures sperm is no longer present (after 10 or more ejaculations)
|
|
|
When can a pt resume sexual activity after a vasectomy
|
Usually in 1 week when comfort allows.
|
|
|
Should there be any bruising or incisional soreness from a vasectomy
|
Yes after the anesthetic wears off.
|
|
|
What is prostaglandins
|
physiologically active substances present in tissues with vasodilator properties
|
|
|
Considerations for home care with epididymitis and orchitis
|
Take prescribed antibiotics, sitz baths, apply heat (not ice) after scrotal swelling subsides. Avoid lifting exercises and sexual intercourse until symptoms are relieved
|
|
|
What is the obstructive and irritative symptom complex caused by BPH
|
Prostatism
|
|
|
How often should you take Viagra
|
Do not take more than once a day.
|
|
|
what type of test may be done in a sleep laboratory
|
a Nocturnal penile tumescence test to monitor changes in penile circumference during sleep
|
|
|
how is the penis measured in a nocturnal penile tumescence test
|
mercury strain gauge placed around the penis or arterial blood flow measured with a doppler
|
|
|
what is ED
|
erectile dysfunction also called impotence
|
|
|
what is impotence
|
inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient to accomplish intercourse
|
|
|
what are the psychogenic causes of ED
|
anxiety, fatigue, depression and pressure to perform
|
|
|
what are organic causes of ED
|
endocrine disorders, cirrhosis, renal failure, neurological disorders, trauma (occlusive vascular disease),
medications and drug abuse, hematological/genitourinary/neurologic D/O |
|
|
what are some medical conditions that cause Ed
|
HTN, DM High cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease
|
|
|
what is the nursing management for ED
|
supportive and educative. Referral to a support group, impotence anonymous or I-Anon for their partners
|
|
|
what antiadrenergic and antihypertensive are associated with ED
|
Ismelin, Catapres, Apresoline, lopressor
decrease peripheral vasoconstriction and/or decreased blood pressure |
|
|
anticholinergic and phenothiazines
|
compazine, Artane
sedative, and act on CNS |
|
|
antiseizure agents
|
tegretol
|
|
|
antifungal medications
|
ketoconazol (Nizoral) causes oligospermia and decreased libido in males
|
|
|
antihormone medications
|
for prostate cancer treatment: Eulexin, lupron
|
|
|
antipsychotic medications
|
Haldol, Thorazine
|
|
|
antispasmodic medications
|
Ditropan
|
|
|
anxiolytics
|
sedative hyponotics, tranquilzers, ativan, halcion
sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant |
|
|
Betablockers
|
corgard
|
|
|
Ca Channel Blockers
|
Nifedipine, adalat, procardia
Antihypertensives |
|
|
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
|
diamox
|
|
|
H2 antagonists
|
axid
have an anticholinergic affect, sedative. blocks parasympathetic to sex glands and organs |
|
|
NSAIDs
|
naprosyn Naproxen
|
|
|
Thiazide Diuretics
|
HydroDIURIL hydrochlorothiazide
Spironolactone Aldactone - dose related |
|
|
Tricyclic antidepressant
|
Elavil, Norpramin
|
|
|
what PO medications help ED
|
Sildenafil - Viagra
Cardenafil - Levitra Tadalafil - Cialis |
|
|
what are phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors PDE-5
|
it is a type of enzyme found almost exclusively in the penis. They slow the release of nictric oxide and temporarily re-store the boy's natural sexual response by increasing the capability of blood flow to the penis. works only when a man is sexually stimulated
|
|
|
What do PDE5 do to the penis
|
smooth muscle relaxant causing blood flow to the penis
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of PDE5
|
can cause H/A and Diarrhea.
contraindicated for men taking nitrate meds. Used w/caution in pts with retinopathy, especially diabetic retinopathy |
|
|
when do you take the PO for ED
|
1 hr before intercourse. can last 1 hr
|
|
|
what is a penile injection
|
firm erections are achieved in 50% of cases. Inject 20 min before intercourse. Erection lasts up to1 hr
|
|
|
what is the urethral suppository (alprostadil)
|
may be used 2 x a day. Not recommended with pregnant partners
|
|
|
what are different types of Penile implants
|
semirigid rod and inflatable
semirod results in permanent semi erection. inflatable is saline from reservoir. |
|
|
considerations for xildanafil Viagra, vardenafil Levitra, and tadalafil Cialis:
|
Vasodilators, take 30min to few hrs before intercourse. need sex stimulation to produce an erection.
|
|
|
what are the s/s of POs for ED
|
H/A, flushing, indigestion, nasal congestion, ABD vision, diarrhea, dizziness, rash. low blood sugar and abnormal liver function tests
|
|
|
what PO medications help ED
|
Sildenafil - Viagra
Cardenafil - Levitra Tadalafil - Cialis |
|
|
what are phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors PDE-5
|
it is a type of enzyme found almost exclusively in the penis. They slow the release of nictric oxide and temporarily re-store the boy's natural sexual response by increasing the capability of blood flow to the penis. works only when a man is sexually stimulated
|
|
|
What do PDE5 do to the penis
|
smooth muscle relaxant causing blood flow to the penis
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of PDE5
|
can cause H/A and Diarrhea.
contraindicated for men taking nitrate meds. Used w/caution in pts with retinopathy, especially diabetic retinopathy |
|
|
when do you take the PO for ED
|
1 hr before intercourse. can last 1 hr
|
|
|
contraindications for ED POs
|
do not take if taking nitrates, uncontrolled BP, CAD or heart attack within past 6 months; dysrhythmia or kidney/liver dysfunction. Avoid with use of PDE5 inhibitors
|
|
|
what is the main Tx of Ed
|
Tx of cause
|
|
|
what are the injection meds for ED
|
alprostadil, papaverine and phentolamine
|
|
|
what are complications for injection meds for ED
|
priapism
development of fibrotic plaques at injection sites |
|
|
What is alprostadil?
|
a gel pellet that is inserted into the urethra, urethral suppository
|
|
|
what is a negative pressure device
|
vacuum device to induce erection and constriction band at base of penis.
|
|
|
what is prostatitis, what is it caused by
|
prostatis is infection of the prostate, caused by STDs. or sexual partners with E. Coli vaginal infections
|
|
|
what are the S/S of prostatitis
|
perineal discomfort, burning, urgency, frequency and pain with/or after ejaculation, fever, chills, rectal or low back pain, UTI
|
|
|
what are complications of prostatitis
|
swelling, urinary retention, epididymitis, bacteremia, pyelonephritis
|
|
|
what is the management of prostatitis
|
broad spectrum antibiotics, bedrest, analgesics, antispasmodics, sitz baths, stool softners.
|
|
|
what are nsg considerations for prostatitis
|
comfort measures, SITZ bath, education, completion of antibiotics, fluids encouraged but not forced, analgesics, foods and liquids with diuretic action or that increase prostatic secretions should be avoided (coffee, alcohol, tea, chocolate, cola and spices)AVOID SITTING for long periods
|
|
|
what are the different zones of the prostate
|
peripheral, central, anterior fibromuscular stroma and transition.
|
|
|
what zone surrounds the urethra
|
the transition zone. It enlarges with age in hormonally dependednt manner.
|
|
|
do castrated males develop BPH
|
no
|
|
|
what part of the BPH can be felt during a DRE
|
posterior superficial surface of the gland
|
|
|
what is the main function of the prostate
|
secretory: producing an alkaline fluid that comprises approxiamtely 70% of the seminal volume.
It is a conduit for semen to pass and prevents retrograde ejaculation by closing off the bladder neck during sexual climax. |
|
|
what does the secretion of the prostate do
|
neutralizes the acidic vaginal environment and provides carbohydrates and nutrients for the sperm
|
|
|
what is BPH
|
Benign Prostatic hyperplasia
|
|
|
when does BPH happen
|
commonly in men over50
|
|
|
what is the disease process of BPH
|
enlargement of the prostate, extending upward and obstructing urine flow
|
|
|
what are the clinical manifestations of BPH
|
frequency, nocturia, decrease in volume and force, dribbling, recurrent UTI, sensation of incomplete emptying of bladder
|
|
|
What is the management of BPH
|
pharmacological, hormonal or surgical
|
|
|
what are high risk factors for BPH
|
smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, hypertenison, heart disease, and diabetes
|
|
|
who is more at risk to get BPH:
African American at 40, Caucasian at 40 or Asian at 50 |
African American at 40, Asians are unlikely to develop BPH, Caucasians develop > 50
|
|
|
what causes the incomplete emptying and urinary retention in BPH
|
Hypertrophied Lobes
|
|
|
what hormones is BPH dependent upon
|
testosterone and dihydrotestosterone DHT production.
|
|
|
what is the med mgmt of BPH
|
dependent upon cause. If emergency, catheterization may be necessary
|
|
|
what type of meds are used for mgmt of BPH
|
Alpha-adrenergic blockers: terazosin (Hytrin), doxazosin (Cardura), tamsuloxin (Flomax)
Anti-androgen agents: finasteride (Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart) |
|
|
what do alpha-adrenergic blockers do for BPH
|
Alpha-adrenergic blockers: terazosin (Hytrin), doxazosin (Cardura), tamsuloxin (Flomax)
They relax the smooth muscle of the bladder neck and prostate improving urine flow |
|
|
what do the hormonal antiandrogen agents do for BPH
|
Antiandrogen agents: finasteride(Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart)
prevent conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone leading to decreased glandualr cell activity and prostate size |
|
|
what is a complication of hormonal meds such as Finasteride and dutasteride?
|
gynecomastia, erectile dysfunction and flushing
|
|
|
what is the second most common cause of cancer death in men over 55
|
cancer of the prostate, skin cancer 1st
|
|
|
risk factors for prostate cancer
|
African American (2x high), increasing age, familial predisposition, diets high in red meat, dairy and fat
|
|
|
s/s of prostate cancer
|
early stages rarely produce symptoms.
urinary obstruction, difficulty and frequency, retention,decrease in size and force of stream, painful ejaculation, Hematuria, late signs RT metastasis: backache, hip pain, perineal and rectal discomfort, anemia, wt loss , weakness |
|
|
diagnosis for prostate CA
|
DRE and PSA!
TRUS advanced lesion is "stony hard and fixed" TRUS helps detect nonpalpable ca, staging and guides needle biopsies |
|
|
complications of Prostate CA
|
sexual dysfunction noted before diagnosis.
Hemorrhage, clot formation, catheter obstruction |
|
|
mg mgmt for prostate ca
|
surgical, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, chemotherapy, cryosurgery
|
|
|
What is the Gleason Score
|
Staging of Cancer of the Prostate
|
|
|
how does the Gleason Score work
|
microscopically 5 specific patterns have been identified and numbered 1-5. taking the biopsy specimen and adding the 2 most common patterns found will give the score. The higher the Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer.
|
|
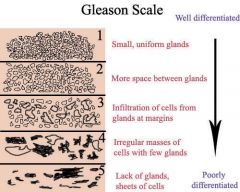
if over 50% is small uniform glands and 35 % is more space between glands, what is the score
|
3
|
|
|
which type of med mgmet cures prostate cancer
|
surgical
|
|
|
what are the side effects of radiation therapy of prostate cancer
|
inflammation of rectum, bowel and bladder, sexual potency is preserved better than with surgery
|
|
|
what are chemo meds used in prostate cancer
|
paclitaxel (taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) for non-androgen dependent prostate cancer
|
|
|
what med is used with chemo to lower testosterone and allow chemo agents to have a direct effect on cancer cells causing cell death
|
Ketoconazole
|
|
|
what are different surgical approaches
|
Open surgical: Suprapubic approach, Perineal approach, Retropubic approach
|
|
|
what is TURP
|
Transurethral Resection (TUR or TURP)
(removal of prostatic tissue by instrument introduced through urethra) STRICTURES ARE MORE FREQUENT |
|
|
what is TUIP
|
Transurethral Incision of the Prostate, when gland is small. Outpatient basis and lower complications rate
|
|
|
What is a problem with TURP
|
STRICTURES ARE MORE FREQUENT, may cause retrograde ejaculation
|
|
|
what is a problem with suprapublic surgery
|
may result in greater blood loss, surgical abd incision with concomitant wound issues
|
|
|
what is problems wit perineal surgery
|
more easily contaminated due to location near rectum. Incontinence, impotence and rectal injury are more likely with this approach.
|
|
|
what is the adv disadv of retropublic surgery for prostate ca
|
more common than suprapublic. suitable for large glands, blood loss better controlled, surgical site easier to visualize, infections can readily start in the retropubic space
|
|
|
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF PROSTATE SURGERY FOR CA
TEST!! |
HEMORRHAGE, CLOT FORMATION, CATHETER OBSTRUCTION AND SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION. IMPOTENCE, BECAUSE OF DAMAGE TO PUDENDAL NERVE. AFTER TOTAL PROSTATECTOMY, IMPOTENCE ALMOST ALWAYS RESULTS
|
|
|
nsg diagnosis for prostatectomy
test!! |
Anxiety RT...
urinary retention RT Imabalance nurtrition: less than body requirements RT... Sexual dysfunction RT... Pain RT.... Impaired physical mobility and activity intolerance RT..... |
|
|
what are nsg interventions for prostatectomy
Test!! |
assess voiding 20-30mL frequently and output - less than, indicates retention.
Catherterize: instruct ways to reduce pressure on operative area after prostatecomy; avoid prolonged sitting, standing, walking; avoid straining, sexual intercourse |
|
|
more nsg interventions for prostatectomy
|
maintain bladder control: urination q 2-3 hrs. avoid drinking caffeine. discourage voiding when supine, perineal exercises q hr schedule. Assess amount of food eaten. routine Wt of patient
|
|
|
more nsg interventions for prostatectomy
|
cater to food preferences, inform pt alterations in taste can occur. measures to control N & V - oral hygiene, small frequent meals; evaluate pain; avoid activities that aggravate pain; encourage use of assisted devices, can e walker.
|
|
|
nsg diagnosis pre-op for prostatectomy
|
anxiety, acute pain (bladder distention) knowledge deficit (factors RT disorder and tx protocol
|
|
|
NSG diagnosis post-op for prostatectomy
|
acute pain (surgical incision, catheter placement, bladder spasms); knowledge deficit (postop care and mangement)
|
|
|
Potential complications from prostatectomy
|
hemorrhage and shock, infection, deep vein thrombosis, catheter obstruction, sexual dysfunction
|
|
|
intervention for prostatectomy preop that includes labs
|
azotemia: accumulation of nitrogenous waste products in blood - a catheter will gradually decompress the bladder
|
|
|
when giving pain relief you need to determine the cause and location. Kidney, Bladder, Constipation... what do you do?
|
flank pain - kidney = analgesics
urgency to void/pressure/fullness - bladder spasms - meds to relax smooth muslces = Urispas or Ditropan, warm compresses or sitz baths. bleeding from urethra around catheter - obstruction may require irrigation 50ml/at a time, don't sit - walk. constipation - enemas.. |
|
|
normal drainage from prostatic surgery
|
drainage normally reddish-pink then clears to light pink within 24 hrs after surgery
|
|
|
bright red with increased viscosity and clots indicates
|
arterial bleeding - surgical emergency, give fluids, blood components, VS IO, meds
|
|
|
first dressing change after prostatic surgery is changed by
|
changed by MD - using aseptic technique.
|
|
|
signs of infection from prostatic surgery
|
fever, sweats, chills, myalgias (muscle pain), dysuria, urinary frequency and urgency
|
|
|
to relieve DVT what do you do
|
low dose heparin, antiembolic stockings
|
|
|
with an obstructed catheter, what s/s might lasix promote
|
diuresis, restlessness, cold sweats, pallor drop in BP, increased HR. - need to irrigate with 50mL
|
|
|
pt complains of incontinence after catheter removal , what do you do.
|
some urinary incontinence may occur and is likely to subside in time.
|
|
|
when pt goes home after prostatic surgery, what s/s should he be concerned with
|
blood in urine, decreased urine output, fever, change in wound drainage, calf tenderness, bleeding, clots, decreased stream, retention or infection
|
|
|
how long for prostatic fossa to heal
|
6 - 8 weeks.
|
|
|
what is orchitis
|
inflammation of testes
|
|
|
what causes orchitis
|
pyogenic, viral, spirochetal, parasitic, traumatic, chemical or unknown factors
MUMPS |
|
|
what is the Tx for orchitis
|
antibiotics, rest, scrotal elevation, icepacks, analgesia
|
|
|
What is epididymitis
|
infection of the epididymis due to infected prstate or urinary tract
|
|
|
what causes epididymitis
|
gonorrhea, chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
Tx of epididymitis:
|
antimicrobial agents to tx organism, bed rest, scrotal elevation (folded towel/bridge to promote drainage) cold compresses, avoid straining, lifting and sexual stimulation
|
|
|
testicular cancer is most common cancer in men ...
|
15-35
|
|
|
what is the outcome of testicular cancer
|
highly treatable and usually curable
|
|
|
what are the risk factors of Testicular cancer
|
undescended testis, family hx, race, ethnicity, occupational hazards, chemical exposure, oil and gas production, leather processing
|
|
|
who is at greater risk for testicular cancer: an african american at 38, a caucasian at 18, an asian at 32
|
caucasian 5 x > than African american
Caucasian 2 x Asian caucasian, asian, african |
|
|
what is undescended testis called
|
crypotorchidism
|
|
|
what is cryptorchidism
|
a congenital condition, failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum.
|
|
|
what is Tx for cryptorchidism
|
position it properly
|
|
|
CA of Testes has s/s
|
LARGE AND PAINLESS
mass/lump, heaviness, backache, abd pain, wt loss, weakness. |
|
|
Where does testicular cancer spread
|
from testis to lymph nodes in retroperitoneum and to the Lungs!
|
|
|
diagnosis for testicular cancer is -
|
TSE done monthly and Looking at markers, intravenous urography deviation by mass lymphangiography to assess extent of spread to lymphatic system.
ultra sound for presence and size of mass CT to determine extent of disease in lungs, retroperitoneum and pelvis. |
|
|
what are the ca markers for testicular cancer
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin HCG and alpha-fetoprotein are the tumor markers that may be elevated in those with testicular cancer
|
|
|
What is the Medical Mgmt for Testicular cancer
|
Orchiectomy with gel-filled prosthesis
retroperitoneal lymph node dissection radiation chemotherapy |
|
|
what are the long term effects from testicular cancer
|
kidney damage, hearing problems,gonadal damage, neurological changes and rarely secondary cancers
|
|
|
what is hydrocele
|
acute: infectious disease
chronic: unknown cause collection of fluid in the tunical vaginalis of the Testes. Can be illuminated by Light. A hernia can't be illuminated by light |
|
|
major complication from hydrocele
|
Hematoma in loose scrotal tissues
|
|
|
what is a varicocele
|
abnormal dilation of veins in the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum - part of the spermatic cord.
|
|
|
s/s of a varicocele
|
pain, tenderness and discomfort
|
|
|
what is a vasectomy
|
ligation and transsection of part of the vas deferens with or without removal of a segment of the vas deferens.
|
|
|
what are complications from a vasectomy
|
scrotal ecchymoses, swell, superficial wound infection, vasitis, epididymitis, epididymo-orchitis, hematomas, spermatic granulomas.
|
|
|
what are spermatic granulomas
|
inflammatory response to the collection of sperm leaking into the scrotum from the severed end of the proximal vas deferens from a Vasectomy.
|
|
|
Can pregnancy happen if pt has vasectomy
|
yes, if they have a spermatic granuloma. it can initiate recanalization of the vas deferens.
|
|
|
med mgmt after vasectomy
|
cold packs, jocky-type briefs, sitz baths sexual intercourse only after medical confirmation that sperm distal to severed vas deferens has been evacuated.
|
|
|
urethral opening on the ventral side of penis
|
hypospadia
|
|
|
urethral opening on the dorsum side of the penis
|
epispadia
|
|
|
what is phimosis
|
foreskin is constricted on top of the penis, so that it cannot be retracted over the glands to expose the urethral opening.
|
|
|
how is phimosis corrected
|
by circumcision
|
|
|
what is Paraphimosis
|
condition in which the foreskin is retracted behind the glans and because of narrowness and subsequent edema, cannot be returned to its usual position.
|
|
|
how is paraphimosis corrected
|
compressing glans and pushing prepuce forward. Circumcision is indicated after inflammation and edema has subsided
|
|
|
common s/s of cancer of the penis
|
painless, wart like growth or ulcer
|
|
|
prevention from cancer of penis is
|
circumcision in infancy
|
|
|
What is Bowen's disease
|
form of squamous cell carcinoma in situ (in its place - epidermis, flat) of the penile shaft
|
|
|
what are the risk factors of penis CA
|
HPV, smoking, smegma, phimosis, psoriasis, 55 or older, AIDS
|
|
|
Tx for cancer of Penis
|
excision, partial or total penectomy, topical chemotherapy , radiation
|
|
|
Priapism is
|
uncontrolled, persistent erection of the penis tha needs medical emergency
|
|
|
causes of Priapism
|
neural or vascular - sickle cell thrombosis, leukemic cell infiltration, spinal cord tumors or injury, tumor invasion of the penis or vessels, medications: Thorazine or antidepressants
black widow spider bites Carbon monoxide poisoning, illicit drugs. |
|
|
Priapism affects
|
any age, but usually men between 5-10, and 20-50
|
|
|
Tx of priapism
|
meds if withing 4-6 hrs
decongestant meds if > 4 hrs Ice packs, surgical ligation to artery, intracavernous injection, surgical shunt, aspiration |
|
|
what is Peyronies Disease
|
build up of plaque in the sheath of the corpus cavernosum. when erect, curvature occurs.
|
|
|
What is iontophoresis
|
electric current to deliver 3 drugs (dexamethasone, lidocaine, verapamil) to reduce lesions and relieve pain for Peyronies disease.
|
|
|
Tx for peyronies disease
|
surgical removal of plaques, iontophoresis, sometimes goes away on its own
|
|
|
Urethral stricture - what is it
|
section of the urethra is narrowed - congenitally or from a scar due to traumatic injury
|
|
|
Tx for Urethral Stricture
|
dilation of the urethra or urethrotomy
|
|
|
circumcision
|
excision of the foreskin, prepuce of the glans penis.
|
|
|
Circumcision is the Tx for what D/Os
|
Phimosis, paraphimosis, recurrent infections of the glans and foreskin
|
|
|
med mgmt for circumcision
|
VASELINE & GAUZE
observe for bleeding, analgesic agents |
|
|
what is prostate antigen testing
|
radio labeled monclonal antibody that is attracted to prostate cancer cells. capable of detecting prostate cancer at low PSA levels.
|
|
|
What is cryosurgical ablation
|
for those pts who cannot tolerate surgery. transperineal probe inserted into prostate under ultrasound guidance to freeze tissue, chemo drugs: doxorubicin, cisplatin, and cylophosphamide may be used.
|

