![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
divides scrotal sac into two compartments externally |
median raphe |
|
|
innermost membrane surrounding the testicle |
tunica albuginea |
|
|
covers the testis and spermatic cord. Aids in protection and temp. control |
cremaster muscle |
|
|
works with cremastor muscle to elevate the testis |
dartos muscle |
|
|
composition of spermatic cord? |
1. testicular artery, cremasteric & deferential artery 2. pampiniform plexus 3. ductus deferens 4. lymphatics and nerves |
|
|
size of tesicle |
sag: 3-5cm trv: 2-4cm AP: 3 cm |
|
|
supplies the coverings of the spermatic cord |
cremasteric artery |
|
|
supplies the vas deferens and epididymis |
deferential artery |
|
|
drains the testes |
pampiniform plexus |
|
|
drains directly into the ivc |
right testicular vein |
|
|
drains into the left renal vein |
left testicular vein |
|
|
Benign germ- cell intraparenchymal cyst filled with keratin and contained within a fibrous capsule. |
epidermoid cyst |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
divides the scrotum into two parts internally |
tunica dartos |
|
|
coiled structure attached to the testicle and the posterior scrotal wall |
epididymis |
|
|
connects epididymis to the seminial vesicles |
ductus (vas) deferens |
|
|
responsible for sperm storage during maturation |
epididymis |
|
|
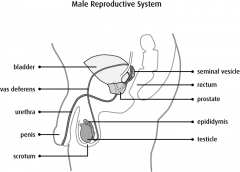
seminal vesicles location |
posterior to bladder, superior to prostate gland |
|
|
small glands that secrete fluid to help create semen |
seminal vesicles |
|
|
these two structures combine to create the ejaculatory duct |
seminal vesicles and vas deferens |
|
|
surgical correction of undescended testicles |
orchiopexy |
|
|
most common location for undescended testicles |
inguinal canal or just above the scrotum |
|
|
common cyst found in the epididymal head composed of nonviable sperm, fat, cellular debris, and lymphocytes |
spermatocele |
|
|
caused by incompetent or abnormal valves within the pampiniform plexus |
varicocele |
|
|
remnants of a formerly torsed testicular appendage |
scrotal pearl |
|
|
most common cause of epididymitis in young men |
chlamydia |
|
|
second most common testicular cancer |
embryonal carcinoma |
|
|
lab values for embryonal carcinomas |
increased AFP |
|
|
lab values for yolk sac tumors |
increased AFP |
|
|
lab values for immature (malignant) teratomas |
increased AFP and bHCG |
|
|
lab values for choriocarcinomas |
increased bHCG |
|
|
malignant tumor with normal AFP, bHCG, and LDH levels |
sex-cord stromal/sertoli-leydig tumors |
|
|
mets to the testicles are rare, but which two sites are the most common? |
prostate and kidney |
|
|
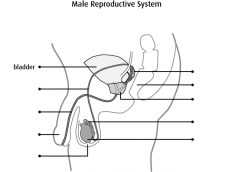
prostate is bordered anteriorly by? |
pubic bones |
|
|
prostate is bordered posteriorly by? |
rectum |
|
|
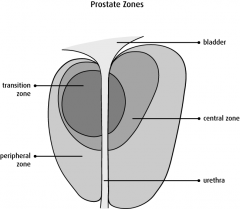
prostate is bordered superiorly by? |
bladder |
|
|
prostate is bordered inferiorly by? |
urogental diaphragm |
|
|
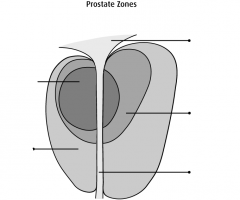
most common location for prostate cancer |
peripheral zone |
|
|
second most common location for prostate cancer |
central zone |
|
|
which zone is the origin of benign prostatic hyperplasia |
transitional zone |
|
|
arterial supply to the prostate? |
internal iliac artery -> inferior vesical artery |
|
|
normal size of prostate |
young patients: 20g or less older patients: 40g or less |
|
|
increased levels of PSA are indicative of? |
BPH or malignancy |
|
|
increased prostatic acid phosphatase is associated with? |
prostate carcinoma |
|
|
sonographically appear as hypoechoic structures superior to the prostate and posterior to the bladder |
seminal vesicles |
|
|
calcifications commonly seen in the inner glands of the prostate |
corpora amylacea |
|
|
birth defect in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis |
hypospadias |
|
|
diverticulum of the prostatic urethra |
prostatic urtricle cyst |
|
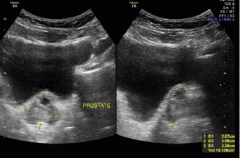
|
prostatic urtricle cyst |

