![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what zone of the prostate are the majority of adenocarcinomas? |
Peripheral zone |
|
|
In what zones of the prostate does BPH arise? (2) |
Transitional & periurethral zones |
|
|
Normal glands in the prostate are lined by ___ layers of cells. Prostatic adenocarcinoma glands in the prostate are lined by ___ layers of cells |
2 1 |
|
|
Growth and differentiation in the prostate is controlled by what hormone, produced from testosterone by what enzyme? |
Hormone: dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Enzyme: 5-alpha reductase |
|
|
Patient presents with dysuria, fever, chills, perineal pain. Prostate is tender and soft, neutrophils in prostatic secretions |
Acute bacterial prostatitis (usu E.coli) |
|
|
Patient is asymptomatic or presents with dysruia, pelvic discomfort, and lower back pain. History of recurrent UTIs. Histology: plasma cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, & neutrophils |
Chronic bacterial prostatitis |
|
|
Most common form of prostatitis, seen in sexually active men |
Nonbacterial chronic prostatitis |
|
|
Vague symptoms, may be secondary to surgical manipulation of prostate; may mimic prostatic carcinoma |
Granulomatous prostatitis |
|
|
Enlargement of the prostate due to proliferation of glands and stroma |
BPH or Nodular hyperplasia |
|
|
Prostatic caliculi are seen in... |
BPH |
|
|
Enlarged, firm-rubbery nodular prostate |
BPH |
|
|
Prostatic adenocarcinoma that is not clinically significant is called: |
latent carcinoma |
|
|
Highest incidence of prostatic adenocarcinoma occurs in what race? |
African-American men |
|
|
2 things that, interestingly, do not contribute to prostatic adenocarcinoma |
Alcoholism (they have lower testosterone) Smoking |
|
|
Histologic features of prostatic adenocarcinoma |
Prominent nucleoli, prostatic crystalloids, blue mucin, and peri-neural invasion |
|
|
What system is used to grade prostatic cancer? |
Gleason Grade 2 scores, 1-5 each, added together |
|
|
What is the doubling time of prostatic cancer? |
4 years |
|
|
Men with benign prostatic disease have a free PSA % ______ Men with prostatic adenocarcinoma have a free PSA % ______ |
Benign: greater than 23 Adenocarcinoma: less than 6 |
|
|
Screening for prostate cancer begins at age... |
40 in African Americans 50 in others |
|
|
A precursor of prostatic malignancy |
prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) |
|
|
Most common sarcoma of prostate is..... Most common prostatic sarcoma of adults (greater than 20 years) is... |
Overall/under 20: rhabdomyosarcoma Over 20: leiomyocarcoma |
|
|
Case: sudden onset of right flank pain, radiated to groin, cramps, 10/10 Construction worker |
Kidney stone! |
|
|
What do you expect to see with a kidney stone in terms of blood/urine? Symptoms? |
Hematuria Possibly high calcium Normal/high BUN & creatinine Sx: pain and nausea, vomiting (vagus nerve) |
|
|
How do you adjust blood calcium for albumin level? |
For every gram% albumin below 4 (4 is normal), you add 0.8 to the calcium |
|
|
Most kidney stones contain ______ 80% of those are ________ |
calcium CaOxalate |
|
|
Stones larger than ____ must be surgically removed |
9mm |
|
|
A struvite/ ammonium magnesium stone is often seen in ______ and caused by _______ |
Women, proteus mirabellus UTI |
|
|
Bent penis is.... Can be caused by: (3) The plaques are in which layer? Treated by? |
Peyronie's disease Beta blockers, genetics, trauma Tunica albuginea Xiaflex |
|
|
Erection for longer than 4/6 hours is.... Tx? |
priapism Tx: surgical intervention or sympathomimetic agent (alpha 1 to decrease blood flow into penis) |
|
|
Scrotum that transilluminates |
Hydrocele, usually due to trauma, will go away on its own |
|
|
Nursing home patient complaining of "swelling" Rash with serpiginous edge |
Yeast infection |
|
|
Whole-body edema |
anasarca |
|
|
1. Swelling of the glans 2. Swelling of the foreskin that traps the glans inside 3. Swelling of the foreskin that traps it in a retracted position |
1.Balanitis 2. Phimosis 3. Paraphimosis |
|
|
Firm, painless swelling in one testicle Most common age/race? Risks? |
Testicular cancer Ages: 20-39 Caucasians Mumps orchitis, undescended testicle |
|
|
25 y/o HTN Aching back pain, bilateral, with blood in urine, occasional fever |
Polycystic kidney disease |
|
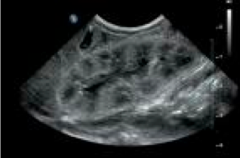
|
Renal ultrasound of polycystic kidney disease |
|
|
Adolescent boy Acute testicular pain, precipitated by cold What test do you use? What is wrong? 90% cases caused by |
Testicular torsion Doppler ultrasound to check for blood flow Twisted spermatic cord Caused by congenital malformation of the tunica vaginalis |
|
|
What hurts more when you raise the testicle? Less? |
More: testicular torsion Less: epididymitis |
|
|
45 y/o with painful nut, especially in right superior area Green discharge, mild dysuria |
Epididymitis caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea |
|
|
Warts ...proper name Caused by? |
Condyloma accuminata HPV |
|
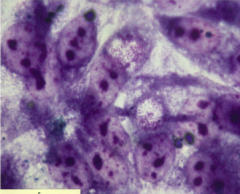
|
Chlamydia |
|
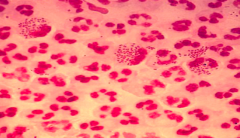
|
Gonorrhea Gram negative intracellular diplococci |
|
|
Burning rash on genitalia with blisters |
Genital herpes |
|
|
Painless sore on penis |
Syphilis (chancre) |
|
|
How to test for primary syphilis? Secondary? Tertiary? |
1: scraping of chancre w/ dark field microscopy 2: VLDR 3: CSF VLDR |
|
|
What is a common manifestation of secondary syphilis? (2) Tertiary? (5) |
2: maculopapular rash, especially on palms and feet & flu-like symptoms 3: syphlitic gummas, thoracic aortic aneurism, gait problems, memory problems, pupillary dysfunction |
|
|
Extreme itching |
Can be uremia from kidney failure |
|
|
What common OTC drug can cause kidney problems? |
NSAIDS! |
|
|
What lab value changes would you expect to see with worsened kidney failure? |
Low bicarb (not reabsorbed) Low calcium High potassium High BUN/creatinine |
|
|
Painless hematuria, no accompanying symptoms |
Renal cell carcinoma (EVEN if urine screen for malignant cells is negative) |
|
|
What is a normal BUN to creatinine ratio? Elevated suggests? |
15:1 Elevated: hypoperfusion, acute kidney injury (pre renal) |

