![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
According to CFR PART 33.37 each spark ignition system must have: |
1. Dual ignition system with at least 2 spark plug for each cylinder. 2. Two separate electric circuit with separate sources of electrical energy. [Important] is because is for reliability; because If you loose one you could use the other. 3. Or have an ignition system of equivalent in flight reliability. |
|
|
|
What are the types of ignition? |
1.MAGNETO (MOSTLY USED) 2.BATTERY (RARELY USED) 3. FADEC (FULL AUTHORITY DIGITAL ENGINE CONTROL) |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the IGNITION SYSTEM? |
1. To produce high voltage needed for ignition. Simple way: to ignite a spark;to ignite the air fuel mixture |
|
|

What is the advantages of DUAL IGNITION? |
*Redundancy;provides a backup ignition system *Gives more complete &quick combustion of the fuel; gives a faster combustion *increases output power of the engine |
|
|
|
1st.Types of ignition; magneto igniting systems. 1.use _____ or _______ tension ignition system. 2.may be battery assisted at ______ __ ONLY. |
1.High,low 2.start up |
|
|
|
What are the three parts of a magnetic ciruit? |
1.permenant magnet 2.electrical steel 3.pole shoes |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the magnetic circuit? |
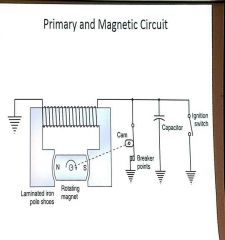
Generates the magnetic Flux lines by switching poles through a rotating magnet and creates electrical energy |
|
|
|
What is INDUCTION? |
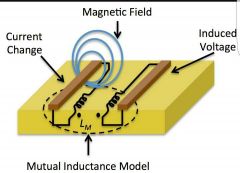
Is to carry from one current carrying inductor to the other current Carrying inducted, magnetically. |
Using a lines of Flux to carry a flow of electricity |
|
|
2ND. Types of ignition;battery ignition systems (older planes) 2. Battery assist with ignition during _______ __ and _________. |
Start up, taxiing |
|
|
|
3RD.Types of ignition System FADEC [Full Authority Digital Control] |
A solid state digital electronic ignition and electronic sequential port fuel injection system with only ONE MOVING PART. The opening and closing of the fuel injector. |
|
|
|
What is the difference between something ELECTRICAL and something ELECTRONIC? |
ELECTRICAL requires wires, you could see it; ELECTRONIC has no wires, is hard to see; an example and SD CARD |
|
|
|
MAGNETOS;BASIC AC GENERATOR;FACTORS 1._________IT TURNS_________ THE OUTPUT. 2.REQUIRES __ ________POWER SOURCE. 3.____ _______ REFERS TO MAGNETOS VOLTAGE OUTPUT (12Kv to 20Kv) 4.___ _______REFERS TO MAGNETOS VOLTAGE OUTPUT (APPROX. 300 VOLTS) 4.Kv= ________ ____. |
1.FASTER,GREATER 2.NO OUTSIDE 3.HIGH TENSION 4.LOW TENSION 5.THOUSAND VOLTS |
|
|
|
3 facts of single magneto? |

1.One self contained unit 2. Most common type in aviation 3.May be in high or low tension |
|
|
|
What are the three circuits for magnetos? |
1. Magnetic 2. primary winding 3. Secondary winding |
|
|
|
What are the 3 parts for a magnetic circuit? |
1. Permenant Magnet 2. Electrical Steel 3. Pole Shoes |
|
|
|
Magnetic Circuit; Electrical steel 1. Is made of ___ ______ iron alloy and containing some _______. 2.Has high __________ and low __________;has the magnet traveling through lines of_____. 3. The _______rotates the lines of flux |
1.low carbon, silicon 2. Permeability, rentetivity,Flux 3.magnet |
|
|
|
What is the difference between PERMEABILITY and RETENTIVITY? |
PERMEABILITY - is the measure of ease with which lines of MAGNETIC [FLUX lines can PASS through a material. ] (Ex.)Make a piece of metal into a magnet. RETENTIVITY- ability of MAGNETIZING MATERIAL to RETAIN ALIGNMENT of the MAGNETIC DOMAINS after the MAGNETIZING FORCE IS REMOVED. (ex.) how long before the piece of metal will retain a magnet after the magnet is removed |
|
|
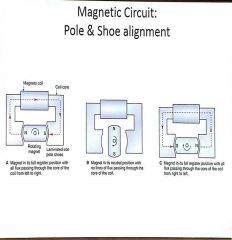
Magnetic Circuit; pole and shoe alignment |
NOTE |
|
|
|
POLE AND SHOE ALIGNMENT FULL REGISTER POSITION. 1.ROTATING MAGNET IS FULLY ALIGN WITH THE_____ ______. 2.STATIC FLUX DENSITY IS AT ___________. 3.MAX AMOUNT OF FLUX FLOWS THROUGH THE ________ _______. |

|
|
|
|
POLE AND SHOE ALIGNMENT;NEUTRAL POSITION 1.ROTATING POLE ARE POSITIONED ________ POLE SHOES. 2.STATIC DENSITY IS AT _____. 3. __ _____ OF FLUX ARE FLOWING THROUGH THE MAGNETIC CIRCUIT. |

|
|
|
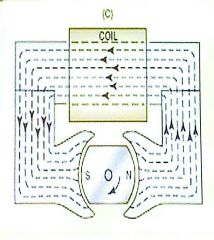
POLE AND SHOE ALIGNMENT;FULL REGISTER. 1. POLARITY HAS NOW ___________. 2. FULL MAGNETIC LINES OF FLUX PRODUCED _________ ________. |
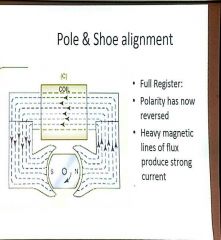
|
|
|
|
How does the E-gap work with the BREAKER POINTS? |
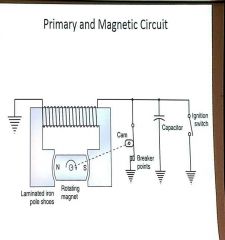
When magnet is at E-GAP position, breaker points break contact,from the primary winding everything is dump to the capacitor. |
|
|
|
What is another name for E-GAP? |
Efficiency gap or e-gap position. |
|
|
|
E-GAP When the magnet is in the Egap position it has rotated just a few degrees beyond it's ________ ________. |
Neutral position. |
|
|
|
Ignition switch grounds out the primary circuit, is to turn____ the switch. |
Off |
|
|
|
What are the parts for the primary circuit? |
P-lead,breaker point,capacitor,ignition switch |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the p-lead? |
To deactivate the ignition switch. By the means that is connected to ground. (It turns off that magneto)(it does not turns off the engine unless you shut down both magnetos) |
Is connected to ignition switch to the coils |
|
|
What is the major disadvantage of a magneto? |
The magneto has low RPM'S then means it has low VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
What are the three types of material we can use for breaker points? |
Tubgsten,platinum, uranium |
|
|
|
What is the acronym for ATA |
Air Transport Association |
|
|
|
What is a capacitor? |
An electrical component that is used to store electrical energy in electrostatic fields. |
|
|
|
What happens to the capacitor as breaker points open? |
It absorbs excess energy. |
|
|
|
Another name for capacitor is ___________? |
Condenser |
|
|
|
Is a FEED THROUGH CAPACITOR installed PARALLEL or in SERIES? |
SERIES |
|
|
|
How do you deactivate a magneto? |
You ground the primary circuit using the switch. |
|
|
|
What is the P-lead? |
Is the primary circuit that goes to the switch. The purpose of the P-lead is to deactivate the magneto. |
|
|
|
What are the three types of auxiliary starting systems in a magneto? |
Induction vibrator, and SHAKE JAKE and IMPULSE COUPLINGS. |
|
|
|
How do get a spark in the spark plug? |
The magnet once it reaches to the e-gap position. the primary winding has been charged. primary winding break points break contact. capacitor dumps the primary winding charge goes out to the magnetic field. induces secondary circuit. it goes to the coil tap. goes to the rotor gear into the distributor block. then to the ignition leads. lastly to the spark plug and BOOOOOM |
|
|
|
What's inside the distributor block? |
A rotor gear |
|
|
|
What is happening in the magnetic circuit during the full register position? |
The rotating magnet is fully aligned, static Flux density is at maximum. |
|
|
|
What is happening to the magnetic circuit during the neutral position? |
Magnet position is at 6 and 12 o' clock. Static Flux density is at zero |
|
|
|
Other than the Flux density and the position of the rotating magnet. What else does the magnetic circuit do? |
It creates AC (alternating current) through the Flux lines |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the breaker points? |
Breaker points is timing mechanism. When it breaks Contact. the resistance increases and the primary winding charge gets dump to the condenser. |
|
|
|
How many volts are going just to the primary circuit? |
300 volts |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a FEED THROUGH CAPACITOR AND REGULAR CAPACITOR. |
FEED THROUGH CAPACITOR IS a FILTER FOR [RFI] RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE. AND STORES ELECTRICAL ENERGY. AND IS ALWAYS CONNECTED IN [SERIES.] CAPACITOR JUST STORES ELECTRICAL ENERGY AND IS ALWAYS CONNECTED IN [PARALLEL] |
|
|
|
What is happening to magnetic circuit during e-gap position? |
The magnet is passing through neutral position. The electricity from the primary winding is going through the breaker points, and the electricity is being dump through capacitor |
|
|
|
What are three materials we can use for breaker points? |
Tungsten,platinum and uranium |
|
|
|
What is the probable reason why a breaker point will be burned? |
The capacitor might not be working. And is taking the full 300 volts. |
|
|
|
The capacitor acts like a_________ with the primary circuit. |
Filter |
|
|
|
Why do we have low tension in the ignition systems? |
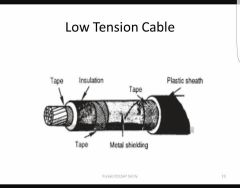
Low tension works better in high altitudes |
|
|
|
By what component do the breaker points open and closed? |
By the camshaft |
|
|
|
What are the spark plugs heat ranges? Why? |
Between 1,000°F to 1,300°F: because there is LOW AMOUNT OF DEPOSITS within this range. At Idle:900°F (above) At full power:1,300°F (below) |
|
|
|
How many volts are in one ampere? |
100 volts or 100 watts |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the spark plugs? |
*To provide an air gap to create the ignition spark. *to complete the path to GROUND for SECONDARY CIRCUIT. > from CENTER to the GROUND ELECTRIC |
|
|
|
Aircraft spark plugs; Gas pressure inside the cylinder can be as high as ______PSI and the temperature can be as _________°F. |
2,000 PSI , 3,000°F |
|
|
|
Aircraft spark plugs; what are the common spark plugs? |
Electrodes:center to ground Insulation:porcelain |
|
|
|
What is the lowest voltage that an electrode spark plug has to be able to jump accross to ground electrodes ? |
At 12,000 volts |
|
|
|
At the beginning of insulation spark,what was the material of the insulation spark plug made of? |
Porcelain |
|
|
|
What was the 2 disadvantages of the insulation spark plugs? |
*It absorbed oil *Physical inconsistencies of the natural material made volume production difficult. |
|
|
|
During World War II, what material was used to the spark plug and is used today? |
Aluminum Oxide |
|
|
|
If a spark plug is dropped why is it that the spark plug has to be replaced automatically? |
Because it may cause damage to the spark plug that cannot be seen by visual inspection. |
|
|
|
What are the 2 possibilities of consequences of damage insulation in a spark plug? |
1.OVERHEATING or HOT SPOTS on the ground electrodes causing PRE-IGNITION or DETONATION. 2. FLASHOVER from the ignition lead terminal to the outer causing of the spark plug either WEAK or NON-EXISTENT SPARK. |
|
|
|
The two classification of spark plugs according to their heat range are: |
1.Hot spark plug= Long 2. Cold spark plug=Short 1.Hot spark plug=long>low compression,LOW PERFORMANCE,low operating temperatures. 2.cold spark plugs=short>high compression,HIGH PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
Two basic types of electrodes used on aircraft spark plugs are: |
1.(massive type):relatively low cost and efficient for wide scope of operations. Excessive amounts of lead in the fuel and can cause fouling 2.(fine wire): (aka all weather):More expensive |
|
|
|
Spark plug massive type (ground electrodes) are made of what kind of material? |
Made of NICKEL ALLOY |
|
|
|
Spark plug FINE WIRE type (ground electrodes) are made of what kind of material? |
Are made of PLATINUM &IRIDIUM ALLOY |
|
|
|
What is the reach for a hot and cold spark plug? |

Hot is 13/16 inch.> long Cold is 1/2 inch.>short |
The reach will tell us if is hot or cold spark plug. |

