![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Magnetic field |
A region where a force is exerted on magnetic materials |
|
|
How are magnetic fields represented? |
By field lines- always from north to south |
|
|
What happens at a neutral point? |
The field cancels out |
|
|
Go through the parts to the right hand rule |
Magnetic field is in the direction of the curled fingers. Current for the thumb |
|
|
Draw the magnetic field for a coil |

|
|
|
Draw the magnetic field for a solenoid |
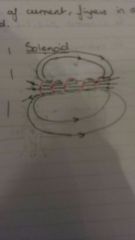
|
|
|
What happens if a wire carries a current in a magnetic field? |
It will experience a force |
|
|
Go through Flemings left hand rule |
Thumb force First finger field Second finger current |
|
|
What is the force acting upon the current- carrying wire proportional to? |
The strength of the magnetic field The current in the wire The length of the wire in the magnetic field Hence, F=BIL |
|
|
What is magnetic field strength equal to? |
Magnetic flux density |
|
|
When is the force acting upon a wire greatest? |
When the magnetic field and the wire are perpindicular |
|
|
When the field lines and wire are not perpindicular, the force is equal to? |
F= BILsintheta |
|
|
Go through the possibilities for directions in terms of wire and field lines |

|
|
|
How can a magnetic field be created? |
By a current moving through a conductor |
|
|
Can you derive F=Bqv |

|
|
|
What happens to a charged particle in a magnetic field? |
They are deflected in a circular path |
|
|
How can scientists analyse samples? |
Using a mass spectrometer |
|
|
What happens first to a sample before it is put into a mass spectrometer? |
It is vaporized and then ionised |
|
|
What and why are the ions accelerated through the mass spectrometer? |
The ions are charged therefore they experience a force as they travel through the electric field. The electric field accelerates them along the tube. |
|
|
Why do the ions follow a circular path within the mass spectrometer? |
Due to the magnetic field. The magnetic force on a charge always moves perpindicular to the movement of the charged particle- hence it moves in a circle. |
|
|
What does the radius of the path of each ion depend upon? |
The strength of the magnetic field The mass to charge ratio. The velocity of the charged particle. |

