![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PPF |
Production Possibilities Frontier Curve Shows trade-off of goods production. |
|
|
Ceteris Paribus |
All other things equal |
|
|
Fallacy of Composition |
Assumption one instance applies to all others |
|
|
Post Hoc Fallacy |
Supposes if one event follows another the first event caused the second. |
|
|
Marginal Analysis |
The impact of one more or less variable upon an economic outcome ex.. 1 worker = ? output |
|
|
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns |
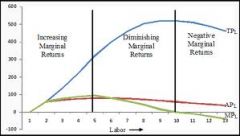
At some point additional inputs start to diminish output |
|
|
Inputs of production |
1. Raw material 2. Labor 3. Capital 4. Entrepreneurship |
|
|
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs |
Productivity decreases, Cost of production increases. |
|
|
Law of Demand |
Inverse relationship b/w price and quantity demanded. |
|
|
Diminishing Marginal Utility |
States the more units of a product are available, the less it is valued. |
|
|
Determinates of Demand |
Taste Income Price and avail. of substitute Future price or quantity expectations # of buyers Gov't regulations |
|
|
Equilibrium Price |
Balance b/w buyer and seller interests. |
|
|
4 Main Economic Systems |
Free-Consumers & producers operate in an unregulated environment. Traditional-Society does not change its methods of prod/cons Command-gov't regulates prod/cons Mixed-blend of 3 other systems. |
|
|
GDP |
Gross Domestic Product, Final g/s produced w/ in country's boarders in 1 year. |
|
|
GNP |
Gross National Product, Same as GDP except US bus. abroad money counts against. |
|
|
Expenditure Measurement |
Household consumption (C) Business Investment (Ig) Gov't (G) Net foreign purchases (Xn)
C + Ig + G + Xn = Expenditure Measurement |
|
|
Business Cycle |
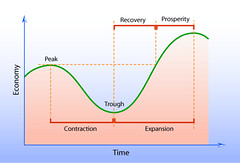
Expansion Peak Contraction Trough Recovery |
|
|
Economic Indicators |
Leading (predict a change) Coincidental (same time) Lagging (after the change) |
|
|
Phillips Curve |

A.W. Phillips, unemployment and inflation inverse relationship. |
|
|
Stagflation |
Inflation and unemployment rise at the same time. |
|
|
LRAS |
Long-run aggregate supply, g/s produced in a given time. |
|
|
NRU |
The natural rate of unemployment (NRU) is defined as the equilibrium rate of unemployment i.e. the rate of unemployment where real wages have found their free market level. It is where the aggregate supply of labor is in balance with the aggregate demand for labor. |
|
|
SRAS |
Short-Run Aggregate Supply suggests an increase in prices leads to a temporary increase in output as firms employ more workers. |
|
|
Types of unemployment |
Structural - mismatch of skill Frictional - between jobs Cyclical - due to decline in total spending |
|
|
CPI |
A measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food and medical care. The CPI is calculated by taking price changes for each item in the predetermined basket of goods and averaging them; the goods are weighted according to their importance. |
|
|
GDP Price Index |
GDP Deflator vs. CPI. The GDP deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy. Unlike the CPI, the GDP deflator is a measure of price inflation or deflation for a specific base year. |
|
|
PCE |
The PCE price index measures the price fluctuations and related consumer behavior for all domestic consumption of durable and non-durable goods and services targeted toward individuals and households. The PCE "core index", however, excludes the more volatile components of food and energy. |
|
|
Cost-push Inflation |
inflation caused by an increase in prices of inputs like labour, raw material, etc. The increased price of the factors of production leads to a decreased supply of these goods. |
|
|
Demand-pull inflation |
A term used in Keynesian economics to describe the scenario that occurs when price levels rise because of an imbalance in the aggregate supply and demand. When the aggregate demand in an economy strongly outweighs the aggregate supply, prices increase. |
|
|
AE |
Aggregate Expenditures is defined as : AE = C+Ip+G+Xn C = Household Consumption. Ip = Planned Investment. G = Government spending. |
|
|
Say's Law |
Supply creates it's own demand. |
|
|
Demand-side Economics |
Advocates use of government spending and growth in the money supply to stimulate the demand for goods and services and therefore expand economic activity. 'Keynesian Economics' |
|
|
Supply-side Economics |
By lowering taxes on corporations, government can stimulate investment in industry and thereby raise production, which will, in turn, bring down prices and control inflation |
|
|
Laffer Curve |
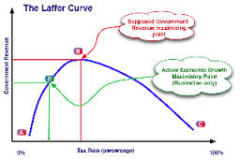
one possible representation of the relationship between rates of taxation and the hypothetical resulting levels of government revenue. |
|
|
MPC/MPS |
The marginal propensity to consume is the portion of extra income that consumers spend.
The marginal propensity to save is the portion of extra income that consumers save. |
|
|
Injections |
An investment of capital generally in the form of cash or equity. |
|
|
Leakage |
A diversion of funds from some iterative process. For example, in the Keynesian depiction of the circular flow of income and expenditure, leakages are the non-consumption uses of income, including saving, taxes, and imports. |
|
|
Multiplier |
An increase in spending produces an increase in national income and consumption greater than the initial amount spent. |
|
|
Crowding Out |
A situation when increased interest rates lead to a reduction in private investment spending such that it dampens the initial increase of total investment spending is called crowding out effect. |
|
|
Federal Reserve |
The central bank of the United States and the most powerful financial institution in the world. The Federal Reserve Bank was founded by the U.S. Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with a safe, flexible and stable monetary and financial system. |
|
|
FOMC |
'Federal Open Market Committee - FOMC' The branch of the Federal Reserve Board that determines the direction of monetary policy. The FOMC is composed of the board of governors, which has seven members, and five reserve bank presidents. |
|
|
Comparative Advantage |
The benefit or advantage of an economy to be able to produce a commodity at a lesser opportunity cost than other entities is referred to as comparative advantage in international trade theory. |
|
|
Balance of Payments |
(BOP) of a country is the record of all economic transactions between the residents of a country and the rest of the world in a particular period (over a quarter of a year or more commonly over a year). |

