![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Adam smith |
Scottish philosopher in 1776 wrote Wealth of Nations. People acting in their own self interest can be better for a society than those trying to be. "Led by an invisible hand" , brings the greatest value product. |
Scottish philosopher - wealth of nations |
|
|
Microeconomics |
Study of individual economic actors such as the individual or corporation. Actors make decisions/allocations concerning scarce resources. |
Small scale players |
|
|
Macroeconomics |
Study of the holistic economy. What happens to the aggregate economy based on actions of all the small actors. Usually addresses questions of economic policy. |
Large scale |
|
|
Law of demand |
All things being equal, If you raise the price of a product it will lower the quantity demanded of the product and conversely if you lower the price of a product it will increase the quantity demanded |
Price v. Demand |
|
|
Demand |
The relationship between price and quantity demanded |
Not a quantity |
|
|
Demand Curve |
A graph showing get the relationship between price and quantity demanded. |
|
|
|
Demand schedule |
A table showing get the relationship between price and quantity demanded. |
|
|
|
Price of substitute products |
As price goes up for a type of good, a specific good which stays the same, shifts curve to the right for that specific good. |
How it effects demand curve |
|
|
Substitute |
2 goods of a class that serve the same purpose (interchangeable) |
As it relates to goods |
|
|
Compliment |
A good that supports another good. A kindle is a compliment to ebooks |
As it relates to goods |
|
|
Price of complimentary products |
As the price of complimentary goods goes up, the demand decreases |
How it effects the demand curve |
|
|
Expectations of future prices |
If people expect price to go up, it will increase demand or shift the graph right, if they expect the price to go down, it will decrease the demand or cause the graph to go left |
How it effects demand curve |
|
|
Impact of income changes |
If income goes up, demand goes up, if income goes down, demand goes down. (Only true for normal goods, not inferior goods) |
Impact on demand |
|
|
All things not being equal |
Price of substitute goods, price of complimentary goods, expectations of future prices, income levels, population, preference |
What we have to keep equal for law of demand to be true |
|
|
Impact of population on demand |
If population goes up or the composition shifts toward the upper class, demand goes up, if population goes down or the composition shifts toward lower class, demand goes down. |
|
|
|
Impact of preference on demand |
If an outside force impacts population preference it will impact demand if preference is shifted toward our away crook a product |
|
|
|
Normal good |
A good that adheres to the law of demand with all things being equal including changes in populace income. |
|
|
|
Inferior good |
A good that does not obey the law of demand when populace income changes. It will behave the opposite of a normal good (think of economy items - they are inferior goods) |
|
|
|
Ceteris Peribus Assumption |
Latin for "other things being equal" and pertains to the law of demand |
|
|
|
Law of supply |
All other things being equal, If the price of a good goes up, the quantity supplied will also go up. If the price goes down, the quantity supplied will also go down. |
|
|
|
Supply Curve |
A graph showing get the relationship between price and quantity demanded. |
|
|
|
Supply Schedule |
A table showing get the relationship between price and quantity demanded. |
|
|
|
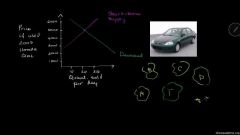
Ex. Supply Curve/Schedule |

|
|
|
|
Ex. Demand Curve/ Schedule |

|
|
|
|
Factors effecting supply |
Price of inputs (cost of production such as labor or shipping), price of related goods (other substitutes the producer can produce), number of suppliers, technology, expected future prices,government policies, natural disasters |
|
|
|
Price of inputs |
If the price of inputs goes up, supply will decrease (graph shifts left), if price of inputs goes down, supply will increase (graph shifts right) |
As it relates to the law of supply |
|
|
Price of related goods (substitutes) |
If the price of related goods goes up, the supply will decrease (shift right on graph),if the price of related goods goes down,the supply will increase (shift left on graph) |
As it relates to supply |
|
|
Number of suppliers |
If the number of suppliers goes up, the supply will go up (shift right), if the number of suppliers goes down, the supply will go down (shift left) |
As it pertains to supply |
|
|
Technology in supply process |
If new tech becomes available, supply will go up |
As it pertains to supply |
|
|
Expected future prices |
If supplier expects that prices for good will increase in the future, immediate supply will go down. If the supplier expects that future prices will decrease in the future, immediate supply will increase. |
As it pertains to supply |
|
|
Equilibrium Price |
The sweet spot where demand curve intersects with th supply curve |
|

