![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
181 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define "GDP" |
- The total market value of all final goods and services produced in the economy - Calculated in monetary terms - Usually in a year |
|
|
Define "Final Goods and Services" |
- Goods and services purchased for final use, not subject to resale, manufacturing or processing |
|
|
T or F: Intermediate Goods and Services are not subject to resale, manufacturing or processing |
- False |
|
|
Define "Intermediate consumption" |
- Cost of intermediate goods and services |
|
|
Define "Double Counting" |
- Inclusion of intermediate consumption in calculation of final goods and services during production process |
|
|
Write the formula for calculating Value Added by a firm |
- Output minus intermediate component added |
|
|
List two types of non-productive transactions |
- Purely financial - Sale of second hand goods |
|
|
List and describe the three methods of calculating GDP |
- Expenditure: Sum of all expenditure in taking total output off market - Income: Sum of the incomes from production of GDP - Production: Sum of value added along production process |
|
|
Write the equation for expenditure approach and income approach |
- Expenditure: GDP = Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Gov. purchases (G) + Net Export (NX) - Income: Wages, salaries and supplements + Gross Operating Surplus + Gross Mixed Income + Indirect taxes (excise taxes, licence fees etc.) |
|
|
List sources of Personal Consumption Expenditure |
- Durable consumer goods: cars, refrigerators, videos etc. - Non-durable consumer goods: milk, bread, shirts etc. - Services: doctors, mechanics, cleaners etc. |
|
|
List sources of Gross Private Investment |
- Final purchases of non-current assets: >> Building/construction >> Changes in stocks/inventories from national accounts, but not buying >> Cultivated products >> Intellectual property products >> Owner transfer costs |
|
|
Define "Gross Investment" (modifier) |
- Total investment goods = Replacement + Investment >> Replacing machinery used up in production: replacement >> Net additions to the economy's stock of capital: investment |
|
|
Define "Net Private Investment" |
- Additions to economy's stock of capital by non-government agencies - Used to define if economy is expanding, static or declining - NPI + Depreciation = GPI >> When NPI +ve it's expanding, when 0 it's static and when -ve it's declining |
|
|
Define "Gross Private Investment" |
- Net private investment plus depreciation - Used to define if economy is expanding, static or declining |
|
|
Define the "private" modifier |
- Only private business spending and not government agencies |
|
|
Describe the two factors of "Government Purchases of Goods and Services" |
- Consumption component (final gross capital/consumption)
- Investment component (increase in stocks) |
|
|
Describe the factors of Net Exports |
- Difference in exports and imports (X - M) - Net export is a measure of spending, where foreign spending on Australian goods outweighs Aus spending on foreign goods |
|
|
List factors composing Income Approach |
- Compensating employees: payment for labour - Gross Operating Surplus: rent, interest & profit - Gross Mixed Income - Taxes less subsidies and imports (indirect) >> treated as costs of production and added to price of goods & services >> Subsidies help production |
|
|
Describe the factors affecting the "Value-Added" approach |
- Avoid double counting by counting only value added at each manufacturer (output - input) |
|
|
List the differences between the "Nominal" and "Real" GDP and write the equation |
- Nominal (money) is measured as prices
- Real GDP is nominal adjusted by the Implicit Price Deflator to deal with inflation - Real = Nominal/Price Index (decimal) |
|
|
Define Consumer Price Index |
- Measure price level of "market basket" for goods and services of typical family |
|
|
Define Implicit Price Deflator |
- Measures average level of price changes for the factors of expenditure approach - GDP/IPD (percentage) = Constant GDP |
|
|
T or F: GDP is an inaccurate measure of social welfare due to non-market transactions |
- True |
|
|
List non-market transactions that affect social welfare |
- Leisure - Quality improvements - Composition and distribution of output - Per capita output - GDP effects on environment - Home productions - Underground economies |
|
|
Define the "International Balance of Payments Account" |
- Statement recording all transactions that take place between country residents and residents of foreign nations |
|
|
Describe the Current subcategory of the Balance of Payments |
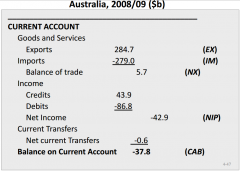
- Reflect goods & services: net difference between exports and - Income: net interest + dividend payments + reinvested earnings + life investment incomes + net payments to expatriotic workers |
|
|
Describe the Capital & Financial subcategory of the Balance of Payments |
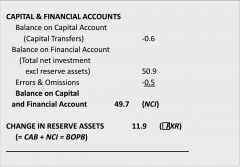
- Capital: Net capital transfers + net sales of government licenses - Financial: Net flow of direct and portfolio share investments + financial derivatives + changes in reserve assets |
|
|
List additional national accounting concepts |
- National turnover: GDP + Imports - Gross national expenditure: C + I + G - National Income: GDP - depreciation - net income paid abroad (Gross doesn't take in dep) - Domestic factor Income: GDP - depreciation - Household Income: Total income of residents - Household Disposable Income: HI - taxes |
|
|
Define the "Business Cycle" |
- The recurring fluctuations in the level or rate of growth in economic activity that show the pattern of progress of the economy's real GDP over time |
|
|
Describe the 4 common phases of the business cycle |
- Cyclical peak: Temporary maximum - Recession: period where rate of growth of output and employment decline - Trough: Temporary minimum at lowest levels - Recovery: Levels of output expand toward full-employment or capacity level |
|
|
List and describe the causes for the business cycle |
- Non-cyclical >> Seasonal variation: regular fluctuations - Cyclical impact >> postponability: Don't have to buy hard goods all the time - durable vs. non-durable >> monopoly power: resist lowering prices |
|
|
List and describe the different types of unemployment |
- Frictional: Moving between jobs because of various reason, but still seeking employment - Structural: Mismatch of skills with geographic location due to change in demand - Cyclical: Business cycle causes deficiency in aggregate demand or total spending |
|
|
Define "Full Employment" |
- AKA. Natural rate of unemployment - Sum of frictional and structural unemployment - When cyclical unemployment is zero |
|
|
List and describe the limitations of measuring unemployment |
- Part-time employment: when workers are underemployed - Discouraged workers: drop out but would prefer to return |
|
|
Describe Okun's Law |
- Relationship between unemployment rate and GDP gap - Growth in real GDP will reduce unemployment rate in Australia |
|
|
Define the "GDP gap" |
- Amount by which the actual GDP falls short of potential GDP |
|
|
List the costs of unemployment |
- economic costs: >> GDP gap >> Unequal burdens - non-economic costs: >> Social impacts |
|
|
Write the equation for Real Wage |
- Real wage = Nominal wage/Price level |
|
|
List and describe some reasons why real wage and prices remains high |
- Job rationing: high wage, low labour demand >> Insider-Outsider problem: insider can influence wage & hiring while outsider has trouble getting the job >> Efficiency wage: wage rate higher than quantity supplied with quantity demanded to increase worker efficiency - People spend lots of time searching for jobs |
|
|
List policies to reduce unemployment |
- Lowering minimum wage - Creating flexible unions - Improve job placement - Give incentives to look for jobs |
|
|
Write the equation for inflation |
- Inflation rate = (Current Year Index - PYI) x 100 |
|
|
Write the equation for GDP deflator |
- GDP def = (nominal GDP/real GDP) x 100 |
|
|
Describe the two theories of inflation |
- Demand-pull inflation: excess demand for output to produce beyond "potential" level of output
- Cost-push inflation: increase in production costs due to market power of unions and businesses through wage & profit (causes inflation - wage price inflationary spiral) |
|
|
Describe the redistributive effects of inflation |
- Affects people living on fixed nominal income - Savings lose value if inflation higher than interest rate - Inflation benefits borrowers, not creditors |
|
|
Define "Real Interest Rate" |
- Percentage increase in purchasing power a lender receives from a borrower in exchange for funds |
|
|
Define "Nominal Interest Rate" |
- Percentage increase in money that lender receives from borrower |
|
|
Describe the effect output has on inflation |
- High spending produces higher output but causes inflation - High costs push wage higher to maintain output causing further inflation |
|
|
List the assumptions made for the Aggregate Expenditures Modell |
- Closed economy - Private economy - All savings is personal savings - Depreciation, income abroad are zero - investment influenced only by real interest rates - Price-wage inflexibility |
|
|
Define price-wage inflexibility |
- Assumption that all prices, wages and interest rates are inflexible |
|
|
Define closed economy |
- When both product and financial markets of the economy are fully isolated |
|
|
Define private economy |
- When there is no explicit contribution by government to product or financial markets |
|
|
T or F: Consumption and savings levels are determined by household disposable income |
- True |
|
|
Define "Consumption schedule" |
- Schedule of income-consumption relationship showing amount households intend to consume at various levels of disposable income |
|
|
Define "Saving Schedule" |
- Schedule of income-saving relationship showing amount households intend to save at various levels of disposable income |
|
|
Define "Average Propensity to Consume" |
- Fraction/percentage of total income that is consumed - consumption/income |
|
|
Define "Average Propensity to Save" |
- Fraction/percentage of total income that is consumed - saving/income |
|
|
T or F: When Disposable Income is 1, sum of APC and APS is 1 |
- False, occurs at all levels of DI |
|
|
What is the difference between "MPC" and "MPS"? |
- Consume vs. Save - Both are divided by Δincome- Both represent slope on respective schedules - Δconsumption/Δincome - Δsaving/Δincome - Neither greater than 1 as MPC + MPS = 1 |
|
|
List non-income determinants of consumption and saving and their effect on the curve |
- Wealth
- Price - Expectations - Consumer debt levels - Taxation - Cause shift in curve |
|
|
Describe the two determinants of investment |
- Expected rate of net profits: Businesses invest if they expect profit
- Real rate of interest = Nominal interest rate - inflation rate --> profit has to be greater than real interest rate |
|
|
Define "Investment demand schedule"
|
- Schedule of investment-interest rate relationship showing accumulated investment demand at all possible levels of interest rate |
|
|
List determinants of investment demand shift |
- Acquisition, operation and maintenance costs - Business taxes - Technological change - Business expectations - Stock of capital goods on hand - Expectations |
|
|
Describe the two types of investment schedule |
- Autonomous investment: Desired level based on future expectations - Induced investment: Level of investment based on current income |
|
|
List the reasons why investment spending is instable |
- Durability of goods (postponing purchase) - Irregularity of innovation - Variability of profits - Variability of expectations |
|
|
Describe the two approaches to explaining the equilibrium level of output |
- Expenditure-output: AE = C + I --> Equilibrium when GDP = AE - Leakages-injection: Savings = investment --> Total at two sectors, planned when equilibrium |
|
|
Describe the main difference between planned and unplanned investment |
- Level of investment in business plan vs. Δlevel of business inventories - At equilibrium, Iu is zero |
|
|
List and describe causes for change in equilibrium GDP |
- Shift in savings-consumption schedule or investment schedule - Autonomous expenditure change --> Expenditure multiplier: ratio of ΔGDP from Δinvestment spending --> Multiplier effect: Δinvestment spending < Δoutput-income level - Multiplier = Δreal GDP/Δincome - Simple Multiplier = 1/MPS = 1/(1-MPC) |
|
|
Define "Paradox of Thrift" |
- When more saving actually creates less saving as multiplier effect causes greater withdrawal of aggregate expenditure - Savings must be matched by income & injection to be beneficial |
|
|
Describe the difference between equilibrium vs. full-employment GDP |
- Recessionary gap: Amount AE falls short of full-employment GDP - Inflationary gap: Amount AE exceeds full-employment GDP, inducing an inflationary effect |
|
|
Describe government expenditure (G) |
- Adds to AE, impacting GDP with multiplier - At equilibrium: AE = real GDP = C + I + G - S = I + G, where S --> saving after tax |
|
|
Describe how tax affects equilibrium GDP |
- Assumes lump-sum tax, same amount taxed at each level of GDP - Reduces level of saving and consumption - Degree of effect determined by MPS and MPC |
|
|
List and describe the different types of fiscal policies |
- Expansionary: Increases government spending, lowers taxes or both - Contractionary: Decreases government spending, raises taxes or both |
|
|
Describe the effect the multiplier has on fiscal policy |
- If T=TLS+MPT(y), then multiplier = 1/[MPT+MPS(1-MPT)] - TLS = lump-sum taxes |
|
|
Define and describe the Balanced-budget multiplier |
- Def: Amount by which the equilibrium GDP increases after use of fiscal policy that doesn't affect budget deficit - Occurs when Δgov expenditure = Δtaxation - ΔEquilibrium GDP = ΔG and ΔT |
|
|
Describe effect of foreign trade on the Aggregate Expenditure equilibrium model |
- Equation AE = C+I+G+NX, where NX = X-M - Export (X) levels depend on foreign income - Import (M) levels depend on domestic income - Exports not controllable |
|
|
Define and describe the Complex Multiplier |
- Recognises that imports are leakage of Aggregate Expenditure-Income flow - Foreign trade reduces expenditure multiplier and slope of AE - Open economy multiplier = 1/(MPS + MPM) - Complex (k) = 1/[MPT + MPS (1-MPT) + MPM] |
|
|
Define "Aggregate Demand curve" |
- Shows amount of goods and services that buyers are willing to buy at certain prices - Price vs. real GDP - Buyers include consumers, businesses, government and foreign buyers |
|
|
Explain why the slope of the Aggregate Demand curve flattens to the right |
- Interest rate effect: As price levels rise, so do nominal interest rates, reducing consumption and investment spending - Real-balances effect: As price levels rise, purchasing power falls and this reduces consumption (wealth effect) - Foreign purchases effect: Rise in domestic price level due to net export |
|
|
Explain how the Aggregate demand curve is derived from the Aggregate Expenditures model |
- Uses 45 degree line & Expenditure equation - Equal rise in spending and GDP - GDP plugged into expenditure equation to find price - Multiplier for Demand-Supply model, where shift in AD curve = Initial change x multiplier |
|
|
Describe the difference between price and non-price determinants |
- Price determinants move along curve where variable is price - Non-price determinants shift curve, where price is fixed |
|
|
List and explain the different ways the Aggregate Demand curve can be shifted |
- Consumer spending: Wealth, expectation, indebtedness and tax rates - Investment spending: Interest rate, expectation, tax rates, technology and degree of excess capacity - Government spending - Net export spending: Foreign GDP and exchange rate |
|
|
Define "Aggregate Supply Curve" |
- Indicates level of output at each price level
- Has direct relationship between price and GDP |
|
|
Describe the differences between short-run and long-run supply |
- Short --> Initial price is P1 and nominal wages based on expectation that P will remain the same --> Input prices remain same --> Shifts left when price increases - Long --> Input price responsive to price level --> Curve at natural rate of unemployment |
|
|
What determines the position of the AS curve? |
- Input prices - Domestic resource availability - Land, labour, capital - Entrepreneurial ability - Import prices - Market power - Productivity (productivity = output/input) - Legal & settings (tax & subsidy, regulation) |
|
|
What can be determined by finding the equilibrium of demand & supply |
- Equilibrium price - Equilibrium output |
|
|
Describe Demand Pull Inflation |
- Demand increases while supply is fixed, due to rise in output - Multiplier affected by available labour and resources |
|
|
Define the "Ratchet effect" and list its' causes |
- Tendency for prices of products and resources to be inflexible in a downward direction --> Wages: fixed short term 'sticky' --> Employer's interests --> Monopoly power --> Menu costs: implementing changes in the first place |
|
|
List causes for shift in Aggregate Supply |
- Changing production costs: high costs shift left - Cost-push inflation: when unions or businesses push for higher wages, causing a rightward shift - Stagflation: High and increasing unemployment and inflation, caused by a leftward shift in AS |
|
|
Define and describe Price-level changes and multiplier |
- Demand shifts at different points of supply curve - Horizontal = full multiplier - Intermediate = reduced - Vertical = no multiplier |
|
|
List Federal Government expenditures |
- Final consumption goods and fixed assets - Specific purpose grants: amount spent by buyers for state government authorities |
|
|
List sources of Federal Government revenue |
- Personal income tax: Taxable income after exemptions and deductions, average and marginal rates increase with income - Company income tax: Profit = Net profit - depreciation - investment, issue of double tax fixed by giving credit for company income - Indirect and other taxes: GST, excise taxes |
|
|
Define "Discretionary Fiscal Policy" and describe the two methods |
- Deliberate manipulation of taxes and spending by government to alter real GDP & employment - Expansionary: When in recession to create deficit, increases gov spending, lowering taxes or both - Contractionary: When demand-pull inflation to create surplus, opposite effect of expansionary, creates surplus |
|
|
Define and describe "Non-Discretionary Fiscal Policy" |
- Built in stabilisers that affect deficit/surplus during recession/inflation respectively - Reduces severity of fluctuations - Can cause fiscal drag, where surpluses make achieving full employment difficult |
|
|
Describe the "Cyclically adjusted budget" |
- Indicates what budget surplus/deficit would be if economy is operating at potential output - Deficits can be caused by fiscal inaction when in recession as the stabilisers affect deficit |
|
|
List some issues with fiscal policy |
- Timing issues
- Political issues: other goals - Political business cycle: voters |
|
|
Describe the "Crowing Out" effect |
- Whenexpansionary fiscal policy increases interest rate, investment spending is reduced, reducing effect of the policy |
|
|
Define "Public Debt" |
- Total accumulation of federal government's total deficits and surpluses over time |
|
|
List and describe the different budget philosophies |
- Annually balanced budget: Pro-cyclical, not economically neutral - Cyclically balanced budget: Counter-cyclical, not balanced annually - Functional finance: Balance economy instead of budget, with growth offsetting debts |
|
|
List some issues with public debt |
- External debt not owned - Increased tax lowers incentive to invest - Bond ownership distributed more to wealthy - Crowding out: deficit financing lowers investment spending, future production lower - can be fixed by an increase in public investment & unemployment |
|
|
What is the positive role of debt? |
- Debt is good for growing economy as it turns savers into spenders to maintain high output |
|
|
Define the "Foreign purchases effect" |
- High domestic prices means more imports and less exports |
|
|
Describe the effect of crowding out on expansionary fiscal policy |
- With crowding out: Expansionary fiscal policy shifts demand right, crowding & inflation reduces effect of expansionary fiscal policy - Without crowding out: Shifts demand right |
|
|
Describe the effect the open economy has on fiscal policy |
- Altered by international conditions - Small economies susceptible to shocks, rendering fiscal policies inappropriate |
|
|
Define "Net Export Effect" and describe its effects on the fiscal policies |
- Changes caused by interest-rate that affect exchange rate and fiscal policy is less effective - Expansionary: Higher interest rates & demand for $, appreciation of $ and decline in net export - Contractionary: Opposite to expansionary |
|
|
Describe how fiscal policy affects Aggregate Supply |
- Tax changes to give businesses & individuals incentives drives Aggregate Supply to the right - Stimulates economy with low price & high GDP - Tax cuts increase Aggregate demand, but induces higher tax revenue for supply |
|
|
Define and describe "Money" |
- Mostly liquid asset - Medium of exchange for goods & services - Unit of account, for relative worth - Store of wealth due to liquidity & convenience |
|
|
List components of "M3" |
- Currency - Current deposits in banks - Non-current accounts |
|
|
T or F: Broad money is a preferred measure over M3 as a medium of exchange |
- False |
|
|
List components of "M0" |
- Currency held by public - Currency held by banks - Bank demand deposit with RBA |
|
|
Describe demand for money |
- Defined as demand for real money balance - Transactions Demand (Dt): Medium of exchange, level depends on GDP, curve vertical - Asset Demand (Da): Store of wealth, level depends on interest rates, curve slopes down |
|
|
Describe total demand for money (Dm) |
- Dm = Dt + Da (added horizontally) - Change in interest rate moves along curve - Change in money GDP shifts demand curve |
|
|
List the responsibilities and functions of the RBA |
- Control of note issue - Banker for banks (settlements & deposits) - Banker for government (deficits) - Management of international payments - Implementation of monetary policy - Regulation of payment system - Membership of APRA - Membership of Council of Financial Regulators |
|
|
Describe the money market (demand vs. supply) |
- Money demand & supply curve intersect determines equilibrium interest rate - Interest rate (y-axis) against amount of money demanded (x-axis) |
|
|
Describe interest rate |
- Interest rate represents opportunity cost of holding money balances - Pbond = Coupon/yield - When increase, more bonds bought, but more demand for bond increases price which decreases yield - When money GDP falls, interest rate also falls |
|
|
Describe the balance sheet of a bank |
- Statement of assets and claims, to summarise financial position of a firm - Assets = claims - Assets = liabilities + net worth |
|
|
Describe the steps to form a bank |
- 1: Selling of shares, gain cash & liability of stock - 2: Acquiring property & equipment (assets) - 3: Starts accepting deposits from community --> Gain cash as asset, deposit as liability - 4: Set required reserves and reserve ratio --> Reserve ratio = required reserves/deposit liab --> Reserve calculated as asset - 5: Grant loans: give cash, record loan as asset |
|
|
Define "Excess reserves" |
- Bank reserves in excess of the reserve requirement |
|
|
Describe the banking system |
- Money created with multiple-deposit expansion - Deposits don't create money, but loans do - Loan drawn from excess, deposited in bank - Calculated by money multiplier: M = 1/Ratio - If reserves withdrawn, money supply reduced - Influences business fluctuations --> Worsen recession by preventing credit expan --> Worsen inflation by increasing lending |
|
|
Describe how the reserve ratio is determined |
- Based on bank's prime assets - Indicated by Prime Assets Ratio (PAR) - PAR determined by APRA and banks |
|
|
List sources of lending leakage |
- Currency drains: loan paid as cash, not deposit - Deposit transfer to non-bank institutions - Larger excess reserves |
|
|
List the objectives of monetary policy
|
- Influence interest rates and credit availability --> Stabilise real GDP, employment & price level - Aim for full employment - Aim for non-inflationary level of output - RBA responsible |
|
|
Describe the cause-effect chain of monetary policy |
- Cash rate --> interest charged for exchange settlement --> sets cost of short-term funds for banks - Short term interest rates --> influences rate banks willing to lend - Aggregate demand: change in cost/availability of bank credit on spending & investment - Monetary policy, increase in interest rate: --> reduce amount of investment --> increase purchasing of financial assets |
|
|
List the differences between easy & tight monetary policy |
- Easy: RBA reduces cash rate, lower cost and increasing availability of credit --> expands spending & real GDP --> Real rate & money - shift supply right, invest - move right along, price & GDP - shift demand right but shifts back a bit (tight is opposite effect) - Tight: RBA increases cash rate, raises cost and lowers availability of credit --> reduces spending & inflationary pressures |
|
|
List the assets & liabilities of the RBA balance |
- Assets --> Gold & foreign exchange --> Government securities - Liabilities --> Notes on issue --> Non-callable deposits --> ESA funds |
|
|
Describe ESA funds |
- Exchange Settlement Account funds - Accounts kept by banks with RBA to settle debts owing to other banks from exchanging cheques and to provide funds - If ESA fund goes into deficit, can borrow from bank or trade in repo |
|
|
Define "Repo" |
- Repurchasing agreement - Agreement detailing price, timing and conditions for banks and RBA to exchange government securities |
|
|
Describe how Open Market Operations are used to determine cash rate |
- Buying & selling government securities in cash money market to affect cash rate --> Buying/selling: RBA buys/sells securities from banks, paid with ESA funds and bank reserve increases/decreases -->Change in bank reserve causes bank monetary base and lending ability to change - Aim to make demand & supply of ESA to balance at target cash rate (inc - tight/dec - ease) |
|
|
Describe how Foreign Exchange Settlement is used to determine cash rate |
- Used as substitute to Open Market Operations - Intervening foreign exchange market by buying & selling Australian dollars - Buying foreign currency is like buying government securities, similar effect on ESA |
|
|
Define the "Rediscount rate" |
- Rate at which RBA buys or sells short-term securities under repo |
|
|
Describe factors regarding implementation of monetary policies |
- Affects three markets, effectiveness depends on shape of demand curve --> Money market --> Investment market --> real GDP (but not aggregate demand curve) - Feedback effects --> Reducing GDP reduces business profits & investments |
|
|
Describe the "Net Export Effect" |
- Change in interest affects exchange rate value - Increase in interest rate appreciates currency, lowering exports & vice versa |
|
|
T or F: External shocks can adversely affect RBA's monetary policies |
- True |
|
|
List the strengths & weaknesses of monetary policies |
- Strength --> Quick & easy to carry out compared to fiscal --> Impacts broadly so not subject to politics - Weakness --> Cyclical asymmetry --> Conflict with treasury goals --> Cost-push inflation --> Investment insensitivity |
|
|
Describe Taylor's Rule |
- Used to determine what interest rate is right - Relates observed interest rates to inflation and deviation between potential & actual GDP - Formula: i - π = 1.5 + a*(π - π*) + b*(y - y*)/y* - π = inflation rate, π* = Target inflation rate - y = GDP, y* = potential GDP - If π > π* or y > y*, slow inflation by raising interest rate |
|
|
Describe the Phillips Curve Model |
- Shows stable inverse relationship between unemployment rate and rate of inflation - Higher rate of growth of Aggregate demand, the higher the inflation and GDP, causing lower unemployment (opposite effect for low growth - Assumes fixed AS curve, but it can shift left - Not a reliable basis for economic policy |
|
|
Describe the use of the Phillips curve |
- Explains trade-off between unemployment and inflation --> Labour market imbalances: bottlenecks & structural problems --> Market power of unions & big businesses: Higher wages with higher price & profit push |
|
|
Define the "Stabilisation Policy Dilemma" |
- Fiscal & monetary policies affect AD, not labour market imbalances or market power |
|
|
Define the "Reversibility problem" |
- Price flexible upwards but not downwards due to the ratchet effect |
|
|
Define "Stagflation" |
- Experiencing high and increasing unemployment and inflation from supply shocks, productivity decline and inflationary expectation and wages (expected future price level) |
|
|
Define "Natural Rate Hypothesis" |
- Suggests a unique level of unemployment as basis for fluctuations - This level, in long run, is full-employment rate |
|
|
Describe the "Theory of Adaptive Expectations" |
- Form expectations of future inflation - Series of short run trade offs of unemployment & inflation, long run vertical - Phillips curve: explains disinflation (reduces rate of inflation) |
|
|
Describe the "Ration Expectations Theory" |
- Increase in money wages lags behind increase in price level, giving temporary increase in profit & employment - Suggests measures to increase employment accelerates inflation - Short run aggregate supply doesn't show change in price level - However, input prices flexible with price level |
|
|
List the new classical policy implication under Natural Rate Hypothesis |
- Price level surprises: Short run instability, but long run works at full employment - Long run occurs quickly - Government intervention not necessary for changes to unemployment & inflation |
|
|
List the Keynesian policy implication under Natural Rate Hypothesis |
- Markets not highly competitive - Nominal wage adjustments slow - Stabilisation policies required for changes to unemployment & inflation |
|
|
Describe the policy dilemma for cost-push inflation |
- Government intervention to increase Aggregate demand causes an inflationary spiral - No government intervention allows recession but nominal wages declines and AS returns |
|
|
List the non-demand management methods of cost-push inflation |
- Market policies --> Employment and training policy --> Pro-competition to reduce monopoly powers --> Trade practice laws - Wage-price policies --> Government constraint of nominal income & prices paid to influence real income --> Wage-price: guidepost (voluntary) & controls (mandatory) |
|
|
Describe the "Purchasing Power Parity" model |
- Converts different countries to the same currency via the exchange rate & identical items cost the same using this common currency - Pd = foreign price = E x Po/s - Pd E = Pd/Po/s |
|
|
List the problems with PPP |
- Non-traded goods - Product differentiation - Difference in consumption patterns/preference - Transportation costs - Tariffs & industry assistance distort prices - Different market structures and productivity - Difference in interest rate |
|
|
Describe "Relative PPP" |
- ∆E/E ≅ ∆Pd/Pd - ∆Po/s/Po/s - Helps explain appreciation & depreciation --> Appreciation is reduction in the units required to buy one unit of another country --> Depreciation is an increase in units - If domestic inflation rate > foreign rate then the currency will depreciate |
|
|
List the different types of exchange rate systems |
- Flexible/floating: Affected by demand/supply - Fixed: Government intervention - Managed float: Central banks buy/sell foreign exchange to smooth domestic rates |
|
|
Describe the balance of payments for a flexible exchange rate system |
- Exchange rate automatically adjusted - Monetary policy deals with interest rates - If domestic decreases as o/s increases (dom depreciates), then Balance of Payments is at a deficit, causing exchange rate to shift |
|
|
List the disadvantages of a flexible ERS |
- Uncertainty & reduced trade from volatile exchange rate - Terms of trade worse when international value declines - Macroenvironment is unstable from shift in net exports & hinders monetary/fiscal policies |
|
|
Describe how a fixed exchange rate system is maintained |
- Require adequate reserves to balance deficits - Trade policies: Increase net exports - Rationing: Restricting imports to exports - Domestic adjustments: Using monetary & fiscal policies to adjust GDP to the fixed exchange rate - Exchange rate set by central bank - Selling reserve shifts supply to right |
|
|
Describe a managed float exchange rate system |
- Encourages international trade & finance - Special Drawing Rights are bookkeeping entries used to settle payment deficits or satisfy reserve needs - Supported by trade growth & turbulence management - However, still has volatility/requires adjustment & reinforcing inflation (inflation --> depreciation) |
|
|
Describe the "Fisher Equation" |
- Describes exchange rate behaviour - i = ri + ∆P*/P (ri = real interest rate, i = nominal interest rate & ∆p*/p = expected interest rate) - International equation is relative --> id - io/s = ∆P*d/Pd - ∆P*o/s/Po/s = ∆E/E - Nominal interest rate reflects difference in expected rates of inflation between countries |
|
|
List the different asset market models and what they model |
- Asset Market Approach/Portfolio Balance Approach: looks at change in exchange rate due to shifts in investors assets, due to change in relative real return on assets - Interest Arbitrage: relationship between returns in asset markets & exchange rate --> rd* ≅ ro/s* - ∆E*/E |
|
|
Describe the role of Expectations/Interest changes in the PBA models |
- Expectations: Value of future exchange rate --> Relative inflation rates --> Relative growth rates --> Expected changes in interest rates --> Expected government intervention in foreign exchange market - Interest rate --> returns from foreign and domestic assets |
|
|
Describe the evaluation of Interest Arbitrage |
- Adjustment to future expected exchange rate - Specific risk: only if assets identical - Transaction costs - Tax Regimes - Government controls - Time lags |
|
|
Describe the monetary approach |
- Looks at relationship between domestic money supply, demand and exchange - Money Supply: M = R + D - Money Demand: L = k x Pd x Y - PPP: ∆E/E ≅ ∆R/R + ∆D/D - ∆Po/s/Po/s - ∆Y/Y |
|
|
List the results of the monetary approach |
- If foreign prices increase, domestic constant, exchange rate appreciates - If domestic income grows, world income constant, exchange rate appreciates - If domestic credit increase, exchange rate depreciates - ∆R not under floating, as E not affected |
|
|
Describe the impact of an easing of monetary policy |
- Short run --> Interest rate on investment tends to rise, as asset sale is inversely related to its yield --> Desire to hold few domestic assets leads to fall in demand for currency, increasing supply - Long run --> Increase in investment associated with lowering of interest rates --> Increase in output, employment & income --> Increase in general level of prices |
|
|
Describe Exchange Rate overshooting |
- Adjustments of short term equilibrium greater than adjustments to long term equilibrium - Due to differences in speed of adjustment between asset and product market prices |
|
|
T or F: Value of currency reflects relative returns on assets or expectations but not current account problems |
- True |
|
|
T or F: Monetary policy can be conducted independently of exchange rate |
- False |
|
|
Define "Growth Economics" |
- Analysing the patterns of long-term trends in an economy's productive capacity - Analysing factors that influence these trends - Calculated by real GDP & real GDP per capita over time |
|
|
List the importances of growth |
- Greater ability to face economic challenges - Small changes in growth can affect economy - Increased opportunities in income, education, social welfare & environment - Lessens burden of scarcity - Helps nation achieve goals and resolve issues |
|
|
List the causes of growth |
- Supply factors --> Quantity and quality of human/nat resources --> Supply and stock of capital goods --> Technology and knowledge --> Increase output by raising amount, quality or productivity of input (labour force productivity) - Aggregate demand and resource allocation --> Demand factor (growing level of demand) --> Efficiency factor (Allocation to goods/services) |
|
|
Describe the Production Possibilities Curve |
- Capital vs. consumer goods - Improvement in supply shifts curve outwards - Economy only on curve with enough demand |
|
|
Describe the relationship between productivity & growth |
- Output (Y) per hour of work (H) - However, this measurement only works with good data, rely on labour (L) instead - Productivity growth = growth in output - growth in hours --> dln(Y/H) = dY/Y - dH/H |
|
|
List the different models of production |
- Labour-only model: Y = F(L) --> assumes diminishing returns to labour - Elaborate production model: Y = F(L,K) - Labour productivity: Y/L = F(L,K)/L - Y = GDP, L = labour input, K = capital input |
|
|
Describe the technology & growth model |
- Tech defined as anything that raises amount of output given labour & capital - Y = F(L,K,T) - L = labour input, K = capital input, T = tech |
|
|
Define the differences between invention, innovation and diffusion of technology |
- Invention: Discovery of new knowledge - Innovation: Application of inventions to create new products or alter old products |
|
|
Define "Real Cost Reduction" |
- Producing the same amount of output for less |
|
|
Define the "Neo Classical approach" |
- Production functions allow allocation of inputs to outputs |
|
|
Describe how organisations are considered technology |
- Tech innovation is producing more for the same amount, like the aim of organisations - Technological change: More effective --> Labour-saving: Fewer workers needed --> Capital-saving: Fewer machines needed - Specialisation: more proficient --> Human capital: accumulated knowledge/skills --> NPV of benefits > NPV of costs |
|
|
Describe the Classical Growth Model |
- Emphasises supply side growth
- Determinants of productive capacity --> Law of diminishing returns: more resources input, less output yielded --> Pop. growth: Optimum growth (Yield greatest income per person) --> Malthus's thesis: Given diminishing returns, growth will force the standard of living down |
|
|
Describe the Full-employment Growth Model |
- Aggregate expenditures: Expanding levels of demand are needed for full-employment GDP - Investments: income/capacity creating - Capital-output Ratio: Relationship between rise in size and value of capital and rise in real GDP |
|
|
List Australia's growth record |
- Real GDP increased by 6.3 times - Real GDP per capita increased by 2.8 times - Growth less than other developed nations - Sources of growth --> Labour inputs: immigration --> Productivity increases: tech, capital, training --> Allocative efficiency & growth --> Political stability & social philosophy |
|
|
List government growth policies |
- Keynesian policies - Supply-side policies - New-classical economics and little intervention |
|
|
List the positives & negatives of growth |
- Positives --> Improved living standards --> Environmental benefits --> Income equality --> Non-material considerations - Negatives --> Pollution & environmental deterioration --> Not preventing poverty --> Obsolescence of humans, human values |
|
|
Describe the Doomsday models and their criticisms |
- Extreme growth of population, output and pollution will outweigh limits of natural resources and pollution absorbing capacity - Criticisms of this view --> Price system --> Behavioural patterns --> Role of technology --> Applying existing knowledge --> New resources and products --> Increasing returns to technology |

