![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of economic growth |
- actual - potential |
|
|
Actual growth |
- short run - usually due to an increase in aggregate demand- can also be caused due to an increase in aggregate supply |
|
|
Potential growth |
- long run - caused by an increase in the capacity or productive potential - rise in quality or quantity of inputs e.g. more advanced machinery |
|
|
Difference between actual and potential growth |
actual - actually produces more goods and services potential - economy could produce more goods and services |
|
|
PPF |
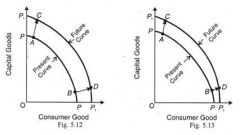
production possibility frontier |
|
|
The economic cycle |
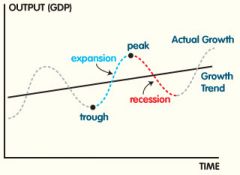
positive and negative output gap |
|
|
Benefits of economic growth |
- consumers can purchase more goods and services - increase in economic welfare meaning consumers can satisfy more of their needs - actual growth = decrease in unemployment - rise in equality - inflation will fall - improvements in the fiscal position |
|
|
Costs of economic growth |
- real GDP could decrease without an increase in GDP per capita - only actual and not potential growth will cause inflation - economic growth tends to rise inequality - negative externalities e.g. global warming and using up fossil fuels |
|
|
Short run Classical Economic growth diagram |
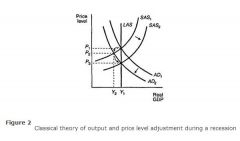
- shift stuck at B - leave AD - supply side policies 1. reduce trade union power 2. reduce minimum wage 3. cut direct taxes and welfare |
|
|
Short run Keynesian Economic growth diagram
|
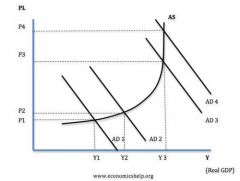
Fiscal policy - spending increase, tax decrease, deficit increase, multiplier effect increase Monetary policy - i/r increase, money supply increase, e/r decrease |
|
|
Long run Classical Economic growth diagram
|

|
|
|
Long run Keynesian Economic growth diagram
|

|
|
|
Supply side policies that long run growth will include |
- can affect labour by giving incentives to work such as reducing direct taxes, decrease unemployment benefit and tax credits - changes in retirement age = increase in the working population - more enterprise by reducing business taxes, regulation and increasing competition |
|
|
Demand-side shocks |
- boost in consumer confidence e.g. house prices rising - recession of country's major trading partners = decrease in exports |
|
|
Supply-side shocks |
- poor harvest = price increase = economy's capacity decreasing - new source of raw material = price reduction and supply increase |
|
|
Speculation |
when people buy assets with a hope to sell them later |
|
|
Requirements of sustainable economic growth that make it hard to achieve |
- expand output every year - find a continuous supply of raw materials - growing markets for the increase output - reduce negative externalities e.g. pollution - do this at the same time as other countries with the same objectives |

