![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the formula for Inactivity Rate? |

It refers to all the demand in the economy.
|
|
|
What is the Formula for AD? |
C + I + G + (X - M) C - Consumption I - Investments G - Government Spendings X - Exports M - Imports |
|
|
What does Demand mean? |
It refers to 1 product (goods or services) |
|
|
What does GDP mean? |
It stands for Gross Domestic Product, which is a measure of how well/bad the economy is performing (economic activity), it also measures consumption. |
|
|
What does a Decrease in GDP mean? |
- A shrinking economy - Rise in unemployment - Possibility of a recession |
|
|
What does a decrease in GDP mean? |
- A shrinking economy - Rise in unemployment - Possibility of a recession |
|
|
What does a Recession mean in an economy? |
- Prolonged economic decline - Higher rates of unemployment - Business activity decreases, impacts the circular flow of income - Consumer spending declines - Government reduces taxes & BoE reduces interest rates (more borrowing & spending) |
|
|
What are the 3 examples of Injections in an economy? |
- Exports - Government spending - Investments |
|
|
What are the 3 examples of Withdrawals in an economy ? |
- Taxation - Imports - Savings |
|
|
What is does the term Soft landing mean? |
It is when the economy grows without falling into recession |
|
|
What is a Depression? |
A depression is a prolonged recession, a significant fall in output and average living standards. When real GDP falls by more than 10% from the peak of the cycle to the trough. |
|
|
What is a Boom? |
When real national output is rising at a faster pace than the trend of growth Faster growth of consumption (strong consumer confidence) Large demand in capital goods, businesses invest in extra capacity Fall in unemployment High demands for imports (can lead to trade deficit) Government tax revenues increase Inflationary pressure increases |
|
|
What is a Slowdown? |
When rate of growth decelerates (but national output is still rising) |
|
|
What is a Recovery? |
When real GDP picks up from the trough reached at the low point of the recession Cuts in interest rates Rise in government borrowing Policy of QE |
|
|
What does Quantity Easing mean? |
QE is when the BoE pumps more money into the banking system in a bid to increase the supply of loans. |
|
|
Explain the Circular flow of Income (Diagram) |
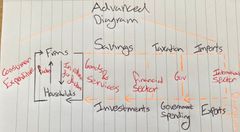
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is a Trade deficit? |
When a firm cannot supply all of the goods and services that consumers are buying |
|
|
What is the Economic Cycle (diagram)? |
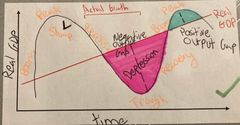
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What factors affect Economic growth? |
Investment Productivity Labour Supply Research Innovation Enterprise |
|
|
What does Economic growth mean? |
It is the sustained rise in a country’s productive potential and real national output |
|
|
What are the benefits of Economic growth? |
Higher Standards of living Fiscal dividend Employment effects Accelerator effect - Businesses will increase capital spendings |
|
|
What does Inflation mean? |
Inflation is a sustained increase in the cost of living leading to a fall in the purchasing power of money The rate is measured by the annual percentage change in consumer prices (CPI) |
|
|
What does Cost-Push inflation mean? |
This is when the cost for a business rise and businesses react by rising prices, therefore pushing prices onto consumers |
|
|
What does Cost-Push inflation mean? |
This is when the cost for a business rise and businesses react by rising prices, therefore pushing prices onto consumers |
|
|
What are the causes for Cost-push inflation? |
Scarcity of raw materials External shocks Workers asking for more money Increase in land rent Rising import prices due to a falling exchange rate |
|
|
What does Demand-pull inflation mean? |
This is when consumers pull prices up as they want more goods, hence the supply can’t keep up |
|
|
How can Government increase/decrease Disposable income? |
To increase disposable income government will reduce tax To decrease disposable income government will raise tax |
|
|
Why does the BoE raise/reduce interest rates? |
BoE will raise interest rates to reduce disposable income and reduce inflation BoE will reduce interest rates to increase disposable income to encourage inflation |
|
|
What does Deflation mean? |
Deflation is the decline in the general price level in an economy, signified by annual inflation rate below 0%. |
|
|
What does Deflation mean? |
Deflation is the decline in the general price level in an economy, signified by annual inflation rate below 0%. |
|
|
What does Disinflation mean? |
Disinflation is a fall in the rate of inflation, where prices are still rising, but at a slower rate |
|
|
What does Deflation mean? |
Deflation is the decline in the general price level in an economy, signified by annual inflation rate below 0%. |
|
|
What does Disinflation mean? |
Disinflation is a fall in the rate of inflation, where prices are still rising, but at a slower rate |
|
|
What does Hyper-inflation mean? |
Hyperinflation is a period of very high rate of inflation, usually leading to a loss of confidence in an economy’s currency |
|
|
What do Unit labour costs mean? |
These costs reflect total labour costs, including social security and employees pension contributions, and including the cost of self-employed labour incurred in the production of a unit of economic output |
|
|
What factors affect Inflation? |
Falling interest rates Cost of labour, materials Productivity Exchange rates The printing of money Tax falling or rising A growing domestic economy A neighbouring economy growing The buying of government bonds |
|
|
Why is Inflation bad for savings? |
It is bad for businesses, as if inflation keeps rising costs will be hard to figure out this creates instability. |
|
|
What does Monetarists believe? |
Monetarists believe that the objective of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply |
|
|
What does Sanction mean? |
Where a country no longer trades with another country UK & USA with Russia |
|
|
What does Deficit spending mean? |
When government spending exceeds its revenue |
|
|
What does Deficit spending mean? |
When government spending exceeds its revenue |
|
|
What causes Demand-pull inflation? |
Excess AD Links with money and credit boom Economy close to full capacity (inelastic AD) Positive output gap |
|
|
What are the Internal causes of inflation? |
Large surge in property prices, rise in business taxes, boom in credit/money supply & higher wages/labour costs |
|
|
What are the External causes of inflation? |
Increase in world oil/gas prices, depreciation of exchange rate, high inflation, in other countries & inflation in global commodity prices |
|
|
What does the Consumer Price Index mean? |
The CPI is a measure of the price level in the economy, based on the prices of a collection of products designed to reflect the consumption basket of the average household |
|
|
Formula for Index number? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What affects the CPI? |
Average family basket differs (low income Vs high income household) Price fluctuations of certain goods (food, energy) Housing costs are not included (CPI H) Basket updates are too slow (once a year) Spending patterns are affected by household size CPI is slow to react to products |
|
|
What are the Impact of Short/Long term economic growth? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What factors affect Short term economic growth? |
Exchange rates & interest rates Fiscal policy Commodity prices Trading conditions in other countries Confidence of businesses & households |
|
|
What are Nominal Wages? |
Wages that are expressed in a monetary form, and do not take into account changes in prices |
|
|
What are Real Wages? |
Real wages are nominal wages adjusted for the effects for inflation, which is a guide to how living standards have changed. |
|
|
What does Unemployment mean? |
Unemployment is someone who are not working but are actively seeking work, but they are still part of the labour force. |
|
|
What does Underemployed mean? |
Someone who is working in a job that requires lower skills than they have. Architect working as a gym instructor It is often a response to cyclical unemployment and a consequence of structural unemployment |
|
|
What are the 5 causes of Unemployment? |
Structural unemployment Cyclical or demand deficient unemployment Seasonal unemployment Frictional unemployment Real wage unemployment |
|
|
What does Structural unemployment mean? |
Occurs when there is a mismatch between jobs & skills in the economy Usually when the structure of an economy changes, when there is no longer a need for a specific type of worker or the relocation of production (western industries to China) |
|
|
What does Cyclical/Demand deficient unemployment mean? |
Caused by a fall in AD in the economy, that occurs usually in a slowdown or during a recession This is when the demand for labour is a demand derived from the demand for goods & services. As output falls in an economy,firms lay of workers |
|
|
What does Seasonal unemployment mean? |
Occurs as certain seasons come to an end and labour is not required until the next season |
|
|
What does Frictional unemployment mean? |
Occurs when workers are between jobs, usually short-term unemployment. When workers have voluntarily left their previous job to search for another |
|
|
What does Real Wage unemployment mean? |
When wages are inflexible at a point higher than the free-market equilibrium wage. Usually caused by the existence of minimum wage laws High wages = an excess supply of labour, which represents real wage unemployment |
|
|
What is Net Immigration? |
It is the difference between inward migration & outward migration (emigration) |
|
|
How is Unemployment measured? |
The Claimant Count The International Labour Organisation Survey (ILO) |
|
|
What is the formula for Employment Rate? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for Employment Rate? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for Unemployment Rate? |
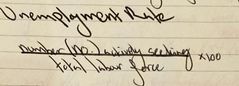
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for Employment Rate? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for Unemployment Rate? |
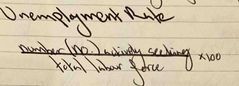
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for Labour Force Participation Rate? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Why can Employment rate rise whilst Unemployment rate increases? |
Caused by an increase in immigration, which increases working age population. Can also be caused by a decrease in the inactivity rate as more people move from inactive to employed |
|
|
What is the problem with Unemployment rates? |
They do not capture the hidden unemployment rate that occurs in the long term, as workers who look for a job may eventually give up and become economically inactive. |
|
|
How does Migration affect Employment? |
Immigration usually fills jobs people will not fill, such as manual labour, dangerous & low skilled jobs. An increase supply of labour may push down wages in the economy, especially for low skilled jobs. Which becomes an incentive for firms to hire more workers, thus increasing employment rate. |
|
|
How does Migration affect Unemployment? |
Immigrants may displace some local workers, increasing the level of unemployment, but this depends on immigrants skill as they may be unable to find work. |
|
|
How does Unemployment affect the Government? |
Increased spending on benefits Less tax revenue Increased spending on retraining |
|
|
How does Unemployment affect Individuals? |
Loss of income Suicide Stress increases Mental instability Health issues Sense of failure Marital failure |
|
|
How does Unemployment affect the Economy? |
Increased crime Vandalism Increased anti-social behaviour Increased homelessness |
|
|
How does Unemployment affect Firms? |
Loss of sales revenues Loss of output/production Changes the skill level in the economy |
|
|
Why is Youth unemployment relevantly high? |
Lack of experience Lack of education or training Age discrimination Economic downturns Automation & technological advantages |
|
|
Who are Discouraged workers? |
Workers constituted of one group of inactive work-seekers. These are people who have ceased to seek work because they believe there are no suitable available jobs |
|
|
What does Hidden unemployment mean? |
Also known as disguised unemployment, which is the number of people who don't have work but who are not counted in government reports. These are people who have stopped looking for a job & people who work less than they want to |
|
|
What causes Hidden unemployment? |
Giving up the active search for work, so they become economically inactive Disabilities |

