![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do you listen for in our patient's stories?
|
-History
-Physical Exam -Labs/Imaging -Assessment -Plan |
|
|
What are some reasons that women go to see their family doctor?
|
Besides depression,
|
|
|
What comes after the chief complaint?
|
History of present illness (HPI)
|
|
|
Comprehensive woman's health history
What is next? |
Chief complaint
History of present illness Gynecologic history Obstetric history Medical history Surgical history Medications Medication allergies Family history Social history Review of systems |
|
|
What are the objectives of the OB-GYN History?
|
-Assess health risks
-Assess compliance with recommended screening -Demonstrate communication skills and build trust by maintaining an awareness of contextual factors. |
|
|
What is objective 1 of the OB-GYN History?
|
Assess health risks
|
|
|
What are the health risks we are assessing?
|
Unintended pregnancy
Sexually transmitted infections Cervical pathology Breast malignancy Gynecologic malignancies Domestic violence |
|
|
What is the second objective of the OB-GYN History?
|
Assess compliance with screening
|
|
|
What screening modalities are we assessing compliance with?
|
-GYN exam: cervical and ovarian pathology
-Breast exam -Breast imaging -Osteoporosis -Cholesterol/Diabetes -Colon cancer |
|
|
What is the third objective of the OB-GYN History?
|
Build trust through an awareness of social factors .
|
|
|
What social factors do we need to be aware of?
|
-Culture
-Ethnicity -Language/literacy -Socioeconomic class -Spirituality/religion -Sexual orientation |
|
|
What are the components of a women's medical history?
|
1. GYNECOLOGIC HISTORY
2. OBSTETRIC HISTORY |
|
|
What does the gynecologic history consist of?
|
-Menstrual history
-Pap smear history -Contraceptive history -Sexual history -Infertility history -GYN surgical procedure |
|
|
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
|
abnormal uterine bleeding that cannot be attributed to medications, blood dyscrasias, systematic diseases, trauma, uterine neoplasms or pregnancy
|
|
|
Menorrhagia (hypermenorrhea):
|
prolonged (> 7 days) or excessive (> 80 ml) of uterine bleeding occurring at regular intervals. (rrhagia=excessive, to burst forth)
|
|
|
Metrorrhagia
|
irregular episodes of uterine bleeding
|
|
|
Menometrorrhagia
|
irregular intervals
|
|
|
Polymenorrhea
|
bleeding occurring at regular intervals of less than 21 days.
|
|
|
Oligomenorrhea
|
bleeding interval greater than 35 days
|
|
|
Amenorrhea
|
bleeding interval greater than 6 months.
|
|
|
Dysmenorrhea
|
Pain immediately before or with the onset of menstruation
|
|
|
What are the components of the menstrual history?
|
-Age of menarche
-age at menopause -Current cycle characteristics -Associated symptoms |
|
|
What current cycle characteristics that we should inquire our patients?
|
• First day of last menstrual period (also HPI)
• Frequency of current flow • Duration of flow • Amount estimate |
|
|
What do we should obtain about the patient's pap smear history?
|
-Date and results of most recent
-Prior abnormal results |
|
|
If a patient has prior abnormal results, we do we need to know?
|
-Evaluation?
-Treatment? -Follow-up? |
|
|
What do we need to know about our patient's contraceptive history?
|
-Methods and dates contraception!!
-Complications -Reasons for changes |
|
|
What do we need to know about our patient's gynecologic infections?
|
-Sexually transmitted infections
-Assessment of past and current risk factors -Results of routine screening tests (HIV, GC, etc.) -Other (bacterial vaginosis, yeast etc.) |
|
|
What do we need to know about our patient's sexual history?
|
• Dyspareunia
• Current/past abuse or assault |
|
|
Dyspareunia
|
pain with intercourse
|
|
|
Examples of gynecologic procedures
|
-Hysteroscopy
-Hysterectomy -Bilateral tubal ligation -Oophorectomy |
|
|
What is the summary of GYN history?
|
-Menstrual history
-Pap smear history -Contraceptive history -Sexual history/orientation -Infertility history -GYN surgical procedure |
|
|
Gravid
|
Number of times a woman has been pregnant
|
|
|
Parity
|
the number of times a female has given birth counting multiple births as one and usually including stillbirths
|
|
|
What are the standard elements of the parity
|
F - Full term
P - Pre-term A - Abortion L - Living |
|
|
Gravity
|
a technical term that refers to the number of times a woman has been pregnant. A gravida is a pregnant woman. A woman who has never been pregnant is referred to as a nulligravida or gravida 0. A woman who is pregnant for the first time is referred to as a primigravida or gravida 1. A woman who has been pregnant some other number of times is referred to as gravida 2, gravida 3, and so on.
|
|
|
Nulliparous
|
A woman who has never given birth is referred to as being nulliparous, a nullipara, or para 0. A woman who has given birth a particular number or times is referred to as para 1, para 2, or para 3, and so on. Biparous or bipara are sometimes used as synonyms for para 2.
|
|
|
Multiparous
|
A woman who has given birth two or more times is referred to as multiparous. Multiparous can also be used to describe someone who has given birth to more than one offspring at once.
|
|
|
Gravida
|
Woman who is or has been pregnant
|
|
|
Nulligravida
|
never been pregnant
|
|
|
Primigravida
|
A woman who is in or who has experienced her first pregnancy
|
|
|
Multigravida
|
pregnant more than once
|
|
|
Parity
|
number of births
|
|
|
Nullipara
|
never had a pregnancy progress to beyond the age of viability
|
|
|
Primiparous
|
completed one pregnancy to the age of viability
|
|
|
Mulitparous
|
completed two or more pregnancies to the stage of viability
|
|
|
Parturient
|
currently in labor
|
|
|
Puerpera
|
just recently given birth
|
|
|
Ms. Jarvis: Currently pregnant, with one prior pregnancy that was an ectopic pregnancy
What are her G’s and P’s??? |
G2 P0010
|
|
|
Ms. Smith: Three prior pregnancies. One was a miscarriage, the other two were full term. Both children are living
What are her G’s and P’s??? |
G3 P2012
|
|
|
Ms. Murphy: One prior pregnancy that was full term and the child is living.
What are her G’s and P’s??? |
G1 P 1001
Or G1P1 |
|
|
Ms. Jones: One prior pregnancy with twins that were born at term and both children are living?
What are her G’s and P’s??? |
G1 P 1002
|
|
|
What are the possible outcomes of pregnancy?
|
-Term and preterm deliveries
-Induced Abortions -Spontaneous abortions -Ectopic -Molar pregnancy |
|
|
What do you need to know about you patient's term & preterm deliveries?
|
-Type of delivery
-Fetal complications -Maternal complications -Treatment history |
|
|
What do you need to know about your patient's induced abortions?
|
-Estimated gestational age
-Associated medical condition -Complications -Methods |
|
|
What do you need to know about your patient's spontaneous abortions?
|
-Estimated gestational age
-Associated maternal conditions -Methods -Complications -Results of recurrent spontaneous abortions |
|
|
What do you need to know about your patient's ectopic pregnancy?
|
-Location of pregnancy
-Treatment modality |
|
|
What do you need to know about your patient's molar pregnancies?
|
Treament history
|
|
|
What websites do you visit to get images of molar pregnancies?
|
embryology.med.unsw.edu.au
www.nzhis.govt.nz/.../gfx/miscarriage2.jpg |
|
|
Ms. Jones, How many times have you been pregnant? What happened with each one of those pregnancies?
|
I have been pregnant 4 times and have two healthy children.
The first pregnancy I delivered April 11 1998. It was my first baby, and labor was long, but both me and my son were healthy. The second baby was exposed to rubella and died. Term, no complications 7/1999 Pre-term, congenital rubella 27 weeks, did not survive 2/2001 spontaneous miscarriage, no procedures 4/2005, term, cesarean, gestational diabetes |
|
|
Ms. Jones OB history
|
G4 P 2112
4/1998 Term, SVD no complications 7/1999 Pre-term, SVD fetal demise in utero congenital rubella 27 weeks 2/2001 spontaneous miscarriage, no procedures 4/2005, term, cesarean for failure to progress, gestational diabetes |
|
|
Ms. Jones OB history
|
G4 P 2112
4/1998 Term, SVD no complications 7/1999 Pre-term, SVD fetal demise in utero congenital rubella 27 weeks 2/2001 spontaneous miscarriage, no procedures 4/2005, term, cesarean for failure to progress, gestational diabetes |
|
|
What do you state at the beginning of every HPI
|
“The patient is a 26 yo gravida X para Y with a last menstrual period on DATE here today for CHIEF COMPLAINT”
|
|
|
What are the locations of ectopic pregnancies?
|
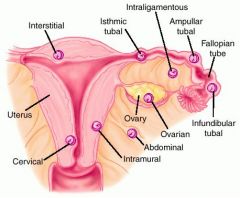
-Ovarian
-Abdominal -Infundibular tubal -ampullar tubal -interligamentous -intramural -interstitial -cervical |
|
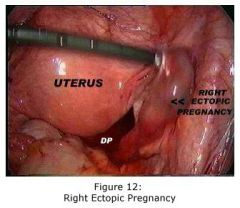
If you can't read? What is this?
|
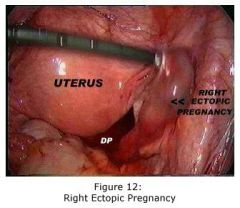
Right ectopic pregnancy.
|
|
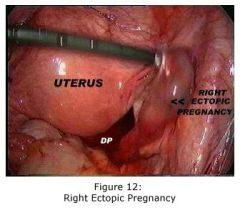
If you can't read? What is this?
|
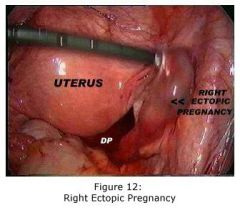
Right ectopic pregnancy.
|
|
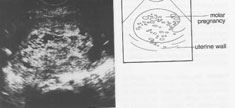
This is a ultrasound of a ______. Ignore the text
|
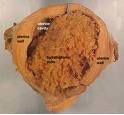
Molar pregnancy. Here is the pathology specimen.
|

