![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
What hypothalamic hormones stimulate ==> FSH ==> LH ==> ACTH ==> TSH ==> Beta-LPH ==> Prolactin ==> Growth Hormone |
- GnRH
- GnRH - CRH - TRH - CRH - PRH - GHRH |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- what 2 adenohypophysis hormones not only have stimulatory, but also Inhibitory hormones from hypothalamus? |
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Prolactin |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- what are the 2 inhibitory hormones? - what hormones do they inhibit? |
- GHIH inhibits GH
- PRH inhibits Prolactin |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- GHIH is also called what? - PIF is also called what? |
- Somatostatin
- Dopamine |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
- which hypothalamic hormone is more dominant as the inhibitory rather than its stimulatory counterpart? |
- PIH (dopamine)
(more dominant than PRH) |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- what type of feedback loop is UNSTABLE? - what type of feedback loop is STABLE? |
- Positive
(no baseline b/c too much or too little) - Negative |
|
|
HORMONE CONTROL LOOPS
- in the HPA, what are the 3 types of Negative Feedback loops? |
- Long loop
- Short loop - Ultra short loop |
|
|
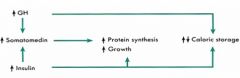
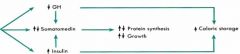
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the Metabolic Effects of GH? x4 |
(ASK ' D)
- Anabolic effect - Sparing of Protein - Ketogenic effect - Diabetogenic effect |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- Excessive GH leads to what effect on Fat utilization? |
- Ketogenic effect
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- how does GH cause a Diabetogenic effect? |
- GH-induced Insulin resistance
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- excessive GH leading to a GH-induced Insulin Resistance is often associated with which Dz? |
- Type 2 DM
|
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH effects on skeleton? |
- stimulates Cartilage growth
- stimulates Bone growth |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH requires what 2 things to have an effect? |
- Carbohydrates
- Insulin |
|
|
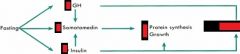
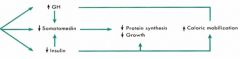
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH exerts most of its effect through? |
- IGFs
(somatomedins) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what is the most important Somatomedin? - what is the most important IGF? |
somatomedin C
(same as) IGF - I |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the mechanisms affected by GH in Adipose Tissue? x2 - thus the resulting effect is what? |
(LG)
- Increased Lipolysis - Decreased Glucose Uptake (thus) - Decreased Adiposity |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the mechanisms affected by GH in the Liver? x4 |
INCREASED: (RPG'S)
- RNA / Protein Synthesis - Glucose Synthesis / Storage - Somatomedins |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what are the Gross effects of Somatomedins (induced by GH) on the body? x3 |
INCREASE
- Linear Growth - Organ Size - Organ Function (organs include Visceral organs, Heart, Lung, Bone, etc) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- GH effects on Adiposity? - GH effects on Lean Body Mass? |
- decreases Adiposity
- increases Lean Body Mass |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what factors would stimulate GH secretion? x10 |
(EGG & FASTED states)
- Estrogen/Testosterone - GHRH - Glucose Decrease - FFA Decrease - Amino Acid Increase - Starvation (Fasting) - Trauma/Excitement/Stress - Exercise - Deep Sleep (stage 2 & 4) |
|
|
GROWTH HORMONE
- what factors would inhibit GH secretion? x7 |
(FAG MESS inhibits Growth)
- FFA increase - Aging - Glucose increase - Morbid obesity - Exogenous GH - SomatoMedins (IGF) - SomatoStatins (GHIH) |
|
|
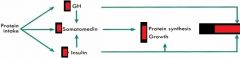
DIETARY REGULATION
PROTEIN effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- increase
- increase - increase |
|
|
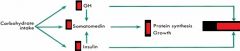
DIETARY REGULATION
CARB intake effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- decrease
- BOTH - increase |
|
|
DIETARY REGULATION
FASTING effects on : - GH - SomatoMedins - Insulin |
- increase
- decrease (b/c insulin effects >> GH) - decrease |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THYROID PHYSIOLOGY BASICS
- Thyroid gland vascularity is? |
- rich in supply
|
|
|
THYROID PHYSIOLOGY BASICS
- general effects of T3 & T4 - general effects of Calcitonin |
- Increase metabolic rate
- Decreases Ca2+ levels (in response to high levels) |
|
|
THYROID PHYSIOLOGY BASICS
- what is Unique about hormones in the Thyroid gland? |
- only hormones stored in Extracellular compartment
|
|
|
THYROID PHYSIOLOGY BASICS
- what molecule is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis? - how much of this should be taken in by diet? |
- Iodide
- 1 mg/week |
|
|
THRYOID POOL OF IODIDE
- Na+ I- Co-Transport System is composed of what transport pump? - Na+ I- Co-transport is dependent on what? |
- Na+ K+ ATPase
- Energy Dependent |
|
|
THRYOID POOL OF IODIDE
- Na+K+ ATPase involved with the Na+I- COTransport system is located where? - synthesis of above transporter is stimulated by what? |
- Cell membrane - basal surface
(G-linked) - TSH |
|
|
THRYOID POOL OF IODIDE
- the Energy dependent Na+K+ATPase of the Na+ I- COTransport system maintains what Thyroid: Plasma ratio for Iodide? - what is above ration with TSH stimulation? |
30 : 1
(thryoid epithelium : plasma ratio) - up to 250 : 1 |
|
|
THRYOID POOL OF IODIDE
- what competitive inhibitors can inhibit the transport system, thus causing rapid iodide discharge? x3 |
(PTT)
- PerChlorate - PerTechnetate - ThioCyanate |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- T3 & T4 are formed WITHIN what molecule? - what is an important component of the above molecule? |
- Thyroglobulin (TG)
- 70 Tyrosine amino acids (per molecule) |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- once iodide is taken in against the concentration gradient, what modifications must be made to it? - why? |
- must become Oxidized Iodine
- only Oxidized Iodide can react with the Tyrosine molecules on Thyroglobulin |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- If 1 Oxidized Iodine binds with Thyroglobulin, than this forms? - If 2 Oxidized Iodine binds with Thyroglobulin, than this form? |
- MIT
(mono-iodo-tyrosine) - DIT (di-iodo-tyrosine) |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- what 2 reactants form T3? - what 2 reactants from Reverse T3 - what 2 reactants from T4 |
- DIT + MIT
- DIT + MIT (with iodide ions at different location) - DIT + DIT |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- which is more potent hormone: T3 or T4? - potent by how much? |
T3 is more potent
by a factor of 3 to 4 times more |
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- when iodide availability is RESTRICTED, the formation of which hormone is Favored? |
T3
|
|
|
THRYOID HORMONE SYNTHESIS
- when the Thyroid Gland is HYPERSTIMULATED, what happens to the T3:T4 ratio? |
- T3:T4 ratio is increased
(more need for potent T3) |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE RELEASE
- Synthesis of Thyroid hormone occurs where? - Storage of Thyroid hormone occurs where? - Digesion of Thyroid hormone prior to release occurs where? |
- Colloid center
(TG tho is made in the follicle cell) - Colloid center - Follicle cell |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE RELEASE
- prior to release, the follicular vesicles containing the hormone will be fused with? - as a result, what gets released from the Thyroglobulin moledule? |
- lysosomes
- MIT - DIT - T3 - T4 |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE RELEASE
- what happens to the MIT & DIT after being cleaved from Thyroglobulin? |
- Deiodinase cleaves off the Iodine
|
|
|
THYROID HORMONE RELEASE
- Deiodinase is located where? - what does it do? - what is its effects on T3 or T4 |
- Follicular cell
- cleaves iodine off of T3 and T4 - does nothing to T3 and T4 (just the iodine for re-use) |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE TURNOVER
- what is the reasons why there is a disproportionate number of T4 in the colloid (extracellular pool) and in the plasma? |
- T4 has a longer Half life
- T3 has a much higher Metabolic clearance (reverse T3 is even higher) - T3 has a much higher Fractional Turnover (reverse T3 is even higher) |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE TURNOVER
- of the circulating T4, what % is actually FROM the Thyroid? - of the circulating T3, what % is actually FROM the Thyroid? - of the circulating Reverse T3, what % is actually FROM the Thyroid? |
- 100%
- 25% (rest is converted from T4) - 5% (rest is converted from T4) |
|
|
THYROID HORMONE TURNOVER
- the thyroid produces what % of T4? - of T3? - of Reverse T3? |
- 100% for all
|
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- list 3 plasma proteins that bind T3 and T4 |
(TAT)
- Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG) - Albumin - Thyroxine-Binding PreAlbumin (TBPA) |
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- TBPA is also known as? |
- TTR
(TransThyRetin) |
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- just by itself (without and T's), which plasma binding protein has the highest plasma concentration? - T4 has the highest affinity for which? - T3 has the highest affinity for which? |
- albumin
- TBG (T4 affinity = TBG > TBPA > Albumin) - TBG (although higher % on albumin, way more albumin in blood) |
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- T3 is almost (1%) nonexistent on which plasma binding protein? |
- TBPA
|
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- which hormone is short acting, with shorter latency and Duration? |
- T3
|
|
|
T3 & T4 TRANSPORT
- what governs T4 distribution btw Free and Bound forms? |
- T4 & TBG equilibrium
|
|
|
CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS
- Patient with "normal" total serum calcium levels, but with LOW serum Albumin, may actually have? |
- elevated IONIZED Calcium levels
and be HYPERCALCEMIC |
|
|
CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS
- Corrected Calcium Formula? |
= (measured Ca2+) + (0.8) x (4 - Albumin)
(note calcium measured in mg/dL) (note albumin measured in g/dL) |
|
|
CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS
- Active Calcium Transport (via GI) is stimulated directly by what compound? |
1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D
|
|
|
CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS
- What type of Calcium is Freely Filterable by the Kidney? - How much of above calcium is freely filtered by the Kidney? - What percentage is REABSORBED back? - Thus how much is normally excreted in urine? |
- Ionized Calcium
- 10 grams - 98% - 200 mg (of urinary calcium +/- 100 mg) |
|
|
CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS
- what compounds will enhance Bone Resorption (thus increasing Ca2+)? - what compound will inhibit bone resorption (thus decreasing Ca2+) |
1,25 DihydroxyVitamin D
PTH Calcitonin |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- Calcium-Sensing Receptor has the Biological Effect of INCREASING what? x2 - Calcium-Sensing Receptor has the Biological Effect of DECREASING what? x2 |
(INCREASES)
- Calcitonin hormone Secretion - Urine Ca2+ Excretion (DECREASES) - PTH Secretion - Reabsorption of Ca2+ AND Mg2+ |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- PTH secretion is inversely related to what? |
- concentration of Serum Calcium
(so low serum calcium = high PTH secretion) |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- activation of the Calcium Sensing Receptor will have the Biologic effect of DECREASING the REABSORPTION of? x2 - above decrease in reabsorption occurs where? |
- Calcium
- Magnesium - THICK Ascending Limb of Henle |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- activation of the Calcium Sensing Receptor will have the Biologic effect of DECREASING the REABSORPTION of? x2 - above decrease in reabsorption occurs where? |
- Calcium
- Magnesium - THICK Ascending Limb of Henle |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- INACTIVATING mutations of the Calcium Sensing Receptor can lead to what Dz? - what lab changes would be associated? x3 |
- Familial HYPOCalciuric HYPERCalcemia
- Increased PTH secretion - Hypercalcemia - Hypocalciuria |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- PTH binding to receptors on the KIDNEY will cause what biological effect INCREASES? x3 - PTH binding to Kidney receptors will cause what biological effect DECREASES? |
(INCREASES URA)
- Urinary Excretion of cAMP - Resorption of Ca2+ @ distal tubules - Activity of Vit. D1 alpha Hydroxylase (DECREASES) - Resorption of PO4- @ the tubules |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- PTH binding to receptors on the BONE will cause what biological effect? |
- Increased Bone resorption of CALCIUM
- Increased Bone resorption of PHOSPHATE (into the ECF) |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- PTH binding to the receptors in the GI tract will cause what biological effect? - is this GI effect by PTH an INDIRECT or DIRECT effect? - explain why |
- Increases ABSORPTION of CALCIUM
- Increases ABSORPTION of PHOSPORUS - INDIRECT - via the effects on RENAL Vit. D1 alpha Hydroxylase (thus increasing 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D levels) |
|
|
DIURETICS & CALCIUM
- what is the effect of LOOP Diuretics (such as Fursemide) on calcium? - Loop diuretics can also do the same effect on what other electrolyte? - what other diuretics can have an OPPOSITE effect to those done by Loop diuretics? |
(LICER - Loop diuretics Increase Calcium Excretion Renaly)
- INCREASES Excretion of Calcium - Sodium (TACER - Thiazides Abates Calcium Excretion Renaly) - Thiazide diuretics (have the opposite effect of decreasing calcium excretion) |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- activation of Calcium-Sensing-Receptors (w/ Ca2+) effects renal reabsorption of what electrolytes and how? - where does this occur renaly? |
INCREASES
- Calcium - Magnesium - Thick Ascending Loop of Henle |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- activation of PTH Receptors (w/ PTH) effect renal reabsorption of what electrolytes and how? - where does this occur renally? |
INCREASED
- Calcium - Phosphorus (PO4-) - Distal Tubules |
|
|
PARATHYROID (PTH) SECRETION
- activation of PTH Receptors (w/ PTH) effects the GI absorption of what electrolytes and how? - describe the INDIRECT mechanism involved |
INCREASED
- Calcium - Phosphorus (PO4-) Increases the RENAL activity of Vitamin D1 alpha Hydroxylase, thus, increasing the levels of 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D |

