![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SPIROMETRY
- Assesses what 4 things? - which one is the likely #1 reason for performing a Spirometry? |
(REDS)
- Response to Inhaled Aerosolized MES - Exercise Tolerance - Degree of Lung Dysfunction (with patients who smoke) - Severity of Lung Disease (Obstructive & Restrictive) (likely #1 reason for doing spirometry) |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- Evaluates what 3 things? |
(POD)
- Preoperative Risks - Occupational Risks - Disability |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- measures the Patients Ability to do what? x2 - Lung Disease can affect which of the above abilities? |
- Take a deep breath IN and blow OUT
(volume) - how FAST a patient can blow OUT - either one or Both |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- what are the 3 most important values that are obtained from Spirometry? |
- FVC
(Forced Vital Capacity) - FEV 1.0 (Forced Expiratory Volume 1 second) - PEFR (Peak Expiratory Flow Rate) |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) is what? - what is the usual normal value range? |
- taking the Deepest Breath Possible and Blowing out until Lung is Empty
- 3 to 5 liters |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV 1.0) is what? - what is the usual normal value range? |
- How much Volume is Exhaled during First second of FVC maneuver
- 70% of FVC or higher |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) is what? - what is the usual normal value range? |
- Fastest a patient can Blow out
- 300 to 600 L/min |
|
|
SPIROMETRY
- Normal FEV 1.0 / FVC ratio is? |
0.7 or greater
(or 70% or greater) |
|
|
COPD
- define COPD - COPD affects what airways? - COPD is due to what mechanism? - COPD mechanism above is a result of what? - is COPD reversible? |
- Fiberotic Narrowing of Small Airways due to inflammation as a result of irritants (e.g. - smoke)
- Small airways - Inflammation - Irritants (smoke) - Partially reversible (for Fibrotic narrowing) |
|
|
COPD
- what spirometry measurement is changed and how? - what physiology is inhibited? - what spirometry pattern is noted? |
- FEV 1.0 is decreased
- Cannot create Sufficient Expiratory Flow - Obstructive spirometry pattern |
|
|
COPD
- COPD patients have what type of pathological conditions associated? x2 |
- Bronchitis
- Emphysema |
|
|
COPD
- what normal lung function is lost? x2 - how do the lungs appear on X-ray? - all of the above are usually due to what? |
- loss of elasticity in lungs
- loss of lung recoil - hyperinflated lungs on x-ray - cigarettes |
|
|
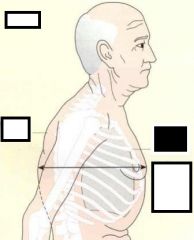
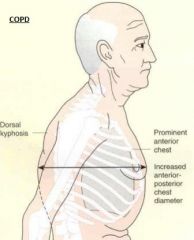
COPD
- what are the clinical signs of COPD? x3 |
(PID)
- Prominent Anterior Chest - Increased Antero-Posterior Chest Diameter - Dorsal Kyphosis |
|
|
COPD
- Barrelling and Wide Chest is due to what etiology? |
- loss of elasticity
(thus) - Lungs don't oppose chest wall and walls go out |
|
|
COPD
T/F : the COPD clinical signs of barrel chest and widening of chest wall is due to lung hyperinflation |
- False
- due to loss of elasticity, thus loss of chest wall opposition by the lungs |
|
what disease does this show?
|
|
|
- what condition seen in the first 3?
- what is going on next 2? - what is going on for last picture? |
Emphysema
(loss of recoil due to loss of elasticity) Complete loss of elasticity / recoil "Popping" of elasticity (its a goner) |
|
|
ASTHMA
- general definiton - spirometry changes? x2 - spirometry pattern? - Reversible? |
- inflammatory response to a trigger
- FEV 1.0 decrease - PEFR decrease - Obstructive Spirometry pattern - Typically REVERSIBLE |
|
|
ASTHMA
- what is the #1 MC trigger for asthma? - what is the #2 MC trigger? - what is the #1 trigger for asthma in URBAN America? - list another trigger that can be antigenic to asthma.. |
- cat saliva
(not the dander) - cockroach poopy - cockroach poopy - House mites poopy |
|
|
ASTHMA
- how come dogs aren't as antigenic to asthma as cats? |
- not so much antigenic protein in saliva as cats
|
|
|
ASTHMA
- what is "obstructing" the airways? |
- Mucous plugs
|
|
|
ASTHMA
- what anatomical structure is usually inflamed? - give 3 pathologies associated with the above anatomical structure. |
- Inflamed Bronchus
(MMR) - Mucous plug - Muscle Layer contraction - Reduced airway opening |
|
|
ASTHMA
- Pathology of Status Asthmaticus x3 |
(status ast-HMA-ticus or HAM)
- Hyperinflation (regional or diffuse) - Mucous plugs in airways (tenacious & viscid) - Atelectasis foci |
|
|
OBSTRUCTIVE DISEASE REVIEW
- list 2 obstructive diseases |
- COPD
- Asthma |
|
|
OBSTRUCTIVE DISEASE REVIEW
- which one hyperinflates the lungs? - which one is mainly caused by cigarettes? |
- both
- COPD |
|
|
OBSTRUCTIVE DISEASE REVIEW
- which one partially reversible? - what is partially reversible for above disease? |
- COPD
- fibrotic narrowing of small airways |
|
|
OBSTRUCTIVE DISEASE REVIEW
- which one decreases FVC? - which one decreases FEV1? - which one decreases PEFR? |
- neither
- both - Asthma |
|
|
OBSTRUCTIVE DISEASE REVIEW
- Obstructive Disease decrease what as opposed to Restrictive Diseases? - Restrictive Diseases decrease what as opposed to Obstructive Diseases - how does the patients manifest the above decreased states? x2 |
- Flow is decreased
(can't BLOW out as much) - Volume is decreased (can't TAKE in enough volume) |
|
|
PNEUMONIA
- changes what spirometry value(s)? - spirometry pattern seen? - how is pulmonary inflammation type different from the COPD or Asthma? |
- FVC decrease (volume decrease)
- Restrictive pattern - Bacterial inflammation |
|
|
PNEUMONIA
- what respiratory symptom is commonly seen? - why do patients do this? |
- panting
- b/c it is the least amount of work |
|
|
PNEUMONIA
- is this an Obstructive or Restrictive disease? |
(CAP = OOR)
- Restrictive |
|
|
RESTRICTIVE DISEASES
- Restrictive diseases usually have decreased what as opposed to Obstructive diseases? |
- Restrictive Dz = decreased Volume
(can't TAKE IN enough volume) - Obstructive Dz = decreased Flow (can't BLOW out as much) |
|
|
SPIROMETRY PERFORMANCE
- what is very important to have when obtaining a quality spirometry result? |
- Good COACHING
(or a well-trained therapist) |
|
|
SPIROMETRY PERFORMANCE
- the respiratory coach needs to make sure the patient breathes out for how long in order to get a good measurement? |
- 6 seconds
|
|

- what does this graph represent?
- what may have caused the increase in volume? - how much volume increase are you wanting? |
- graphical representation of an Asthmatic patient blowing out at Pre-Tx and Post-Tx (20 min later)
- Bronchodilator Tx - 12% |
|
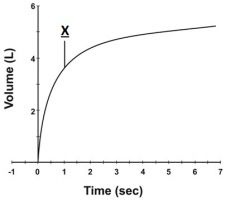
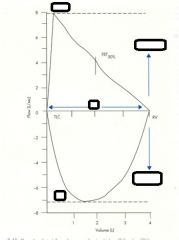
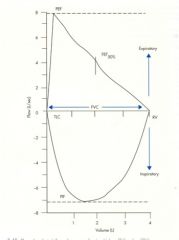
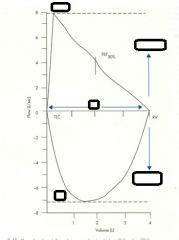
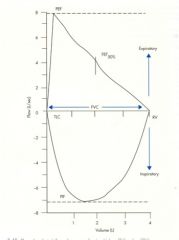
- what does this represent?
- what is the peak called? - what is X? |
- graphical representation of expiration
- FVC (about 5 L) - X is the FEV 1.0 (about 3.5 L) |
|
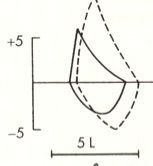
|
|
|
|
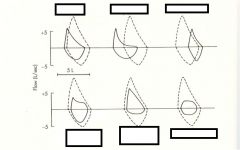
asthma
|
|
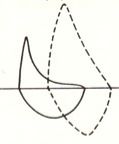
|
Emphysema (COPD)
|
|

|
Fixed Obstruction
(Fixed right thar' in middle) |
|
|
mixed pattern
|
|

|
Normal pattern
|
|
|
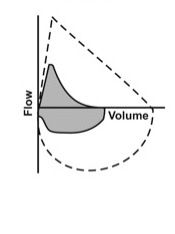
Obstruction pattern
(note the "bowed out" area) |
|
|
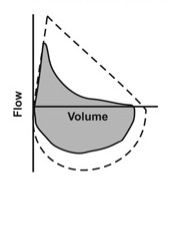
Restriction
(to da "R"ight is da "R"estriction) |
|
|
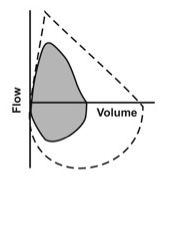
Restriction pattern
|
|
|
|
Variable Extrathoracic Obstruction
("Extra" because most of it in the Expiratory region) |
|
|
Variable Extrathoracic Obstruction
("Extra" because most of it in the Expiratory region) |
|

|
Variable Intrathoracic Obstruction
(Intra b/c in Inspiration region mostly) |
|
|
|
|
|
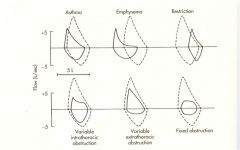
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- Spirometry prediction numbers are baed on what 2 things? |
- Age
- Height |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- what med treatment might help differentiate between Asthma & COPD? - how can you use above drugs to differentiate asthma and COPD? |
- Bronchodilators
- upon Post-med expiration, Asthmatics will show 12% increase - COPD'ers will not have this increase |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- Blowing out (expiratory flow) is decreased in what lung disease type? |
- Obstructive
(Out Blowing = OBstructive) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- Decrease in inspiratory volumes is due to what lung Dz type? |
- Restrictive
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- which lung dz type shows panting? |
- Restrictive
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- Decrease in FVC seen in what Dz? - Decrease in FEV1 seen in what Dz? - Decrease in PEFR seen in what dz? |
- Pneumonia (restrictive)
- COPD (obstructive) - Asthma (obstructive) - Asthma (obstructive) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- what causes the "obstruction" in Obstructive Lung Dz? x2 |
- Mucous plugs in airways
(Asthma - Inflammatory trigger) - Fibrotic narrowing of small airways (COPD - inflammatory irritant) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- which spirometry value has a normal range of about 300 to 600 Liters / min? |
- PEFR
(Peak Expiratory Flow Rate) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- what lung dz type has patients feeling fatigued and "don't have wind" |
- Obstructive Lung Dz
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- cigarettes mostly affect which spirometry value? |
- FEV 1.0
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- in COPD, what is the "obstruction" - in Asthma, what is the "obstruction" - in Pneumonia, what is the "restriction" |
- Fibrotic narrowing of small airways
- Mucous plugs that are tenacious & viscous - Volume of air capacity (can not inspire as much) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- which lung type dz has a "scooped out" or "bowed out" feature in the spirometry loop graph |
- Obstructive
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- normal values are what % of predicted? - predicted is based on what? x2 |
70%
- Age - Height |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
T/F : can Chihuahuas remove the effects of Asthma from adult patients. |
Fuck NO! Dat shit is False biaaatch!!!
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
(something i found on Wiki) - in Obstructive Dz, the FEV1/FVC ratio changes how? - in Restrictive Dz, the FEV1/FVC ratio changes how? |
- reduced ratio
(b/c FEV1 primarily affected) - approximately normal (b/c both values decrease) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- which lung disease type affects primarily airways? - which lung disease type affects primarily lungs? |
- Obstructive Lung Dz
- Restrictive Lung Dz (the lung volume is affected) |
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS
- in COPD, the chest wall goes out because why? |
- the chest is NOT opposed by the Lungs anymore
|

