![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T/F - Some species of Archaea live in digestive tract.
|
True. Some do live in digestive tract.
|
|
|
T/F - Archaea have peptidoglycan.
|
False. They don't have peptidoglycan
(Membrane Biochemistry different from bacteria) |
|
|
T/F - Colony appearance will give important clues relating to the shape of individual bacteria.
|
False. Does NOT relate to shape of individual bacteria. Though it may provide keys to its type.
|
|
|
Mucoid appearance of bacterial colony indicates what?
|
Indicates Capsule
|
|
|
Waxy appearance of bacterial colony indicates what?
|
Indicates High Lipid Content
|
|
|
Mycobacterium would have what type of colony appearance?
|
It would have WAXY appearance.
Indicating high lipid content. |
|
|
Thin, spread out appearance in bacterial colonies would indicate what?
|
It would indicate Highly motile organism
|
|
|
Pigments of bacterial colony would indicate what?
Why? |
Natural habitat.
b/c it is a form of protection against light. |
|
|
What does a cell envelope consist of? x4
|
1. Cell membrane(s)
2. Cell wall (if present) including imbedded proteins 3. Glycocalyx / Capsule (if present) 4. Flagella |
|
|
T/F - Bacterial cell envelopes have peptidoglycan.
|
True. It does contain peptidoglycan.
|
|
|
Which type of bacteria has thick cell envelopes? thin envelopes?
|
Gram positive
Gram negative |
|
|
Gram Positives has what kind of acids imbedded in its Cell Envelope? x2
What is this info used for? |
Teichoic acid
Lipoteichoic acid Serotyping |
|
|
What give Gram positive bacteria its negative charge?
|
Teichoic and Lipoteichoic acids in the cell envelope
|
|
|
Which physical character of Gram negative bacteria has significance in respect to Penicillan.
|
Outer membrane (LPS) limits accessibility of penicillan
|
|
|
Where would you find virulence factors in the bacterial cell envelope?
|
The periplasmic space
of Gram negative bacteria |
|
|
Gram Staining:
- What color means positive? - Not reliable for what kind of organisms? x3 |
Purple
Dead/damaged organisms Organisms with no peptidoglycan MYCOBACTERIA with waxy coating |
|
|
Describe the components of lipids in Eurkaryotic membrane. x2
|
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
with Sterols |
|
|
Describe the components of lipids in Prokaryotic membrane. x3
|
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) Cardiolipin No sterols |
|
|
Which two Prokaryotes DO HAVE sterols in their cell membrane?
|
Helicobacter
Mycoplasmas |
|
|
In Prokaryotes, glucose is modified:
- where - with what - what type of transport is used |
cytosol
PTS (Phosphotransferase System) Group Transport |
|
|
Describe ABC Transport in:
- Gram Negative - Gram Positive |
Periplasmic binding proteins used
Cytoplasmic membrane proteins used |
|
|
Peptidoglycan Layer:
- AKA - Important for what? x3 |
Murein
1. Resistance to osmotic stress 2. Antibiotic target 3. Pyrogenic activity |
|
|
T/F - Peptidoglycan layer is permeable, thus allowing diffusion.
|
True. It is NOT impermeable
|
|
|
What is the backbone of the peptidoglycan made up of?
|
NAM (N-Acetylmuramic acid)
NAG (N-Acetylglucosamine) |
|
|
What is unique about the beta(1,4) bond in the glycan backbone of the peptidoglycan layer?
|
It is sensitive to lysozymes.
|
|
|
Lysozymes are most active against which bacteria?
Where can you find lysozymes? |
Gram Positive bacteria
Tears, saliva, egg whites |
|
|
Describe the E. coli (Gram Negative) crossbridge within the Peptidoglycan
|
Bond between DAP and D-Alanine
|
|
|
Describe the S. aureus (Gram Positive) crossbridge within the Peptidoglycan
|
Bond between L-lysine and a chain of Glycines
|
|
|
DAP (Diaminopimelic acid):
- related to which amino acid |
Lysine
|
|
|
Which one is NEVER found in Eukaryotes:
- NAM - NAG - DAP |
NAM and DAP
|
|
|
Which of these has Ribosomes sensitive to Cm/Strep/Kan?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Bacteria
|
|
|
Which of these has Ribosomes resistant to Diptheria Toxins?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Bacteria
|
|
|
Which of these has Introns?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Eukarya
|
|
|
What are the Initiator tRNA for the following?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Formylmethionine
Methionine Methionine |
|
|
What are the ribosomes for the following?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
70S
70S 80S |
|
|
Which of these has a Peptidoglycan?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Bacteria
|
|
|
Discuss the lipids linkage for the following?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
Ester-linked
ETHER-linked Ester-linked |
|
|
Discuss the RNA Polymerase for the following?
- Bacteria - Archaea - Eukarya |
ONE (4 subunits)
several (8-12 subunits) THREE (12-14 subunits each) |
|
|
Important clinical types of bacteria are? x4
|
Gram Positive
Gram Negative (Proteobacteria) Spirochetes Chlamydia |
|
|
The typical bacterial diameter is?
|
0.5 - 1.0 micrometer
|
|
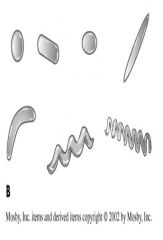
Name the following bacterial morphology
|
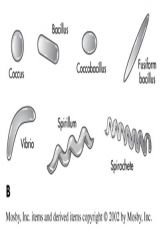
Answers
|
|
|
Which bacterial groups have branched filamentous? x2
|
Actinomyces
Nocardia |
|
|
PURPLE pigmented pus seen in cultures may be an indication for what organism?
|
Chromobacterium Violaceum
|
|
|
PYOCYANIN (light bluish) pigmented pus seen in cultures may be an indication for what organism?
|
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
|
|
|
List the functions the Cell Envelope in bacteria. x6
|
Barrier
(osmotic protection & environment regulator) Motility Solute transport Lipid biosynthesis Electron transport Electrochemical gradients / ATP synthesis Protein secretions |
|
|
Cell membrane components in Gram POSITIVE organisms?
|
Peptidoglycan (THICK layer)
Inner membrane |
|
|
List the Cell envelope components for Gram NEGATIVE organisms.
|
Outer membrane (LPS & protein)
Periplasm layer (w/ THIN layer of Peptidoglycan) Membrane (inner) |
|
|
List the 4 steps on gram staining.
|
1. Crystal Violet
2. Gram staining (precipitates crystal violet) 3. Decolorizer 4. Safranin Red |
|
|
What types of decolorizer can be used in gram staining?
|
Alcohol or Acetone
|
|
|
List the Cell envelope components for Gram NEGATIVE organisms.
|
Outer membrane (LPS & protein)
Periplasm layer (w/ THIN layer of Peptidoglycan) Membrane (inner) |
|
|
In Gram POSITIVE cell envelopes, the functions of Teichoic & Lipoteichoic acids are? x3
|
1. Net Negative charge on cell wall
2. Serotyping 3. Sheds & elicits immune response |
|
|
In Gram NEGATIVE cell envelopes, the functions of the Periplasmic space is? x2
|
May contain Virulence factors
Contains thin peptidoglycan layer |
|
|
List the 4 steps on gram staining.
|
1. Crystal Violet
2. Gram staining (precipitates crystal violet) 3. Decolorizer 4. Safranin Red |
|
|
What types of decolorizer can be used in gram staining?
|
Alcohol or Acetone
|
|
|
Prokaryotic lipid, Phosphatidylethanolamine, is targeted by what antibiotic?
|
Polymyxins
|
|
|
In prokaryotes, what molecules diffuse with HIGH permeability?
|
Hydrophobic, UNcharged molecules
(followed by Small, uncharged Polar) (followed by Large, uncharged Polar) |
|
|
In prokaryotes, what molecules diffuse with LOW permeability?
|
Ions (charged molecules)
|
|
|
In Prokaryotic cell membrane transport, what is required in SIMPLE transport?
|
PMF only
|
|
|
In Prokaryotic cell membrane transport, what is required in GROUP transport?
|
Energy (ATP or PMF)
|
|
|
In Prokaryotic cell membrane transport, what is required in ABC system transport?
(any exceptions?) |
Periplasmic binding proteins
& ATP (except in Gram POSITIVE, protein comes from cytoplasmic membrane) |
|
|
Specialized secretion systems can do what with its proteins?
|
Inject proteins directly in to the host cell
|
|
|
What is clinically significant about the protein secretion systems?
|
Host antibodies do NOT have access to injected proteins.
|
|
|
The peptidoglycan layer has which type of activity?
- Pyogenic - Pyrogenic |
Pyrogenic
|
|
|
What gives peptidoglycans its rigidity?
|
Repeating structures
with Crosslinks |
|
|
Describe the properties of Peptidoglycan in terms of Layer Thickness.
|
Gram NEG --> 1 to 3 layers thick
Gram POS --> 10 times thicker |
|
|
Describe the properties of Peptidoglycan in terms of mechanical properties.
|
More similar to Viscous Gel (than crystalline structures)
It can Stretch |
|
|
What can diffuse across the Peptidoglycan?
|
Proteins < 50 kDa
DNA Nutrients |
|
|
What Peptidoglycan component(s) is never found in Eukaryotes?
|
NAM
DAP |
|
|
DAP is found in what organisms?
|
ALL Gram NEGATIVE
Some Gram + |
|
|
Transpeptidation reactions are inhibited by what antibiotics?
|
Beta Lactam Antibiotics
|
|
|
During Transpeptidation reactions, the Beta-Lactam ring will resemble?
|
Transition state of D-alanyl-D-alanine
|
|
|
During Transpeptidation reactions, PCN will bind to what proteins?
|
PBP (Penicillin Binding Proteins)
|
|
|
By binding to PBP, PCN will inhibit what enzymes? x2
|
Bacterial
Transpeptidases & Carboxypeptidases |
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what are 2 important components of the LPS outer membrane?
|
Oligosaccaride O-side chain
(O Antigen) Core |
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what is the function of the core in LPS outer membrane?
|
Resistance to hydrophobic compounds
|
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what is the clinical significance for the Oligosaccharide side chain found in LPS outer membrane?
|
Loss of O-side chain by pathogens will reduce virulence
|
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what is the clinical significance for the core of the LPS outer membrane?
|
Basis for resistance to bile acids by enteric bacteria
|
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what is the clinical significance for the diffusion properties of the outer LPS membrane?
|
Large compounds such as Vancomycin can NOT pass thru pores in outer membrane
|
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what can strengthen the LPS intermolecular interactions?
|
Divalent MAGNESIUM
Divalent CALCIUM |
|
|
In Gram - organisms, what can weaken the LPS intermolecular interactions?
|
EDTA
|
|
|
In Gram - organisms, Lipid A of the LPS contains only what?
|
Saturated Fatty Acid
(adds rigidity) |
|
|
What is considered the toxic portion of the LPS, endotoxin?
|
Lipid A
|
|
|
In Gram NEG organisms, the Lipid A portion is inserted where?
|
Outer membrane
|
|
|
In Gram NEG organisms, the Lipid A portion is essential for?
|
Viability
|
|
|
The 3 components of LPS, endotoxin are?
|
O-specific polysaccharide
Core polysaccharide Lipid A (outer) |
|
|
Describe the polar properties for each of the LPS, endotoxin components.
|
HydroPHILIC, Negative charge
O-specific polysaccharide & Core polysaccharide HydroPHOBIC Lipid A (outer) |
|
|
LPS activates what immune cells?
|
Activates B-cells
|
|
|
LPS stimulates what immune cells and what does this lead to?
|
Macrophages/Dendritic cells
Release of - IL-1 - IL-6 - TNF-alpha |
|
|
LPS would show what conditions based on labwork? x2
|
Leukopenia
Hypoglycemia (possibly) |
|
|
LPS can enhance what pathway?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
|
LPS is fatal in what doses?
|
10 - 100 micrograms
|
|
|
Which is more potent for causing fatalities, LPS or PG?
|
LPS
(1000 x's more potent) |
|
|
Septic / Endotoxin Shock can be caused by what alone?
|
LPS alone
(other bacterial components can also cause same symptoms) |
|
|
Septic / Endotoxin Shock can cause what symptoms? x4
|
1. Flu-like
(fever, chills, malaise, confusion) 2. Heart rate increase 3. Respiratory rate increase 4. Hypotension to the extreme |
|
|
Septic / Endotoxin Shock can lead to extreme hypotension because?
|
Induction of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-alpha
produces VASODILATION via NO & other mediators |
|
|
Septic / Endotoxin Shock can lead to Multiorgan failure due to?
|
HypoPerfusion
|
|
|
Septic / Endotoxin Shock can lead to DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation) by activation of?
|
Coagulation pathway
|

