![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define LMN.
|
Neurons which directly innervate skeletal muscle
|
|
|
What are the types of LMN's and where do they go innervation?
|
Alpha --> Extrafusal muscle
Gamma --> Intrafusal muscle |
|
|
What is the NT for LMN's.
|
ACh (nicotinic receptors)
|
|
|
The axial muscles are innervated from where?
|
Medial nucleus of the anterior horn
|
|
|
The limb muscles are innervated from where?
|
Lateral nucleus of the anterior horn.
C5-T1, L1-S4 Flexor innervating center is more POSTERIOR than Extensor innervating center. |
|
|
The Diaphragm is innervated from where?
|
Phrenic nucleus (C3, C4, C5)
|
|
|
The trapezius and sternocleidomastoid are innervated from where?
|
Spinal Accessory Nucleus
C1-C6 |
|
|
Reciprocal innervation is done by what type of neurons? Describe the NTs involved.
|
Internuerons
Glutamate - Excitatory Glycine - Inhibitory |
|
|
Define recurrent inhibition.
|
Where LMN have recurrent axon collaterals which synapse on inhibitory (glycinergic) interneurons (Renshaw cells), which will inhibit the SAME LMN as well as other lower motor neurons
|
|
|
Triceps DTR
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
C7
Radial |
|
|
Patellar DTR
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
L4
Femoral |
|
|
Achilles DTR
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
S1
Tibial |
|
|
Jaw Jerk DTR
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
No spinal cord
Trigeminal-Mandibular division |
|
|
Biceps DTR
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
C5
Musculocutaneous |
|
|
Brachioradialis
- Spinal Cord - Nerve |
C6
Radial |
|

Question
|

Answer
|
|
Question
|

Answer
|
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of LMN lesions in general? x5
|
1. FLACCID PARALYSIS / PARESIS
2. Muscular Atonia / Hypotonia 3. Areflexia / Hyporeflexia 4. Muscular Fasciculations / Fibrillations 5. Muscular Atrophy |
|
|
What is the correlation between LMN lesions and the observed deficit?
|
Same side
Same level |
|
|
How do you test for fibrillations?
|
Electromyographic testing
|
|
|
What causes ALS?
|
Demyelinated anterior roots
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of familial neuropathy?
|
Atrophy of thenar & hypothenar eminence.
|
|
|
What are the possible sites for LMN lesions?
|
1. Myoneural junction
2. Anterior horn 3. Ventral root 4. Spinal nerve |
|
|
Atrophy of left infraspinatus and deltoid muscles would result following what event?
|
Protrusion of C5
|
|
|
A LEFT tibial nerve lesion would indicate what symptoms? What level is this lesion at?
|
Sacral level
1. Plantar flexion impaired 2. Shortening of extensor tendons 3. Dorsiflexion of foot 4. Flaccid paralysis/atrophy of soleus and gastrocnemius 5. Contracture and joint distortion 6. Arthritic changes and pain |
|
|
A LEFT median nerve lesion would indicate what symptoms? What level is this lesion at?
|
Cervical level
1. Flaccid paralysis/atrophy of thenar emminence, wrist, and finger extensors (1-3) 2. Wrist and finger flexion impaired. 3. Extension of wrist and digits 1-3; papal sign |
|
|
A LEFT Spinal Accessory nerve damage would indicate what symptoms? What level is this lesion at?
|
Rostal cord to Caudal medulla
1. Flaccid/atrophy of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius 2. Impaired ability to raise left shoulder. 3. Impaired ability to turn head contralaterally. |
|
|
A LEFT Hypoglossal nerve lesion would indicate what symptoms? What is the level of lesion at?
|
Mid Medulla
1. Flaccid paralysis/atrophy of left tongue 2. Dysarthria (inarticulate speech) 3. Deviation of tongue towards left on protrusion |
|
|
A LEFT Vagus nerve lesion would indicate what symptoms? What is the level of lesion at?
|
Mid Medulla
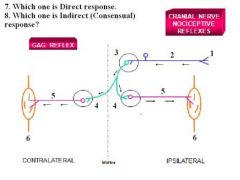
1. Flaccid paralysis/atrophy of pharynx, larynx, and palate on left side 2. Dyphonia (Voice weak and hoarse) 3. Dysphagia (Swallowing impaired) 4. Deviation of uvula toward RIGHT side 5. Gag reflex impaired |
|
|
A LEFT facial nerve damage would indicate what symptoms? What is the level of lesion at?
|
Caudal Pons
1. Flaccid paralysis/atrophy of facial expression muscles 2. Bell's Palsy 3. Corneal reflex impaired |
|
|
Describe the symptoms associated with Bell's Palsy.
|
1. Hyperacusis
2. Widening of Palpebral Fissure 3. Drooping of face 4. Corneal reflex impaired |
|
|
A LEFT Trigeminal nerve lesion would indicate what symptoms? What is the level of lesion at?
|
Mid Pons
Flaccid paralysis / atrophy of mastication muscles + MATT Chewing impaired Deviation of Jaw to left side Jaw Jaw jerk impaired Maybe corneal reflex impaired? |

