![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is dietary calcium absorption poor?
|
B/c it is in divalent form
|
|
|
Vitamin D aids in absorption of what?
|
Dietary calcium
|
|
|
Where does the body get vitamin D from?
|
Diet
UV light (via skin) |
|
|
What does the liver do in vitamin D processing?
|
Converts vitamin D into 25-hydroxycholecalciferol
|
|
|
What does the kidney do in vitamin D processing?
|
Converts 25-hydroxycholecalciferol into the active or inactive form.
|
|
|
What is the active form of vitamin D?
|
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol
|
|
|
What is the inactive form of vitamin D?
|
24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
|
|
|
What circumstances would promote the formation of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol? x3
|
Phosphate deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency Calcium deficiency |
|
|
What circumstances would promote the formation of 24,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol? x3
|
Phosphate excess
Active form present Calcium excess |
|
|
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol:
- duration of effect - activates what? x3 |
Several weeks of CBP
Alkaline Phosphate CBP Calcium ATPase |
|
|
What inhibits the conversion of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and where?
|
It will inhibit itself if there is enough
In the liver |
|
|
What hormone activates the conversion of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in the kidney?
|
Parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
A high increase in plasma calcium ion concentration will inhibit what hormone?
|
Parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
50% of plasma calcium is in what form?
41% of plasma calcium is in what form? 9% of plasma calcium is in what form? |
Divalent form
Bound to protein Bound to X |
|
|
Stress on bones will stimulate what?
|
Bone remodeling
|
|
|
What would promote PTH secretion?
|
Low plasma calcium concentration
|
|
|
What would inhibit PTH secretion?
|
High plasma calcium concentration
|
|
|
Parathyroid gland:
- where is it - how many are there - how many needed for normal function |
Behind thyroid
4 2 |
|
|
What are the two cells in the parathyroid that differentiates it from the thyroid?
|
Chief cells
Oxyphil cells |
|
|
PTH responds to what?
|
Low calcium levels in plasma
|
|
|
What is the MAIN hormone essential for calcium homeostasis?
|
PTH
|
|
|
What is the normal levels for calcium?
|
9 - 10 mg/dl
|
|
|
What hormone works in opposition to PTH?
|
Calcitonin
|
|
|
Parathyroid hypertrophy can result in what? x3
|
Rickets
Pregnancy Lactation |
|
|
Parathyroid atrophy can result in what? x3
|
Vitamin D excess
Calcium excess Bone absorption |
|
|
PTH plateaus in how many hours
|
4 hours
|
|
|
Calitonin plateaus in how many hours
|
2 hours
|
|
|
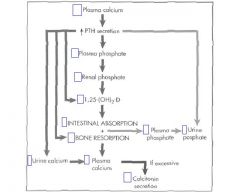
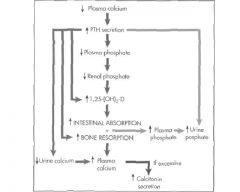
What are the direct effects of an increase in PTH secretion? x5
|
1. Increase in Bone resorption
2. Increase in Active D vitamin 3. Increase in Urine Phosphate 4. Decrease in Urine Calcium 5. Decrease in Plasma Phosphate |
|
Answer
|
Answer
|
|
|
Hypoparathyroidism
- osteoclasts - dangers x2 - treatment x2 |
Becomes almost dormant
Tetany Paralysis of laryngeal muscles (possibly lethal if resp. effected) PTH administration ($$) Vitamin D and Calcium administration |
|
|
Hyperparathyroidism
- osteoclasts - dangers x2 - treatment |
Elevated activity
Weak bones Cystic areas of osteoclastic giant cell tumors Surgical removal of tumors |
|
|
Calcitonin:
- Source - Effective strength - Mechanism x2 |
Parafollicular cells of thyroid
Weak Quick -> inhibits osteoclast activity Slow -> inhibits osteoclast formation |

