![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy Source - Light Electron Donor - Inorganic Carbon Source - CO2 |
Photolithoautotrop |
|
|
Energy Source - Light Electron Donor - Inorganic Carbon Source - organics |
photolithoheterotroph |
|
|
Energy Source - Chemicals Electron Donor - Inorganic Carbon Source - CO2 |
chemolithoautotroph |
|
|
Energy Source - Chemicals Electron Donor - Inorganic Carbon Source - organics |
chemolithoheterotroph |
|
|
Energy Source - Chemicals Electron Donor - Organic Carbon Source - organics |
chemoorganoheterotroph |
|
|
Fermentation |
Substrate-level phosphorylation. ATP directly synthesized from an energy rich intermediate |
|
|
Respiration |
Oxidative phosphorylation. ATP produced by proton motive force formed by transport of e- from organic/inorganic donors. |
|
|
Competitive Inhibition |
Vmax, aKm. Km increases, Vm constant. I takes away E from S. Y intercept stays the same for all alpha values. Slope increases. |
|
|
Uncompetitive Inhibition |
Vmax/a' and Km/a'. Vmax and Km decrease at same rate. Line has the same slope but different x and y intercepts. ES combines with I, takes away from products. |
|
|
Mixed Inhibition |
Combination of both. Vmax/a' and aKm/a'. Vmax decreases, Km unknown. |
|
|
Noncompetitive Inhibition |
Special case of mixed inhibition. a = a'. Vmax/a' and aKm/a'=Km. Km stays the same, Vmax decreases. Slope and y intercept change. |
|
|
Aerobic Respiration - Carbon Cycle |
(CH2O)n -> CO2 EA: O2 ED:(CH2O)n |
|
|
Anaerobic Respiration - Carbon Cycle |
(CH2O)n -> CO2 EA: organics ED: (CH2O)n |
|
|
Anaerobic photosynthesis - Carbon Cycle |
CO2 -> (CH2O)n EA: CO2 ED: H2S or H2 |
|
|
Aerobic photosynthesis - Carbon Cycle |
CO2 -> (CH2O)n EA: CO2 ED: H2O |
|
|
Methantrophy |
Carbon Cycle - aerobic. CH4 -> CO2 EA: O2 ED: CH4 |
|
|
Methanogenesis |
Carbon cycle - anaerobic. CO2 -> CH4. EA: CO2 ED: H2 CO2 + H2 -> CH4 + H+ OR EA: organics ED: organics C H3COOH -> CO2 + CH4 |
|
|
Nitrogen fixation |
Conversion of N2 to ammonia (NH3). Oxic and Anoxic. N2 -> NH3 EA: N2 ED: organics |
|
|
Nitrification |
Ammonia to nitrate (2 steps). Aerobic. NH3 -> NO2- -> NO3- EA: O2 ED: NH3 |
|
|
Denitrification |
Reduction of NO3- to N2. Anaerobic. NO3- -> N2 EA: NO3- ED: organics |
|
|
Anammox |
Anaerobic oxidation of NH3 to N2. NH3 + NO2- -> N2. EA: NO2- ED: NH3 |
|
|
Sulfure/Sulfide Oxidation |
H2S -> S0 -> SO4 2- 1) H2S -> S0 EA: O2 ED: H2S 2) S0 -> SO4 2- EA: O2 ED: S0 |
|
|
Anaerobic oxidation - Sulfur Cycle |
1) H2S -> S0 EA: organics ED: H2S 2) S0 -> SO4 2- EA: organics ED: S0 |
|
|
Sulfure disproportionation |
Anoxic Process. S0 -> H2S + SO4 2- EA & ED: S0 |
|
|
Sulfur reduction |
Anoxic Process. S0 -> H2S EA: S0 ED: organics |
|
|
Sulfate reduction |
Anaerobic. SO4 2- -> H2S EA: SO4 2- ED: organics |
|
|
Iron Redox Cycle |

|
|
|
Microbial Leaching |
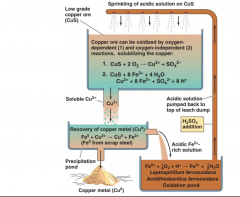
|
|
|
Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons |
aerobic oxidation |
|
|
Bioremediation of PAHs |
Aerobic oxidation; fungal/anaerobic |
|
|
Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons: BTEX |
Aerobic oxidation; anaerobic oxidation |
|
|
Bioremediation of chlorinated aliphatics |
anaerobic reductive dehalogenation; aerobic cometabolic oxidation |
|
|
Bioremediation of highly chlorinated PCBs |
reductive dechlorination |
|
|
Bioremediation of Mono and di chlorinated PBCs |
Aerobic oxidation |
|
|
Bioremediation of explosives |
reduction of nitro groups |
|
|
Bioremediation of pesticides/herbicides |
Many types. Mainly aerobic for organo-phosphatesand non-chlorinatedcompounds |

