![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney?
|
Uriniferous Tubule, composed of a nephron and a system of collecting ducts.
p. 193 |
|
|
|
True or False:
The kidney produces erythropoietin (for RBC production). |
True
p. 193 |
|
|
|
How much urine does the kidney produce per day?
|
1-2 Liters per day
p. 194 |
|
|
|
_______ is ultrafiltrate of plasma, ~ 180 Liters filtered/day.
A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion |
A. filtration
p. 194 |
|
|
|
Additional substances added to filtrate.
A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion |
C. secretion
p. 194 |
|
|
|
Intratubular filatrate returns across tubular cells back into renal interstitium.
A. filtration B. reabsorption C. secretion |
B. reabsorption
p. 194 |
|
|
|
Formation of 1-2 Liters/day of urine has three phases/steps. What are they?
|
1. Filtration - ultrafiltrate of plasma, approx 180 Liters filtered/day
2. Secretion - additional substances added to filtrate 3. Reabsorption - intratubular filtrate returns across tubular cells back into renal interstitium p. 194 |
|
|
|
The _____ is a vertical slit on medial concave border through which the renal artery and vein, nerves, lymphatics, and ureter pass. ________ is the flattened cavity within the kidney that communicates with the [first blank].
A. Renal Hilus B. Renal Pelvis C. Renal Sinus |
A. Renal Hilus; C. Renal Sinus
p. 194 |
|
|
|
The _______ , an expanded part of the ureter found in the area of the renal hilus has major and minor calyxes.
|
Renal pelvis
p. 194 |
|
|
|
Major calyxes have ____ branches of renal pelvis and lie in renal sinus. Minor calyxes have ___ branches arising from major calyxes.
|
Major calyxes have 3-4 branches; minor calyxes have 7-14 branches.
p. 194 |
|
|
|
The kidney ________ consists of renal corpuscles and convoluted portions of renal tubules, renal columns, and medullary rays.
A. Cortex B. Medulla C. Renal Hilus D. Renal Pelvis E. Renal Hilus |
A. cortex
p. 194 |
|
|
|
The ______ is formed by the medullary pyramids which vary in number, conical and striated appearance.
A. Cortex B. Medulla C. Renal Hilus D. Renal Pelvis E. Renal Hilus |
B. Medulla
p. 194 |
|
|
|
Differentiate between a renal lobe and a renal lobule.
|
A renal lobe is a medullary pyramid and the cortical substance that surrounds it. A renal lobule is the cortical tissue surrounding a medullary ray. p. 194
|
|
|
|
Which is smaller- a renal lobe or renal lobule?
|
Renal lobule! A renal lobe is a medullary pyramid and the cortical substance that surrounds it. A renal lobule is the cortical tissue surrounding a medullary ray. p. 194
|
|
|
|
Put these in order of blood flow through the tubular and collecting system of the nephron:
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
B. Bowman's capsule
F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle D. Descending thin limb of Henle A. Ascending thin limb of Henle H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule E. Distal Convoluted Tubule C. Collecting Tubule P. 196 |
|
|
|
Draw out the tubular and collecting system of the nephron.
|
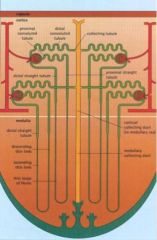
|
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE regarding a renal corpuscle?
A. It is located in the medulla B. It consists of a tuft of capillaries (the glomerulus) with its supporting (mesangial) cells and a Bowman's capsule. C. Its parietal layer and visceral layer are composed of simple squamous epithelium. |
A. Is incorrect. The renal corpuscle is located in the cortex.
p. 196 |
|
|
|
The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries (_________) with its supporting (__________) cells and a Bowman's capsule.
|
Tuft of capillaries = glomerulous , supporting cells = mesangial
p. 196 |
|
|
|
The renal corpuscle is comprised of three things. Name em.
|
- tuft of capillaries (glomerulus)
- supporting mesangial cells - Bowman's capsule p. 196 |
|
|
|
The renal corpuscle's parietal layer is the [ inner / outer ] layer composed of [ what kind of epithelial cells].
|
Outer, composed of simple squamous epithelium
p. 196 |
|
|
|
What is the space between the renal corpuscle parietal and visceral layers called?
|
Bowman's space
p. 196 |
|
|
|
[ urinary / vascular ] pole is where the afferent glomerular arteriole enters and the efferent arteriole leaves the glomerulus.
|
Vascular pole
p. 196 |
|
|
|
[ urinary / vascular ] pole is where Bowman's space goes continuous with the epithelium of the tubule system.
|
Urinary pole
p. 196 |
|
|
|
What are "podocytes"?
|
Podocytes are the special ame given to simple squamous epithelial cells adjacent to the endothelial cells of the glomerulus.
p. 196 |
|
|
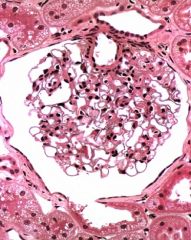
What is this an image of?
|
Renal Corpuscle. Note the nuclei protruding from the capillary tuft denote podocytes while those that have the nuclei within are just lil' capillaries.
|
|
|
|
True or False:
The glomerulous is projected into the Bowman's capsule and thus has a parietal and visceral layer. |
True! Parietal layer is the outer layer of the capsule, and visceral layer is the epithelial cells (podocytes) adjacent to endothelial cells of the glomerulus. Both are simple squamous epithelium. P. 196
|
|
|
|
The glomerulus (small tuft of capillaries) has about it five structures/areas of significance. Name them.
|
Podocytes
Basal lamina Endothelium Filtration barrier Mesangium |
|
|
|
______ are stellate shaped simple squamous epithelial cells that comprises the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule. They have pedicels, which are what and do what?
|
Podocytes; pedicals are secondary processess radiating from podocytes. The pedicels interdigitate with adjacent podocytes and yield filtration slits.
p. 196 |
|
|
|
True or False:
There is no basement membrane between podocytes and endothelium in a glomerulus. |
TRUE. We have epithelial cells but there is no basement membrane because there is no CT! Thus, we just have a basal lamina layer located between podocytes and endothelial cells. P. 196
|
|
|
|
True or False:
The podocytes in a glomerulus form a fenestrated capillary. |
FALSE. The endothelium in a glomerulus form a fenestrated capillary.
p. 196 |
|
|
|
The basal lamina (between podocytes and endothelium) in a glomerulus has three areas. Which does this describe: zone adjacent to the endothelium.
A. lamina densa B. lamina rara externa C. lamina rara interna |
C. lamina rara interna
p. 197 |
|
|
|
The basal lamina (between podocytes and endothelium) in a glomerulus has three areas. Which does this describe: zone adjacent to podocytes.
A. lamina densa B. lamina rara externa C. lamina rara interna |
B. lamina rara externa
p. 197 |
|
|
|
The basal lamina (between podocytes and endothelium) in a glomerulus has three areas. Which does this describe: intermediate zone, most electron dense.
A. lamina densa B. lamina rara externa C. lamina rara interna |
A. lamina densa
p. 197 |
|
|
|
The filtration barrier in a glomerulus filters blood plasma allowing what type of items to enter Bowman's space? (3) What is excluded? (2)
|
Filtered: water, ions, small molecules
Not: proteins > 69 kD and high net negative charge. p. 197 |
|
|
|
Why does the filtration barrier not filter proteins greater than 69kD and high net negative charge?
|
The slits in fenestrated capillary and podocytes' slits are too smaller to let 69kD proteins through and the basal lamina is already negatively charged and like repels like.
p. 197 |
|
|
|
What is a mesangium?
|
It is a mesangial cell that phagocytoses rpoteins and molecules "caught up" in the filtration barrier area. It "lives" in the interstitial spaces of glomerulus between the capillaries. p. 198
|
|
|
|
Which part of the nephron forms the largest and longest tubule in cortex?
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
F. Proximal convoluted tubule
p. 199 |
|
|
|
The proximal convoluted tubule is lined by simple [ cuboidal / squamous ] epithelium with a well-developed brush border along the lumen.
|
The proximal convoluted tubule is lined with simple CUBOIDAL epithelium .
p. 199 |
|
|
|
Why do abundant mitochondria lie in the bases of the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule?
|
Provides energy for the active transport needed to transport sodium out of cells into lateral intercellular spaces which then contributes to the osmotic movement of water out of the cell as well, and thru basement membrane into the loose CT of the kidney. p. 199
|
|
|
|
This portion of the nephron's major functioni is to reduce the volume of glomerular filtrate by approximately 80%.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
F. Proximal convoluted tubule
p. 199 |
|
|
|
How does the proximal convoluted tubule reduce the volume of glomerular filtrate by ~ 80%?
|
By active transport of sodium out of cells into lateral intercellular spaces. Chloride moves along with sodium passively. Accumulation of ions causes an osmotic movement of water out of the cell. Water moves thru basement membrane into the loose CT of the kidney. p. 199
|
|
|
|
This portion of the nephron is located in the medullary ray and forms the first part of the loop of Henle. It may also ectend intothe medullary pyramid.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
G. Proximal straight tubule
P. 199 |
|
|
|
True or False:
The straight portion of the proximal tubule is the region of the nephron that is often damaged in acute renal failure and mercury poisoning. |
True.
p. 199 |
|
|
|
Which part of the nephron is the region often damaged in acute renal failure and mercury poisoning?
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
G. Proximal straight tubule
p. 199 |
|
|
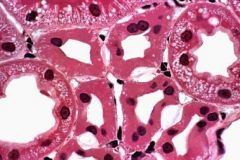
What is this portion of the nephron knowing this is a convoluted tubule?
(hit: "H" for choices) |
F. Proximal convoluted tubule, because they have a good prominent brush border! The convoluted and straight tubules pretty much look the same. This is at such a high mag that we'd have to be given whether it is convoluted or straight. But since we have a brush border there, we can at least identify that it is a proximal tubule.
30:07 of lecture |
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle
B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
|
|
This portion of the nephron forms a hairpin loop in the medullary pyramid creating the middle portion of Henle's loop.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle
p. 200 |
|
|
|
This area of the nephron is lined by a simple squamous epithelium, plays an important role in further concentrating urine,and usually forms within the medullary pyramid.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle
p. 200 |
|
|
|
This part of the nephron is located in the medullary ray and forms the third component of the loop of Henle. Microvilli is NOT prominent over luminal surface.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule
p. 200 |
|
|
|
True or False:
Microvilli are not prominent over luminal surface of the straight portion of the distal tube. |
True.
p. 200 |
|
|
|
This portion of the nephron is located in the cortex and begins at the macula densa. Cells actively transport sodium from the filtrate into the interstitium and makes urine more hypotonic.
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
E. Distal Convoluted Tubule
p. 200 |
|
|
|
In which portion of the nephron is the macula densa located?
A. Ascending thin limb of Henle B. Bowman's capsule C. Collecting Tubule D. Descending thin limb of Henle E. Distal Convoluted Tubule F. Proximal convoluted tubule G. Proximal straight tubule H. Straight Segment of the Distal Tubule I. Thin limb of the loop of Henle |
E. Distal Convoluted Tubule, near the afferent glomerulus arteriole
p. 200 |
|
|
|
The cells of the ________ are thought to monitor fluid in distal tubule and send signals via gap junctions to the juxtaglomerular cells in the afferent glomerular arteriole.
|
macula densa
p. 201 |
|
|

What is in the center of the image?
|
macula densa! (see the all-lined up string of nuclei) The lower right hand vessel is an arteriole. below the macula densa are juxtaglomerular cells. p. 201
|
|
|
|
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is located at the [ vascular / urinary ] pole of the renal corpuscle.
|
vascular pole
p. 201 |
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
A. afferent arteriole B. macula densa C. mesangial cells D. modified smooth muscle cells of afferent arteriole |
A. afferent arteriole
The afferent arteriole itself is NOT part of the juctaglomerular apparatus though many things around it are. p. 201 |
|
|
|
The _______ functions in response to a decrease in extracellular fluid volume. It triggers the juxtaglomerular cells to release renin.
A. Distal Convoluted tubule B. Juxtaglomerular apparatus C. Macula densa |
B. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
p. 201 |
|
|
|
What does renin do?
|
Renin acts on angiotensinogen in plasma converting it to Angiotensin I. In lungs, angiotensin I is converted to angiontensin II. AII is a potent vasoconstrictor which elevates blood pressure and causes release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex.
p. 201 |
|
|
|
Describe the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system as it starts in the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
|
Renin is released from juxtaglomerular cells --> Renin acts on angiotensinogen in plasma and turns it into Angiotensin I --> in lungs, AI is turned into AII. AII does two things: is a potent vasoconstrictor that thus raises blood pressure, and it also causes the release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex which stimulates distal tubule cells to retain sodium (and thus water). p. 201
|
|
|
|
[ Angiotensin I / Angiotensin II / Aldosterone ] is a potent vasoconstrictor which elevates blood pressure.
|
Angiotensin II
p. 201 |
|
|
|
[ Angiotensin I / Angiotensin II / Aldosterone ] stimulates the distal tubule cells to retain sodium and water follows.
|
Aldosterone
p. 201 |
|
|
|
Where does each of the following parts of the RAA system take place?
A. angiotensinogen --> AI B. AI --> AII C. Aldosterone released from D. Aldosterone acts |
A. plasma
B. in lungs C. Aldosterone released from adrenal cortex D. stimulates distal tubules cells to retain sodium and water follows p. 201 |
|
|
|
True or False:
The collecting ducts are found in the cortex and medullary ray. |
True
p. 202 |
|
|
|
How can you differentiate a collecting duct from the portions of a nephron?
|
The collecting duct is much more regular- they are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium cells with very regular nearly uniform height and regularly placed nucleus. p. 202
|
|
|
|
Both the collecting ducts as well as Papillary Ducts of Bellini respond to which hormone in particular?
A. ADH B. Aldosterone C. Epinephrine D. Renin |
A. ADH
p. 202 |
|
|
|
This portion of the intrarenal collecting duct is located near the apex of the medullary pyramid and have simply columnar epithelium and large, straight ducts that empty their contents into the minor calyxes.
A. Collecting Ducts B. Papillary Ducts of Bellini |
B. Papillary Ducts of Bellini
p. 202 |
|
|
|
True or False:
The area cribrosa are holes through which papillary ducts of bellini empty into a minor caylx. |
True
p. 202 |
|
|
|
Which portion of the intrarenal collecting duct plays a primary role in producing a concentrated urine when affected by ADH?
|
Papillary Ducts of Bellini
p. 202 |
|
|
|
Regarding the blood supply of the kidneys, the _______ enters the renal hilus and gives rise to interlobar arteries that go between medullary pyramids.
|
renal artery
p. 202 |
|
|
|
[ Interlobar arteries / Interlobular arteries ] give rise to afferent arterioles of glomeruli.
|
Interlobular arteries
p. 202 |
|
|
|
[ Interlobar arteries / Interlobular arteries ] divide into several arcuate arteries, travel along corticomedullary junction, parallel to surface . From these arcuate arteries, small [ interlobar arteries / interlobular arteries ] arise and enter cortical tissue.
|
Interlobar arteries ; interlobular arteries
p. 202 |
|
|
|
[ Efferent glomerular arterioles / Interlobar arteries / Interlobular arteries ] give rise to an extensive peritubular capillary network that supplies convoluted tubules and some will form vasa recta which are long straight capillaries that extend into medullary pyramids.
|
Efferent glomerular arterioles
p. 202 |
|
|
|
[ Efferent glomerular arterioles / Vasa Rectae ] drain into interlobular or arcuate veins and then into interlobar veins which at the hilus form the renal vein.
|
Vasa rectae
p. 202 |
|
|
|
Which portion of the kidney is lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium known as transitional epithelium?
A. Renal Hilus B. Renal Pelvis C. Renal Sinus |
B. Renal Pelvis
and also Ureter and urinary bladder are lined with transitional epithelium p. 203 |
|
|
|
This serves as a conduit between the renal pelvis and urinary bladder and has smooth muscle component of inner longitudinal and outer circular layer.
|
Ureter
p. 203 |
|
|
|
The smooth muscle component of the [ ureter / urinary bladder ] consists of three layers. How are they arranged?
|
The urinary bladder has three layers: innermost longitudinal, middle circular and outermost longitudinal again.
p. 203 |
|

