![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the constituents of the extracellular matrix?
|
1. Collagen
2. Glycoprotein 3. Proteoglycan |
|
|
What are the modular building blocks of connective tissue?
|
1. Collagen
2. Glycoproteins 3. Proteoglycans |
|
|
ECM is basically a composite material of what two element?
|
1. Semi-rigid linear elements (e.g.-collagens)
2. Flexible, space-filling elements (e.g.-glycoproteins and proteoglycans) |
|
|
What are the two "themes" in ECM?
|
1. Interstitial Connective Tissue
2. Basement membrane |
|
|
What is the composite of polyproteins found in basement membranes?
|
1. Fibrillar proteins
2. Glycoproteins 3. Proteoglycans |
|
|
What are the two layers that make up the basement membrane?
|
1. Basal Lamina
2. Reticular Lamina |
|
|
What are the two layers of basal lamina?
|
Lamina Rara (top layer)
Lamina Densa (bottom layer) |
|
|
What are the components of intertitial connective tissue?
|
1. Fibrillar component
2. Glycoproteins 3. Proteoglycans |
|
|
What is the general structure of collagen?
|
Three polypeptide chains (alpha chains) which are wrapped around one another to form a LEFT handed triple helix.
|
|
|
What is the seqeunce found in the polypeptide chain of collagen?
|
Gly-X-Y (where X is usually a proline and Y is usually a hyrdoxyproline)
|
|
|
What happens when proline is in the Y position of the Gly-X-Y triplet?
|
Prolyl hydroxylase will come in and convert it to 4-hydroxyproline.
|
|
|
What happens when lysine is in the Y position of the Gly-X-Y triplet?
|
Lysyl hydroxylase will convert it to hydroxylysine
|
|
|
How would you read α1[I]?
|
Alpha chain, number 1, from the Type I collagen family.
|
|
|
How would you read [α1(I)]1 [α2(II)]2?
|
A Type I trimer of 2 alpha 1 chains, and 1 alpha 2 chain.
|
|
|
What occurs on the α chains have translation?
|
Immediate posttranslational modification.
|
|
|
Give an example of posttranslational modification in collagen synthesis.
|
Prolines become modified to hydroxyprolines (by prolyl hydroxylase) or lysines become modified to become hydroxylysines (by lysyl hydroxylase)
|
|
|
Is there any further modifications seen after immediate posttranslational modification?
|
Yes. Hydroxylysine residues are further modified via glycosylation.
|
|
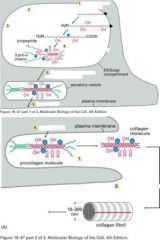
Describe`
|
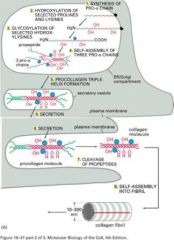
Answers
|
|

What is this and describe its structure.
|

This is a fibril forming collagen. In "native" fibrils, the collagen molecules have repeat structures of 1 "hole zone" and 1 "overlap" zone with 1/4 staggared conformation.
|
|
|
The fibrous backbone of ECM is also known as?
|
Collagen
|
|
|
Describe the organization of interstitial ECM in comparison to basement membrane ECM.
|
Similar in organization
|
|
|
Glycosylation of alpha chains occurs when?
|
When you have hydroxylysine
|
|
|
Which end does the assembly of collagen begin?
|
At the carboxy end. Then proceeds to the amine end in zipper like fashion.
|
|
|
The information needed for processing and assembly of collagen is located where?
|
Inherent in the collagen structure.
|
|
|
Where does procesing occur for collagen?
|
Outside of cell.
|
|
|
Within collagen, what is the enzyme responsible for INTRA-molecular crosslinks and where do they crosslink?
|
Lysl-oxidase.
Crosslinks at between hydroxylysines. |
|
|
What type of modification is VERY important in collagen structure?
|
Post-translational modification.
|
|
|
Structure of FACIT collagens allow for what?
|
Globular domains allow for stability.
|
|
|
Type IV collagens are used for what structures?
|
Basement membrane.
|
|
|
Describe the structure of Type IV collagens.
|
Globular domains dimerize head to head on the carboxy terminus. These dimers then form a tetramer in the 7s region at the amino terminus. Leads to big network.
|
|
|
How do you decrease the melting temperature Point of collagen?
|
Decrease the number of hydroxyproline
|
|
|
What are the cofactors required in collagen post-translational modification.
|
Ascorbic acid and Iron
|
|
|
How is Osteogenesis Imperfecta associated with collagen formation?
|
A mutation leads to a frameshift leading to the loss of a cysteine in the carboxy end (meaning assembly is tough) causing non-incorporation to a trimer.
|
|
|
Give two examples of post-secretory modification in collagen synthesis.
|
1. Cleavage of N and C terminus propeptides.
2. Covalent cross-linking |

