![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In terms of metabolism, what is insulin responsible for in a fed state?
|
1. Uptake of carbohydrates
2. Metabolism of lipolipids |
|
|
Where do you find fatty acid synthase?
|
In the cytoplasm
|
|
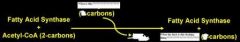
What the @#$% is going on here?
|
Answer
|
|
|
Fatty acid synthesis takes many steps with how many enzymes?
|
Just one
|
|
|
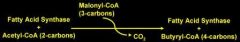
How do you elongate fatty acids with how many added carbons each time?
|
Sequential additions of malonyl CoA, and release of CO2. Thus 2 carbons added each time.
|
|
|
Fatty acid synthesis ends with formation of what? How many carbons is this molecule?
|
Palmitate (16 carbons)
|
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for forming malonyl-CoA and what special molecule is on it?
|
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase containing biotin.
|
|
|
How does malonyl-CoA get formed?
|
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase adds a carbon on to acetyl-CoA from HCO3-
|
|
|
During a fed state, what molecule does what to the regulation of malonyl-CoA formation?
|
Insulin activates formation of citrate to acetyl-CoA
|
|
|
During a fasting state, what molecules signal what to the regulation of malonyl-CoA formation?
|
Glucagon and epinephrine inhibit Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
|
|
|
Give an example of feed-forward activation for malonly-CoA formation.
|
High levels of citrate will activate Acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
|
|
|
Give an example of feedback inhibition for malonly-CoA formation.
|
Palimate inhibits Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
|
|
|
What are all the activators of malonyl-CoA formation?
|
1. Citrate
2. Insulin |
|
|
What are all the inhibitors of malonly-CoA formation?
|
Palmitate, Epinephrine, and Glucagon.
|
|
|
Palmitate elongation occurs where?
|
Smooth ER
|
|
|
T/F - Palmitate elongation and fatty acid synthesis occurs using the same enzymes.
|
False - although both use malonyl CoA to contribute the carbons, the enzymes are different
|
|
|
Acetyl-CoA is formed in mitochondria and fatty acid syntheisis occurs in the cytoplasm. What allows acetyl-CoA to get to cytoplasm?
|
Acetate shuttle
or Citrate cleavage pathway |
|
|
In the acetate shuttle, what does citrate break down into?
|
Acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate
|
|
|
How does oxaloacetate re-enter the mitochondria?
|
Must be reduced to malate or pyruvate to enter the mitochondria
|
|
|
Conversion of oxaloacetate to malate yields what?
|
NADH
|
|
|
Conversion of oxaloacetate to pyruvate yields what?
|
NADH and NADPH
|
|
|
Conversion of malate to pyruvate yields what?
|
NADPH
|
|
|
What is the enzyme responsible for forming NADPH from malate to pyruvate?
|
malic enzyme
|
|
|
Is cholesterol required in the diet?
|
No. All cells can synthesize it from simple precursors
|
|
|
What is the enzyme catalyzing the final step in cholesterol synthesis?
|
7-dehydrocholesterol D7 Reductase
|
|
|
What is the disorder associated with a defect or absence of 7-dehydrocholestrol D7 Reductase?
|
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS)
|
|
|
What is the beginning precursor of cholesterol?
|
Acetyl-CoA
|
|
|
General description of stage 1 of cholesterol synthesis.
|
3 Acetyl CoA form Mevalonate
|
|
|
General description of stage 2 of cholesterol synthesis.
|
Mevalonate conversion to Isoprolene
|
|
|
General description of stage 3 of cholesterol synthesis.
|
6 Isoprolene (5C) forms Squalene
|
|
|
General description of stage 4 of cholesterol synthesis.
|
Squalene goes through cyclization and subsequent modifications to form cholesterol.
|
|
|
What is the first committed step in cholesterol synthesis?
|
HMG-CoA (3 acetyl CoA condensed together) will be reduced to mevalonate with the help of HMG CoA reductase
|
|
|
What three things regulate the biosynthesis of cholesterol?
|
1. Intracellular cholesterol concentration.
2. Insulin 3. Glucagon |
|
|
How does cholesterol take part in it's own feedback inhibition?
|
Cholesterol (or one of it's derivative) will inhibit GENE TRANSCRIPTION or activate DEGRADATION of HMG CoA Reductase
|
|
|
What phosphorylates HMG-CoA Reductase, and what does this do?
|
Glucagon phosphorylates it to inactivate HMG CoA Reductase.
|
|
|
What dephosphorylates HMG-CoA Reductase, and what does this do?
|
Insulin dephosphorylates it to activate HMG-CoA Reductase.
|
|
|
Cholesterol is primarily made where?
|
Liver
|
|
|
What are the two forms that cholesterol is exported in from the liver?
|
1. Bile salts
2. Cholestryl esters (lipoproteins) |

