![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Name this shit!
|
Answers
|
|
|
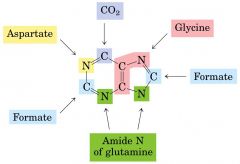
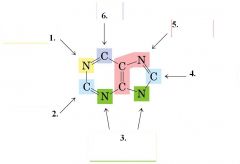
For purine synthesis, what do we need to start out with?
|
PRPP (5-phosphoribosyl 1 pyrophosphate)
|
|
|
How do you make PRPP?
|
From Ribose 5 phosphate of the Pentose phosphate pathway and use the enzyme PRPP synthetase.
|
|
|
What is the first committed step of purine synthesis?
|
PRPP becomes 5-phosphoribosylamine with the help of glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase.
|
|
|
In purine synthesis, what is the first purine made?
|
Inosine
|
|
|
From Inosinate (IMP), what is used for AMP synthesis?
|
GTP
|
|
|
From Inosinate (IMP), what is used for GMP synthesis?
|
ATP
|
|
|
IMP is the precursor for what? x 2
|
AMP and GMP
|
|
|
If ATP is higher than GTP, more IMP will be converted to what?
|
GMP
|
|
|
If GTP is higher than ATP, more IMP will be converted to what?
|
AMP
|
|
|
Reciprocal use of GTP and ATP does what?
|
Equilibrates AMP and GMP synthesis
|
|
|
What regulates PRPP and how?
|
AMP, GMP, and IMP in an inhibitory manner
|
|
|
What regulates Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase and how?
|
AMP, GMP, and IMP in an inhibitory manner
|
|
|
What regulates adenylosuccinate synthetase?
|
AMP in an inhibitory manner
|
|
|
What regulates IMP dehydrogenase?
|
GMP in an inhibitory manner
|
|
Answer this!
|
Answers
|
|
|
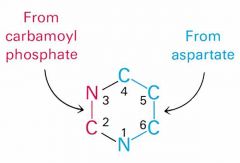
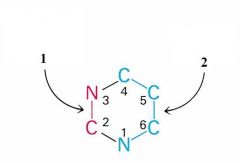
In pyrmidine synthesis, what do you need to start out wtih and how do you make it (enzyme and reactant)
|
You need Carbamoyl phophate made from glutamine and carbamoyl synthetase II.
|
|
|
Where is carbamoyl phosphate made?
|
cytosol
|
|
|
Carbomoyl synthetase I - where is it, what does it do, and act in what cycle?
|
In mitochondria and utilizes NH4 as a nitrogen source.
Also seen in Urea cycle |
|
|
What is the first committed step of pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Carbamoyl Phosphate + Aspartate ---> N-Carbamoylaspartate
Use of Aspartate transcarbamolyase |
|
|
What is CAD?
|
A multifunctional trimer enzyme that is:
1. Carbamoyl Synthetase II 2. Aspartate transcarbamoylase. 3. Dihydroorotase |
|
|
What does dihydrooratase catalyze?
|
N-carbamoylaspartate to dihydroorotate. (RING CLOSURE)
|
|
|
What happens to dihydroorotate?
|
Diffuses to mitochondria where it is oxidized by dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in to orotate.
|
|
|
What happens to orotate?
|
Orotate and PRPP (with the enzyme Orotate phophoribosyl transferase) is converted into Orotidylate.
|
|
|
What happens to orotidylate?
|
Orotidylate with the help of orotidylate decarboxylase becomes UMP (uridylate)
|
|
|
What happens to UMP?
|
Kinase acts on it to become UTP
|
|
|
Describe the character of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase AND orotidylate decarboxylase.
|
They are on the same damn enzyme.
|
|
|
What happens to UTP?
|
UTP becomes CTP with the help of Cytidylate synthetase, glutamine, and ATP
|
|
|
How is Carbamoyl Synthetase II regulated?
|
ATP and PRPP activate it
UTP and CTP inhibit it |
|
|
What does UMP regulate?
|
Inhibits OMP
|
|
|
A rare example occurs where the first commited step is not the regulated step. Why?
|
Because carbamoyl phosphate is made in the Urea cycle.
|
|
|
What is oroticaciduria type I?
|
A defect in the orotate phosphoribosyltransferase AND orotidyl decarboxylase.
|
|
|
What is oroticaciduria type II?
|
A defect in the orotidyl decarboxylase
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of patients with oroticaciduria?
|
Anemia, and high levels of orotate accumulation.
|

