![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Excess ____ produced during the metabolism of amino acids is excreted
as_______ formed in the ______ Cycle. |
NH3, Urea , Urea Cycle
|
|
|
What are the three general reactions involved in amino acid metabolism?
|
- Transfer or removal of the NH3 group
- Removal of carboxyl group - Transfer of Methyl groups |
|
|
Amino acids are generated from dietary protein and breakdown of intracellular protein over time. If amino acids are not needed for protein synthesis, they are catabolized. People with liver disease (cirrhosis, cancer, hepatitis) have a buildup of ________ in the blood.
|
ammonium ion
|
|
|
If the ammonium ion, NH4+ , is not needed for the biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and biologogical amines, what cycle does it go to?
A. aspartate-arginine-succinate shunt of citric acid cycle B. Urea cycle C. TCA cycle |
B. Urea Cycle
note: 3 ATPs are needed to get rid of urea in the urea cycle so it's a pretty energy-costly cycle. |
|
|
What organ is the central organ responsible for most amino acid metabolism?
|
Liver
|
|
|
What amino acid plays a central role in amino acid metabolism?
A. Alanine B. Asparganine C. Glutamate D. Glycine |
C. Glutamate
|
|
|
If a person has a diet rich in protein and has excess amino acids, they cannot be stored and will be degraded. For example, people on the _________ diet eat abundant amounts of protein and very little carbohydrates.
|
Atkins
|
|
|
Under what circumstances must proteins be used for an energy source?
(ex. after a meal, fasting, etc.) |
during STARVATION or in patients with DIABETES when carbs are not available for energy
|
|
|
Amino acids lose their amino groups forming ________ , which in turn undergo oxidation to ____ and ____.
|
alpha-keto acids, CO2 and H2O
|
|
|
When protein is broken down for ENERGY, then most of the energy is derived from [what checmical reaction of what intermediate]?
|
oxidation of alpha-keto acids
|
|
|
____________ (inactive Zymogen), secreted by chief cells, is converted to the active enzyme _______ by the low pH environment in the stomach.
|
Pepsinogen --> pepsin
|
|
|
Where does pepsin cleave ( amino / carboxyl terminal) ? And which amino acids?
|
Pepsin cleaves on the amino-terminal side of aromatic amino residues Tyrosine, Phenylalanine
and Tryptophan. |
|
|
What type of cells make up the gastric glands in the stomach lining? What does each type of cell secrete?
|
Gastric glands in stomach lining has parietal cells (secrete HCl) and chief cells (secrete pepsinogen).
|
|
|
As the contents pass into the small intestine, the pancreas secretes
____________ to neutralize the acid and allow other protein degrading enzymes to function. |
bicarbonate
|
|
|
__________ is produced in the upper portion of the small intestine (duodenum) and inhibits gastric acid secretion & stomach motility; stimulates the pancreas to release bicarbonate ions and stimulates the gall bladder to secrete bile.
|
Secretin.
|
|
|
Tell me about secretin.
A. Where is it produced and released? B. What does it stimulate? |
Secretin: produced in the upper portion of the small intestine (duodenum) and inhibits gastric acid secretion & stomach motility; stimulates the pancreas to release bicarbonate ions and stimulates the gall bladder to secrete bile.
|
|
|
The zymogen Trypsinogen is converted to the active protease
called Trypsin by an enzyme called ___________________. |
enteropeptidase (enterokinase)
|
|
|
Trypsin cleaves proteins at sites of [ two amino acids ] on the
[ carboxy / n -terminal ] side. |
Lysine and Arginine, carboxy
|
|
|
Chymotrypsinogen is converted to
Chymotrypsin by .... A. Trypsin B. Elastase C. Enteropeptidase (enterokinase) |
Trypsin
|
|
|
Proelastase is converted to the active enzyme Elastase by__________ .
|
Trypsin
|
|
|
The zymogen Trypsinogen is converted to the active protease
called Trypsin by an enzyme called enteropeptidase (enterokinase). Trypsin then cleaves proteins at sites of Lysine and Arginine on the carboxy-terminal side. Chymotrypsinogen is converted to Chymotrypsin by Trypsin.Proelastase is converted to the active enzyme Elastase by Trypsin. The Chymotrypsin then cleaves on the carboxy-terminal side of what three amino acids? |
Tyrosine, Tryptophan and Phenylalanine.
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
During normal synthesis & degradation of cellular proteins…
some amino acids will undergo oxidative degradation if they [ are / are not ] needed for new protein |
some amino acids will undergo oxidative degradation if they ARE NOT needed for new protein
|
|
|
Pepsinogen is changed to pepsin via....
|
low pH (H+)
|
|
|
Trypsinogen is changed to Trypsin via...
|
Enteropeptidase
|
|
|
Chymotrypsinogen is changed to Chymotrypsin via...
|
Trypsin
|
|
|
Proelastase is changed to elastase via...
|
trypsin
|
|
|
Procarboxypeptidases change to carboxypeptidases via....
|
trypsin
|
|
|
What are the essential amino acids?
|
PVT TIM HALL
Phenylalanine, Valine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Isoleucine, Methionine, Histidine, Arginine, Leucine, Lysine |
|

What type of reaction is this and what is the enzyme involved?
|
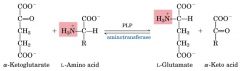
transamination. note: PLP, PYRIDOXAL PHOSPHATE, is a co-factor (aminated form)
|
|
|
For amino acid metabolism reactions involving the amino group, what is a co-factor in the transamination reaction?
|
PYRIDOXAL PHOSPHATE, PLP is a co-factor
(aminated form) aminotransferase picks up amino group and transfers it to PLP then the amino group can be transferred to alpha-keto Glu or some other alpha keto acid. |
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism and reactions involving the amino group, what are the two types of deamination that can occur?
|
Oxidative deamination or non-oxidative deamination.
In deamination, amino group is split off to form ammonia and an alpha ketoglutarate which can be oxidized for energy or used to form a new amino acid. Oxidative because losing ammonia. There is also a non-oxidative type. |
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism and reactions involving the amino group, ____________ refers to the direct removal of the NH4 group.
|
deamidation
|
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism and reactions involving the carboxyl group,
decarboxylation forms.... [ general category ] |
important biological amines
ex. Tyrosine -> Dopamine -> Norepinephrine ->epinephrine Glutamate -> gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) Histidine -> Histamine Tryptophan -> Serotonin |
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism and reactions involving the carboxyl group, general reaction for decarboxylation includes:
Specific decarboxylases, also utilizing PLP as a co-factor, remove the carboxyl group from the amino acid thus forming new ________ and liberating ____ |
biological amines and liberating CO2
|
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism, reactions involving the carboxyl group include:
A. histidine --> __________ B. Tryptophan --> _________ C. Glutamate --> __________ |
A. Histidine --> Histamine
B. Tryptophan --> Serotonin C. Glutamate --> GABA note: Tyrosine ---> dopamine |
|
|
Histamine is formed from ____________ by this General Reaction
of ______________ utilizing PLP as a co-factor. |
Histidine, decarboxylation.
Specific decarboxylases, utilizing PLP as a co-factor, remove the carboxyl group from Histidine thus forming a new biological amine and liberating CO2 |
|
|
True or False:
Histamine stimulates acid secretion in the stomach. |
True.
Cimetidine (Tagamet), an H2 receptor antagonist and an analog of Histamine is used to treat duodenal ulcers because it blocks gastric acid secretion. |
|
|
___________ is a neurotransmitter in the brain and causes contraction of smooth muscle of arterioles
and bronchioles. ________ is also formed from Tryptophan and is a "sleep inducing" molecule. Ingestion of foods rich in Tryptophan (meat & milk) leads to sleepiness because the resulting items are sleep-inducing. Tryptophan also reduces anxiety & depression and has been called "Nature's Prozac". A. Melatonin; Serotonin B. Serotonin; Melatonin |
B. Serotonin; Melatonin
|
|
|
Spermine & Spermidine
are formed by __________ reactions…. They are involved in DNA packaging. Precursors are __________ and __________. |
decarboxylation; Methionine & Ornithine
|
|
|
When the following are decarboxylated, what results?
A. Tyrosine B. Tryptophan |
A. Dopamine
B. Serotonin |
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism reactions involving the carboxyl group, an example of this type of reaction would be the ultimate transfer of a methyl group
from Methionine to the methyl donor S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM). |
transmethylation. A variety of enzymes called methyl will then transfer the methyl group to other molecules.
|
|
|
Regarding amino acid metabolism reactions involving the carboxyl group, in transmethylation, _____________ is an important methyl donor.
|
SAM, or S-Adenosyl Methionine
|
|
|
What three amino acids are NOT degraded in the liver?
|
Leucine, Isoleucine & Valine. They are oxidized as fuels primarily in muscle, adipose, kidney & brain tissue. These tissues contain an enzyme called Branched-Chain Aminotransferase that converts these 3 amino acids to corresponding alpha keto acids.
A defect in the complete catabolism of branched chain amino acids leads to the metabolic defect called Maple syrup urine disease. |
|
|
A defect in what leads to the metabolic defect called Maple syrup syndrome?
|
A defect in the complete catabolism of branched chain amino acids (defect of branched-chain alpha keto acid dehydrogenase complex) leads to the metabolic defect called Maple syrup urine disease. (Leucine, Isoleucine & Valine, are not degraded in the liver but are oxidized as fuels primarily in muscle, adipose, kidney & brain tissue. These tissues contain an enzyme called Branched-Chain Aminotransferase that converts these 3 amino acids to corresponding alpha keto acids.)
|
|
|
Which amino acid has a central role in many amino acid metabolic pathways?
A. Alanine B. Glutamine C. Glutamate D. Methionine |
C. Glutamate
|
|
|
Which amino acid has the most complex degradation pathway?
A. Tryptophan B. Tyrosine C. Threonine D. Cysteine |
A. Tryptophan
(byproduct of the decarboxylation step is Serotonin) |
|
|
A deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase, the enzyme required
to convert Phenylalanine to Tyrosine, can lead to the pathologic condition known as __________. |
phenylketonuria PKU
|
|
|
Phenylketonuria PKU occurs when you are deficient in the enzyme ___________________ which turns amino acid _____________ into ______________.
|
phenylalanine hydroxylase;
turns Phe intoTyr |
|
|
Name a few dietary sources of phenylalanine from the nine given in class.
|
Cheeses
Nuts and seeds Meat (excluding fat) Poultry (excluding skin) Fish, including shellfish Milk Eggs Aspartame (nutrasweet) |
|

|

|
|
|
This is an inherited disorder that affects phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism. This leads to excretion of homogentistic acid in the urine, which makes the urine appear black.
|
Alkaptonuria.
Usually, the condition does not result in any serious ill effects |
|
|
Why is tetrahydrofolate important in amino acid metabolism?
|
It is a key co-factor in many metabolic pathways of amino acids. It exists in several oxidation states and mediates the transfer of methyl groups. Meats and green veggies provide folic acid that is eventually reduced to tetrahydrofolate. N10-Tetrahydrofolate is the precursor of FORMATE that contributes 1 Carbon units to the ring structure of the Purines, too!
|
|
|
True or False:
There are several pathologies associated with folate deficiency including affected tyrosine and phenylalanine metabolism which leads to an excess of homogentistic acid. |
False. Folate deficiency has symptoms of weakness, anemia and anorexia. The symptoms described are for alkaptonuria.
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE:
A. Alcoholism may compound folate deficiency. B. Folate deficiency has symptoms of anemia, weakness and anorexia. C. Folic acid is needed to reduce the level of homocysteine in blood as a high level of these is associated with higher risk of coronary heart disease and stroke. D. Women at increased risk for a baby with Ehler's-Down Syndrome should take an increased amount of folic acid 1-3 months before becoming pregnant. |
D. is false. Not Ehler's Down Syndrome but spina bifida.
|
|
|
Ammonia itself cannot be transported to the liver for further
metabolic processing. Therefore it is incorporated into Glutamate by the enzyme__________ to form the non-toxic amino acid _________. This is a 2 stage reaction and requires ATP. |
Glutamine Synthetase to form Glutamine.
Bottom line: Glutamine is "blood friendly" whereas ammonia is NOT. |
|
|
What amino acid transports ammonium in the blood stream?
|
Glutamine ;
It is then carried by the blood to the liver where in the mitochondria of the hepatocyte, the amide nitrogen is released as ammonia when the enzyme Glutaminase converts the Glutamine back into Glutamate |
|
|
___________ is a neutral, non-toxic compound and can readily pass through cell membranes whereas Glutamate cannot.
|
Glutamine ;
It is then carried by the blood to the liver where in the mitochondria of the hepatocyte, the amide nitrogen is released as ammonia when the enzyme Glutaminase converts the Glutamine back into Glutamate |
|
|
What two amino acids have their own "cycles" due to their "blood-friendliness"?
|
Glutamine and Alanine.
|
|
|
In the _____ cycle, excess ammonia is incorporated into __________ and then transferred to ________ by the action of the enzyme _________________ to form _______. This amino acid, with no net charge at pH near 7, readily passes into the blood where it is transported to the liver. In a reversal of the reaction that took place in the muscle, this is converted back.
|
ALANINE cycle, excess ammonia is incorporated into GLUTAMATE and then transferred to PYRUVATE by the action of enzyme ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE to form ALANINE.
|
|

What cycle does this show?
|
Alanine cycle.
|
|
|
True or False:
The urea cycle takes place in the liver mitochondria only. |
FALSE. It takes place in both the liver mitochondria and the cytosol.
|
|
|
How many ATP molecules are required for the production of 1 molecule of urea?
A. 1 ATP B. 2 ATPs C. 3 ATPs D. 5 ATPs |
C. 3 ATPs
|
|
|
Which of the following is false about the urea cycle:
A. Cycle begins in the liver mitochondria B. Urea is produced in the cytosol C. Aspartate donates a nitrogen directly to the urea molecule D. Urea is hydrolyzed from arginine by arginase and excreted, leaving citrulline which goes back into the mitochondrial matrix E. All of the above are true |

D. Urea IS hydrolyzed from arginine by arginase and excreted but what is left is ornithine, not citrulline, which goes back into the mitochondrial matrix.
|
|
|
When is SAM the cofactor and when is PLP the cofactor?
|
SAM = transmethylation reactions
PLP = decarboxylation, transamination,and deamination reactions |

