![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the basic principles of production methods |
Lean thinking ie focus in value and waste 1) encourage staff to participate and reward contribution 2)organise the work place and tidy 3) remove waste and continuously strive for improvements 4) reduce the time and cost of productions to increase profitability |
|
|
What are the 5 s |
1)sort 2)set in order 3)shine 4) standardize 5)sustain |
|
|
What is value added |
Customer is willing to pay for it so it increases the market value |
|
|
Non value added |
Customer couldn't care less so it should be eliminated or reduced |
|
|
Waste |
Any non value added activity that exceeds the minimum required to facilitate the value added activity |
|
|
What are the 7 deadly wastes |
TIM WOOD
Transport Inventory Motion Waiting Overproduction Over processing Defective product |
|
|
What is the difference between methods and process |
Production process A method of producing components from raw materials eg injection molding Production method A group of processes brought together to manufacture products eg batch production |
|
|
Finish the line A production method may be based on one or more of the following |
Minimum cost Minimum distance Maximum volume of work moved Maximum rate of work moved |
|
|
3 production method diagrams |

And cellular |
|
|
How do u pick the right production method |
Type of product Market size and segment Complexity of design Factory cost-land labour and capital |
|
|
What are the 3 common productions methods |
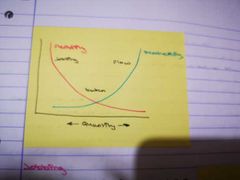
1) manufacture of a unique object Jobbing
2) manufacture of a quantity of similar items Batch
3) subassembly or final assembly Flow |
|
|
Explain jobbing |
One off item Bespoke or made to order Production layout but fixed position Examples Boats ships Prototype Tooling Aircraft Large plant machinery Building Service repair |
|
|
Draw a diagram for jobbing |
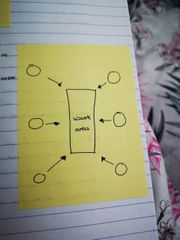
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of jobbing |
+ Versatile general purpose tools can be used Little need for QC Good job satisfaction due to variation Suitable to wide variety of complex and large products - High labour costs Poor economy of scale as overheads are recovered from a single article High set up cost |
|
|
What is jobbing + / boutique manufacture |
Limited quantities of custom item Fill gap between 1 off and batch May use cellular manufacturing techniques Exploits standardisation more than jobbing |
|
|
Advantages of boutique manufacture |
Relative low investment in dedicated equipment High level of flexibility and quick change over time Improves product customisation Increased economies of scale |
|
|
Explain batch production |
Manufacture of a quantity of similar items Production layout by process Balance quantity and flexibility Batches of products follow a set path according to their processing requirements |
|
|
Draw a diagram of batch processing |
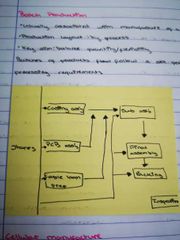
|
|
|
Explain cellular manufacture with diagram |
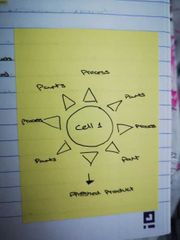
Stand alone work cells set up go manufacture specific components All parts and processes are close to hand May be used with boutique and batch production |
|
|
Explain pros of batch production |
Reduction of throughput time reduces unit cost Set up cost and overheads can be spread over batch quantity Special jigs tools and fixtures remove the need for skilled workforce Variety of job can be processed simultaneously Can adapt to a wide range of products Allow product variation |
|
|
Cons of batch production |
Versatility is inversely proportional to batch size Work in process ties up money in storage cost Job satisfaction may reduce as expertise is removed Quality must me monitored Stock control must maintain quantities of raw material and components Production planning is necessary to link sales qty to manufacturing qty Careful planning is necessary to avoid idle time |
|
|
What is it meant by batch production and idle time |
Unit is in one of three stages 1) waiting to be processed 2) being processed 3) waiting to proceed to next process Work in process results from large batch quantities |
|
|
Explain work in process and flow |
The batch que approach Items sit idle before processing>delay up stream Items sit idle before moving to the next stage>delay downstream
Waiting is waste |
|
|
How do u work out idle time in batch production |
n-1/n. *100% Of total processing time
Very large batches = units sit idle for long periods of time Ie work in process
Very small batches = operators frequently setting up different jobs Ie inefficient and rejects will be higher
|
|
|
Explain flow production |
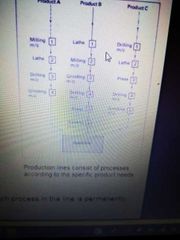
Mass production Minimisation of throughput time QC is inline part of process Production layout is by product Little to no set up time as each process in the line is permanently dedicated to one product and it's components |
|
|
Advantages of flow |
Suitable for mass production of components subassembly and final assembly High quantities reduce set up cost and overheads Production activities are simple tasks so unskilled labour/automation is possible Output is maximised due to speed and efficiency |
|
|
Cons of flow |
Under/overloading workstation must be avoided to prevent bottlenecks Material handling procedures must be efficient Continuous supply of materials and parts is necessary Preventive maintenance is Required to avoid down time Stand in operators required incase of absenteeism Repetitive so reduces motivation Standardized part is preferably |
|
|
A semi continuous one piece flow approach reduces |
Idle time and work in process |
|
|
What is the one piece flow approach |
Items flow continuously throughout the production system Pressure is even across all production Production is paved using carefully calculated takt time |
|
|
Indication of waste in production |
Tired staff Empty rework department Sparsely stocked inventory of parts/ finished products |

