![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Primary immune system organs |
1- Bone marrow - immune cell production B cell maturation 2- Thymus - T cell maturation |
|
|
Secondary immune system organs |
1- Spleen, lymph nodes, tonsil and peyers patches 2- Allows immune cells to interact with antigen |
|
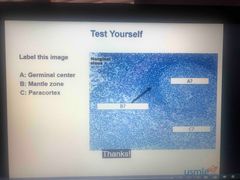
Lymph nodes |
A - secondary follicular B - area around secondary follicle C - Paracortex |
|
|
Lymph node |
1- Secondary lymphoid organ that have many afferents, 1 or more deferents 2- Encapsulated with tribulations 3- Function are non- specific filtration of macrophages, circulation of B and T cells and immune response activation |
|
|
Follicle of the lymph nodes |
1- B cell localization and maturation 2- Primary follicle - dense and dormant 3- Secondary follicle - pale germinal center and active |
|
|
Medulla of the lymph nodes |
1- Medulla cord - closely packed lymphocytes and plasma cells 2- Medullary sinus- communicate with efferent lymphatics and contain reticular cells and macrophages |
|
|
Paracortex of medulla |
1- Contain T cells 2- Between follicle and medulla 3- Contain endothelial venous through which B and T cells enter from the blood 4- Not well developed in patients with DiGeorge syndrome 5- Enlarge in a extreme cellular immune response (EBV and other viral infections - paracortical hyperplasia- lymphaedmea |
|
|
Function of lymph node |
1- Regulate fluid from tissue 2- Filter fluid in lymph node 3- Trigger immune response |
|
|
What is the region immediately surrounding the germinal center in a secondary follicle |
Mentle zone |
|
|
Location of follicles found within a lymph node |
Located primarily in the outer vortex of the lymph node |
|
|
Cervical and supraclavivular lymph nodes |
1- Head and neck 2- Disease 1- upper respiratory tract infection 2- Infectious mononucleosis 3- Kawasaki disease |
|
|
Mediastinal lymph nodes |
1- Trachea and lymph nodes 2- Disease 1- Pulmonary TB 2- Sarcoidosis 3- Primary lung cancer 4- Granulomatous disease |
|
|
Hilar lymph node |
1- Lungs 2- Disease 1- Pulmonary TB 2- Sarcoidosis 3- Primary lung cancer 4- Granulomatous disease |
|
|
Ancillary lymph nodes |
1- Breast, upper limb, skin above umbilicus 2- Disease 1- Mastitis 2- Metastasis (esp breast Ca) |
|
|
Ancillary lymph nodes |
1- Breast, upper limb, skin above umbilicus 2- Disease 1- Mastitis 2- Metastasis (esp breast Ca) |
|
|
Celiac lymph nodes |
1- Liver, stomach, spleen, pancreas and upper duodenum 2- Disease 1- Mesenteric lymphadenitis 2- Typhoid fever 3- Ulcerative colitis 4- Celiac disease |
|
|
Superior mesenteric lymph nodes |
1- Lower duodenum, jejunim, ilium and colon to splenic flexure 2- Disease 1- Mesenteric lymphadenitis 2- Typhoid fever 3- Ulcerative colitis 4- Celiac disease |
|
|
Inferior mesenteric lymph nodes |
1- Colin splenic flexure to upper rectum 2- Disease 1- Mesenteric lymphadenitis 2- Typhoid fever 3- Ulcerative colitis 4- Celiac disease |
|
|
Para aortic lymph nodes |
1- Testes, ovaries, kidney, uterus (Fallopian tube) 2- Disease 1- Metastasis |
|
|
External iliac lymph nodes |
1- Superior bladder, body of uterus and cervix 2- Disease 1- STI |
|
|
Internal iliac lymph nodes |
1- Lower rectum to anal canal (above pectinate line) bladder, cervix, vagina (mid 1/3) prostate 2- Disease - STI |
|
|
Superficial Inhibin all lymph node |
1- Anal canal, scrotum, vulva, Skin below umbilicus ( except poplitial area) 2- Disease- STI Medial foot/leg cellulitis |
|
|
Popliteal lymph nodes |
1- Dorsolateral aspect of foot, Posterior calf 2- Disease 1- Lateral foot/leg cellulitis |
|
|
Thoracic duct |
Thoracic duct drains below diaphragm the left thorax and upper limb into junction of left subclavian vein and internal jugular vein |
|
|
Right lymphatic duct |
1- Drain the right side of the body above the diaphragm into junction of right subclavian vein and internal jugular vein |
|
|
What chest condition can occur as a result of thoracic duct rupture |
Chylothorax |
|
|
What lymph node is likely to be enlarged in association with a malignancy in the abdomen or pelvis |
Supraclavicular lymph node ( virchow node) |
|
|
Which superficial lymph node is likely to be enlarged in a patient with gastric cancer |
Periumbilical (sister Mary Joseph node) Left supraclavicular node (virchow node) |
|
|
Which disease is indicated by epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (draining hand and forearm) |
Secondary syphilis |
|
|
Which lymph node cluster is associated with a malignancy of the oral cavity |
Submandibular lymph nodes |
|
|
Spleen |
1- Located in LUQ, anterooateroial to left kidney protected by 9th-11th ribs 2- Sinusoids have long vascular channels in red pulp with fenestrated barrel hoop basement membranes 3- T cells are located in the periarteriolar lymphatic sheat (PALS) within the white pulp 4- B cells are located in the follicle of the white pulp 5- The marginal zone contains macrophages, specialized B cells and antigen presenting cells (APC) that capture blood born antigens for recognition by lymphatics 6- Splenic macrophages remove encapsulated organism 7- Splenic dysfunction (post splenectomy, HBSS autosplenectomy) decrease IgM- decrease complement activation - decrease C3b opsonisation- increase susceptibility to encapsulate organisms 8- Post splenectomy findings 1- Howell jolly bodies (nuclear remnant) 2- Target cells 3- Thrombocytosis (losss of sequestering) 4- Leukocytosis |
|
|
Encapsulated organisms |
1- Yersinia pestles 2- Strep pneumonia (and Group B) 3- Neisseria menigitides 4- Klebsiella pneumoniae 5- Haemophilus influenza type B 6- Salmonella typhi 7- Cryptoccocus neoformans 8- Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
Type of vaccine for patients with splenectomy |
Streptococcus pneumonia Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenza B |
|
|
Post splenectomy blood finding |
1- Howell jolly body (nuclear remnant) 2- Target cells 3- Thrombocytosis (loss of sequestering) 4- Leuckocytosis |
|
|
Thymus |
1- Located in anteriosuperior mediastinum 2- Location of T cell differentiation and maturation 3- Encapsulated thymus epithelium is derived from the thirds pharyngeal pouch (endoderm) whit the thymus lymphocytes are mesodermal origin 4- Medulla is pale with mature T cells and hassle corpuscles containing epithelial reticular cells 5- Neonate thymus sail shaped on CXR involuted by age 3 6- Cortex is dense with immature T cells 7- Thymoma - neoplasm of the thymus Associated with myasthenia graves, superior vena cava syndrome, pure red cell aplasia and good syndrome |
|
|
Thymoma |
1- Neoplasm of the thymus 2- Associated with myasthenia graves, superior vena cava syndrome, pure red cell aplasi and good syndrome |
|
|
What 2 immunodeficiency syndrome are commonly associated with a hypoplastic thymus or absent thymus shadow |
DiGeorge syndrome Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) |
|
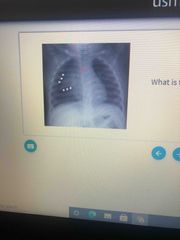
Diagnosis |
Sail shaped Neonate thymus |
|
|
What structure surrounds the thymus |
Capsule (It’s encapsulated) |

