![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where are the lymph nodes located?
|
Neck, armpit, stomach, inguinal region, knee.
(Those are the main ones, but they're actually all over the body) |
|
|
What are the names of the lymph nodes?
|
Occipital (behind ear), submandibular (under mandible), cervical (neck) , axillary (armpit), intestinal, Iliac, inguinal (pubic), popliteal (knee)
|
|
|
How does air flow through the respiratory system?
|
1. Air flows in through the nose
2. Goes through nasal cavity and is warmed/moisturize/cleaned in the nasal concha (nasal turbinates), also the air is slowed down and reduced in pressure 3. Goes into pharynx (aka throat) 4. Pharynx opens into glottis 5. Epiglottis opens and enters into larynx (voicebox) 6. Air travels through larynx into the trachea (hyaline cartilage keeps airway opened) 7. Airway branches off into right and left bronchi and into the lungs where the air goes into the bronchioles 8. From the bronchioles the air goes into alveoli (covered with capillaries) and air oxygenated blood and goes through gas exchange (O2 exchanges with CO2) |
|
|
Type of epithelium from nose to bronchi?
|
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated (aka "respiratory epithelium")
- cilia move upwards, sweeping mucus up towards the throat, where it is swallowed. |
|
|
Type of epithelium in bronchioles?
|
Cuboidal, but still ciliated.
|
|
|
Goblet cells are responsible for what?
|
Production of mucus.
|
|
|
What type of tissue are the bronchi and bronchioles composed of?
|
Elastic tissue.
|
|
|
* Type of epithelium at alveolar sac.
|
Simple squamous.
Allows for higher diffusion rate. |
|
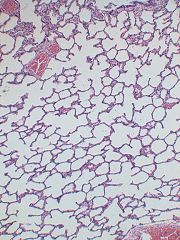
|
Alveolar sac.
|
|
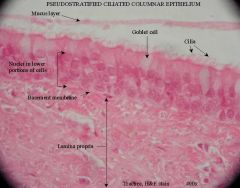
|
Trachea.
|
|
|
What type of cartilage does the trachea have?
|
C-rings have hyaline cartilage.
- allows expansion of esophagus - expands and contracts |
|
|
How many lobes does each lung have?
|
Right - 3
Left - 2 (has to compensate for the size of the heart) |

