![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Blood components |
1. Blood plasma # it is the liquid medium #makes up 55% of blood 2. Formed elements A. RBCs (erythrocytes) B. WBCs (leukocytes) i. Granulocytes - neutrophils - eosinophils - basophils ii. Agranulocytes - t and b lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells كلهم ليمفوسايتس - monocytes C. Platelets |
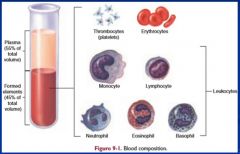
|
|
|
Neutrophils function |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
|
Eosinophils function |
Allergy, animal parasites |
|
|
|
Basophils function |
Inflammation mediator, anticoagulant properties |
|
|
|
B cells function |
Humoral immunity |
|
|
|
T cells function |
Cellular immunity |
|
|
|
What is a lymph |
Clear fluid, present in tissue spaces, that circulats in lymph vessels |
|
|
|
Lymph vessels are |
Small tubes that carry the lymph fluid throughout the body |
|
|
|
Lymph nodes are |
Stationary collections of lymph tissue throughout the body |
|
|
|
The thymus is |
A gland present in the mediastinum, produces lymphocytes, which plays an important role in immunity |
|
|
|
The spleen is |
Blood-forming organ in early life, later a storage organ for red blood cells and a source of lymphocytes |
|
|
|
Tonsils are |
Masses of lymphatic tissue that is found in the pharynx |
|
|
|
Thym/o |
Thymus gland |
|
|
|
Splen/o |
Spleen |
|
|
|
Lymphangi/o |
Lymph vessels |
|
|
|
Lymphaden/o |
Lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Lymph/o |
Lymph fluids |
|
|
|
Functional relationship between blood, lymph, immune system, and other systems of the body |
1. Provides a medium for transport and exchange of productsthroughout the body 2. Protect and repair cells damaged by disease or trauma |
|
|
|
Pathological conditions related to the lymphatic system include |
1. Aquired immune deficiency syndrom (AIDS) 2. Lymphoma 3. Mononuceosis 4. Sarcoidosis |
|
|
|
Aquired immune deficiency syndrome |
Supperession or deficiency of the immune response (destruction of lymphocytes) caused by exposure to human immune deficiency virus (HIV) |
|
|
|
Lymphoma |
Malignant tumor of lymph nodes and lymphatic tissue for example hodgkin disease |
|
|
|
Mononucleosis |
Acute infectious disease with enlargement of lymph nodes and increase in lymphocytes and monocytes |
|
|
|
Sarcoidosis |
Inflammatory disease in which small nodules or tubercles form in lymph nodes and other organs N.B: Sarc/o means flesh -oid means resembling |
|
|
|
Diagnostic procedures include |
1. Computed tomography (CT) scan 2. Laboratory tests A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbentassay (ELISA) B. Western blot test |
|
|
|
CT scan |
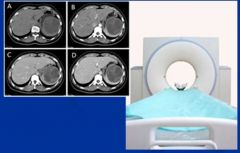
X-ray image in a cross-sectional plane for diagnosis of lymph node abnormalities |
|
|
|
ELISA |
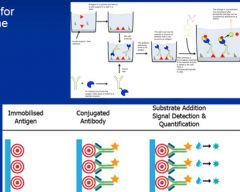
Screening test for antibodies to the AIDS virus |
|
|
|
Western blot test |
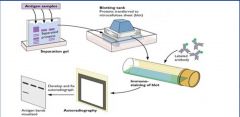
Precise blood test to detect antibodies to specific antigens, as in hive infection |
|
|
|
Treatment procedures include |
1. Chemotherapy 2. Radiotherapy |
|
|
|
Chemotherapy |
Treatment with powerful drugs to kill cancer cells |
|
|
|
Radiotherapy |
Treatment with high-dose radiation to destroy malignant tissue |
|

