![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is Lymphatic system? |
system of vessels, cells, and organs that carry excess fluids to bloodstream & filter pathogens |
|
|
Describe Immune system? |
complex collection of cells & organs that destroy or neutralizes pathogens |
|
|
what is the main function of Lymphatic system? |
drains body fluids & returns them to bloodstream |
|
|
If lymphatic system doesnt reurn fluid leaked from blood capillaries into subclavian veins what will happen? |
blood volume and pressure will be very low |
|
|
what moves fluid? |
Lymphatic capillaries |
|
|
what does Lymph mean? |
term used to describe intersttual fluid once its entered lympatic system |
|
|
How does lymphatic system attack and eliminate pathogens? |
done by different leukocytes(mainly live in lymphatic system, but can move throughout blood/tissues during infection, but most cant enter brain) |
|
|
what are pathogens? |
something that causes disease |
|
|
what are the different types of pathogens? |
1-Bacteria=major extracellular pathogen 2-Viruse=main intracellular pathogen 3-some protits, fungi, parasites= also can be pathogens |
|
|
what is the Lymphatic structure? |
Begin as open capillaries, which feed into larger and larger lymphatic vessels & eventually empty into bloodstream |
|
|
Describe lymph flow? |
lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels & then dumped into circulatory system via lymphatic ducts |
|
|
what type of fluid is inside lymphatic capillaries and duts? |
Lymph (similar to blood plasma) -contains H2O, ions & leukocytes -lacteals= specialized lymph vessel near intestine that carries fat "lact" |
|
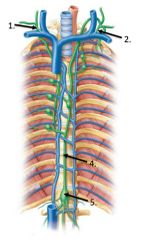
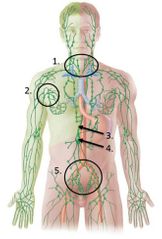
lable #1 |
right lymphatic duct |
|
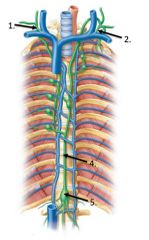
lable #2 |
Thoracic duct |
|
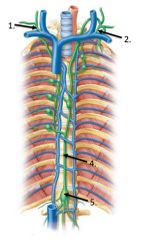
lable #4 |
Thoracic duct |
|
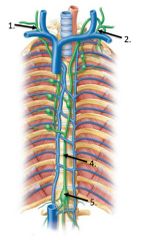
Lable #5 |
Cisterna chyli |
|
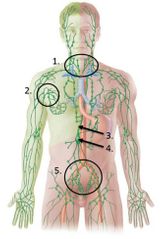
lable #5 |
Inguinal lymph nodes |
|
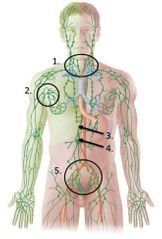
lable #3 |
Thoracic duct |
|
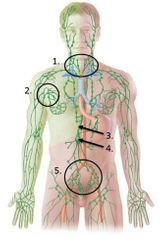
lable #2 |
Axillary lymph nodes |
|
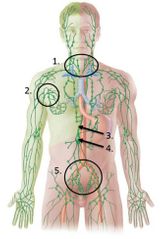
lable #4 |
Cisterna chyli |
|
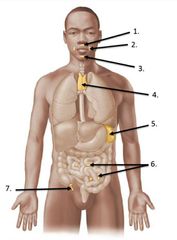
lable #1 |
Cervical lymph nodes |
|
lable #1 |
pharyngeal tonsil |
|
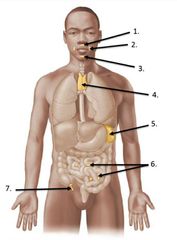
lable #3 |
Lingual tonsil |
|
lable #2 |
Palatine tonsil |
|
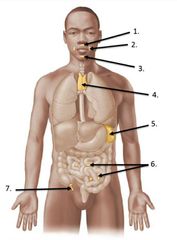
lable #5 |
Spleen |
|
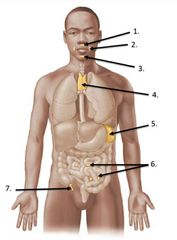
lable #4 |
Thymus |
|
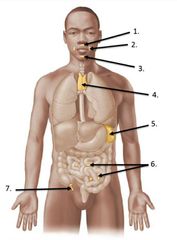
lable #6 |
Peyer's patches |
|
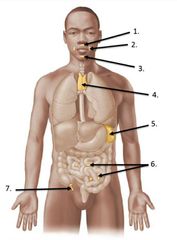
lable #7 |
Appendix |
|
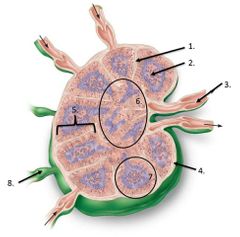
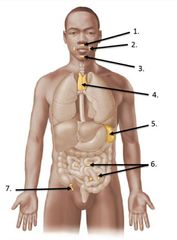
lable #3 |
Efferent vessel |
|
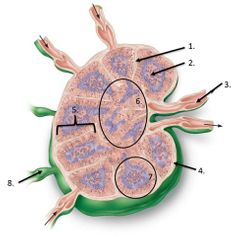
lable #8 |
Afferent vessel |
|
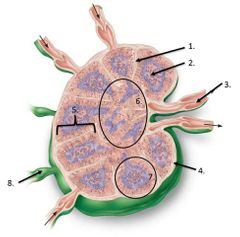
lalbe #1 |
Trabeculae |
|
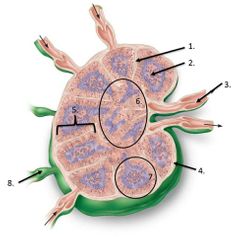
lable #2 |
Germinal center |
|
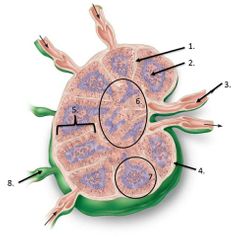
lalbe #6 |
Medulla |
|
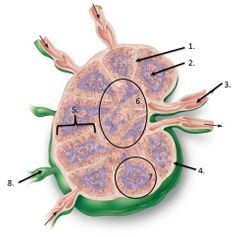
Lalbe #7 |
Follicle |
|
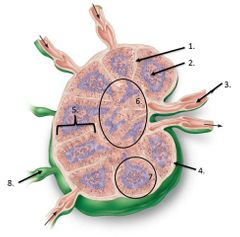
lable #5 |
cortex |
|
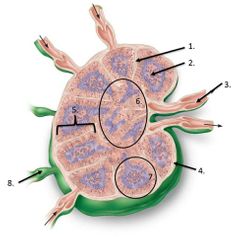
lable #4 |
Capsule |
|
|
which of these is part of second line of defense? -stomach acid -normal microbiota -phagocytosis -antibodies |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
What things are lymphatic nodules |
-appendix -peyer's patches -tonsils |
|
|
what causes heat during inflammatory process? |
increased premeability of blood vessels in affected area |
|
|
which defenses would be most effective against intracellular pathogens such as viruses? |
-Interferon -NK cells |
|
|
Primary lymphatic organs are places where? |
T & B cells receive their receptors -doesnt actually fight infections(thymus & bone marrow) |
|
|
Describe Dendritic cell |
Professional antigen presenting cell |
|
|
Decribe Cytotoxic T cell |
Has a receptor that attaches to MHC class 1 |
|
|
what type of cell can be infected by HIV? |
Helper T cell |
|
|
what cell proliferates in germinal centers? |
B cell |
|
|
which areas ultimately drain lymph into thoracic duct? |
-lower right/left body quadrant -upper left body quadrant |
|
|
which is NOT normally found in lymph? |
erythrocytes |
|
|
white blood cells that squeeze out of capillary walls is known as? |
Diapedesis |
|
|
what is an example of Artificially acquired active immunity? |
child gets a vaccine containing weakned or dead chickenpox antigens |
|
|
what is an example of Artifically acquired passive immunity? |
child receives injections of antibodies to chicken pox |
|
|
what is an example of Naturally acquired active immunity? |
child gets chicken pox. Now they are immune from getting it again |
|
|
what is an example of Naturally aquired passive immunity? |
breastfeeding baby gets antibodies to chicken pox from mothes milk |
|
|
what is not actively pumped by the heart? |
lymph= forced through vessels by movement of body |
|
|
what called terminal lymphatics |
lymphatic capillaries |
|
|
what are lymphatic capillaries? |
vessels where interstitual fluid enters lymphatic system to become lymph fluid |
|
|
what do capillaries have that dont connect to other tubes? |
blind ends |
|
|
what helps capillries ends connect to nearby cells? |
flap- like mini valves - swelling causes cells to spread apart pullig mini-valves open & allowing extra fluid to enter lymphatic capillaries |
|
|
why are there more afferent vessels in lymph nodes then efferent? |
forces fluid to move slowly, providing time for leukocytes in lymph nodes to detect any pathogens |
|
|
where are large clusters of lymph nodes found? |
-cervical, axillary & inguinal regions |
|
|
where doe sfluid from upper right side of body go? |
through right lymphatic duct into right subclavian vein |
|
|
where are B and T cells developed? |
bone marroe |
|
|
when T cells get to thymus from bone marrow what do they mature into? |
immunocompletent (active during childhood) -doesnt secrete antibody performs tests |
|
|
where do B cell become immunocompetent? |
stay in bone marroe, there immune cells that function primarily by producing anibodies |
|
|
what is plasma cell?t |
type of lymphocyte; B cell that has differentiated in response to antigen binding & gained ability to secrete soluble antibodies |
|
|
what are secondary lymphoid organs ? |
-spleen and lymph nodes (have capsules) |
|
|
what does spleen do? |
helps filter & remove dying RBCs & contains many WBCs to fight infection (especially blood born pathogen) |
|
|
what do lymph nodes do? |
-contain B & T cells & macrophages to detect/ fight pathogens -macrophages & dendritic cells internalize & kill many of pathogens that pass through |
|
|
what do lymphoid noduels not have around them? |
capsule -mostly reticular connective tissue which is delicate netlike, soft, easly for blood to flow |
|
|
what do leukocytes do in lymphoid nodules ? |
recognize what is normal vs. what is harmful |
|
|
what is 1st line of defense? |
surface barriers -prevent pathogens from entering body (skin & mucous membrane=nasal cavity, intestines) -Normarl microbiota are major part(leads to secondary infection sometimes) |
|
|
what is second line of defense? |
Innate defense -nonspecific, can function against multiple types of pathogens -quick to activate as soon as pathogens makes it past surface berriers -does phagocytosis |
|
|
what is Interferon? |
type of antriviral protein(switches on genes to make interferon proteins when cells infected) - exocytosed, attaches to receptorson neighboring cells (makes defenses against viruses) |
|
|
what do NK cells look for in Lymphatic system? |
body cells that have something wrong with them(usually abnormal surface proteins indicating mutations or viral infection) |
|
|
when NK cells find a cell with abnormal surface protein what does it do? |
use perforin proteins to punch holes in abnormal cell's membrane & shoot Granzymes(digestive enzyme) -cell begins to digest from inside out; causing to switch on apoptosis gene (cell suicide) and breaks up into tiny vesicles & dies |
|
|
what is lymph nodules important role in? |
developing immunit in childhood (by the age of 4) |
|
|
Describe cellular eating phagocytosis? |
-cell folds its membrane around pathogen to trap it in vesicle -lysosome full of digestive enzyme fases with vesicle to break-up pathogen -waste products can exocytose to leave cell |
|
|
Describe Neutrophils of phagocytosis? |
specialize to phagocytose bacteria, but dies quickly |
|
|
Describe Monocytes of phagocytosis? |
can differentiate into macrophages or dentritic cells after they leave blood vessels |
|
|
what do Macrophages generaly phagocytose? |
bacteria, viruses that havent entered cells and dead cells |
|
|
what do Dentritic cells phagocytose? |
pathogens & then display pieces of pathogens of surface; then trvel to lymph nodes to show T & B cells= antigen presenting |
|
|
whats the fist step in Inflammatory response once injured? |
Injured cells release signaling molecules called= cytokines - which attract leukocytes & cause nearby blood vessels to dilate & become more leaky |
|
|
what is the 2nd step of the Inflammatory response? |
Leukocytosis=leukocytes (mainly neutrophils & macrophages) move into bloodstream from bone marrow |
|
|
what is the 3rd step of Inflammatory response? |
Margination= when they get near injury site, leukocytes stickto walls of blood vessels |
|
|
what is the 4th step of Inflamatory response? |
Diapedesis=leukocyte squeeze through walls of blood vessels |
|
|
what is the 5th step of Inflammatory response? |
chemotaxis=leukocytes follow trail of cytokines until they reach site of injury - there they phagocytose any pathogen entered -pus forms when to many Neutrophils die (macrophage cleans up) |
|
|
what does redness, heat, swelling and pain mean during Inflammatory response? |
redness=increased blood flow heat= blood is warm swelling=fluid leaking out of dilated blood vessels pain=leaked fluid increases pressure on nonceptors in area |
|
|
what is the complement system? |
group of antibacterial proteiens that are normally inactive in blood |
|
|
what are the 2 ways to activate complement system? |
1-classical pathway=in adaptive immune(antibodies attaches to antigens causes activate) 2-Alternative pathway=in innate immune(presence of some kind of bacterial molecuels causes activation) |
|
|
what happens once complement system is activated? |
1- Enhances inflammation 2-Opsonization (bacteria is coated causing to stick to receptors on macrophages) 3-Membrane attack complex (MAC) = giant hole in bacteria is made and it bursts |
|
|
what is 3rd line of Defense? |
Adaptive Immune system -main players are B cells and T helper (CD4) and cytotoxic T cell (CD8) -takes over a week to complete (very effective) -has memmory (by activating B and T cells) |
|
|
what is B cells main role in 3rd line of defense? |
humoral immunity=makes antibodies that attack extracellular pathogens (bacteria) |
|
|
what is the main role of cytotoxic T cells in 3rd line of defense? |
cellular immunity= kills body cells that are infected with intracellular pathogens (viruses) |
|
|
what is the main role of Helper T cell (CD4) in 3rd line of defense? |
release cytokines to activate other cells & parts of immune response |
|
|
what is it called when immune systems first exposed to a pathogen? |
primary adaptive response |
|
|
Describe primary adaptive response? |
first infection always severe b.c it takes time for initial adaptive immune response to pathogen become effective |
|
|
what is Secondary adaptive response ? |
-re-exposure, stronger and faster acting -eliminates pathogens before it can cause significant tissue damage |
|
|
what does Immunological memory do? |
protects body from getting diseases reppeateadly from same pathogen |
|
|
what mechanism cleaves antigen into smaller pieces? |
antigen processing |
|
|
what is MHC |
molecule on outside of cells that can hold antigens, T cell receptors can only recognize antigens if they're displayed on MHC -2 types |
|
|
what is MHC class 1 |
-found on all body cells with nuclie -holds antigens that originated inside cells -cytotoxic T cells attach to this |
|
|
what is MHCclass 2 |
-only found on antigen presenting cells (APCs) -holds antigens that originated outside of cells & got phagocytosed -hepter T cells attach to this |
|
|
what does Negative selection test for? |
make sure T cells receptor doesnt attach to your self-antigen |
|
|
What does red pulp do? |
Helps spleen in filtering/getting rid of old and damaged RBCs |
|
|
Is maintainign blood pH a function of lymphatic? |
no |
|
|
what needs to happen in order to activate cytotoxic T cell(CD8)? |
-attaches to costimulatory molecules at the same time if finds antigen -attaches to specific antigen displayed on another cells MHC1 |
|
|
what type of pathogen is Complement system? |
Extracellular pathogen |
|
|
what type of pathogen is Cytotoxic T cells? |
Intracellular pathogen |
|
|
what type of pathogen is B cells? |
Extracellular pathogen |
|
|
what type of pathogen is phagocytes? |
Extracellular pathogen |
|
|
what kind of pathogen is NK cells? |
Intracellular pathogens |
|
|
what kind of pathogens are Interferons? |
Intracellular pathogens |
|
|
Adaptive immune system? |
-is systemic -includes B & T cells |
|
|
when a patient is unable to opsonizate what is less effective in patients body? |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
what happens when lymph doesnt return and stays in one area? |
swelling occurs and BP lowers |

