![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adenoids |
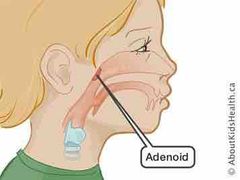
Mass of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx antibody |
|
|
Antibody |
Proteins produced by B cells to destroy antigens |
|
|
Antigen |
Substance that the body recognizes as foreign; evokes an immune response. most antigens are proteins or protein fragments found on the surface of bacteria, viruses, or organ transplant tissue cells |
|
|
Adaptive immunity |
The ability to recognize and remember specific antigens and mount and attack on them. Humoral (B cells) and cell-mediated immunity (T cells) are examples |
|
|
Axillary nodes |
Lymph nodes in the armpit |
|
|
B cells (B lymphocyte) |
Lymphocytes the matures into a plasma cell to secrete antibodies. The B refers to the bursa of Fabricius, an organ in birds in which B cells differentiate and growth were first noted to occur |
|
|
Cell mediated immunity |
T cells cytotoxic )helper and suppressor) respond to antigens and destroy them; a type of adaptive immunity |
|
|
Cervical nodes |
Lymph nodes in the neck region |
|
|
Complete system |
Set of proteins in the blood that help antibodies kill their target |
|
|
Cytokines |
Proteins secreted by cytotoxic T cells to aid an antigen destruction examples are interferons and interleukins |
|
|
Cytotoxic T cells |
Lymphocyte that directly kills antigens called (CD8+) T cell |
|
|
Dendritic cell |
Antigen-presenting cell. shows T and B cells and what to attack |
|
|
Helper T cell |
Lymphocyte the aids B cells and stimulates T cells. also called (CD4+) T cell |
|
|
Humoral immunity |
B cells produce antibodies after exposure to specific antigen; type of adaptive immunity |
|
|
Immunity |
Body’s ability to resist forien organisms and toxins that damage tissue and organs this includes natural immunity and adaptive immunity |
|
|
Immunoglobin’s |
Antibodies such as IgA, IgE, IgC, IgM, and IgD; Secreted by plasma cells (mature B cells) in response to the presence of an antigen |
|
|
Cytotoxic T cells |
Lymphocyte that directly killed antigens called; (CD8+) T cell |
|
|
Acquired immunity |
Cell (specialized macrophage) that digests foreign cells and helps B and T cells recognize and mark antígena for destruction. |
|
|
Lymph |
Thin, watery fluid found within lymphatic vessels |
|
|
Lymph capillaries |
Tiniest lymphatic vessels |
|
|
Interferons and interleukins |
Proteins (cytokines) secreted by T cells to aid and regulate the immune response |
|
|
Immunoglobin |
Antibodies that are secreted by plasma cells in response to the presence of an antigen |
|
|
Immunitu |
Bodies ability to resist foreign organisms and toxins (immune response) |
|
|
Inguinal nodes |
Lymph nodes in the groin |
|
|
Lymphoid organ |
Lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus gland |
|
|
Immunotherapy |
Use of immune cells and antibodies or vaccines to treat and prevent disease |
|
|
Interstitial fluid |
Fluid in the space between the cells |
|
|
Lymph node |
Stationary, solid lymphatic tissue along lymph vessels |
|
|
Mesenteric nodes |
Lymph nodes in the intestinal region |
|
|
Paraaortic nodes |
Lymph nodes associated with a major artery |
|
|
Thoracic duct |
Large lymphatic vessel in the chest that receives lymph from below the diaphragm and from the left side of the body above the diaphragm |
|
|
Thymus gland |
Organ in the mediastinum that conditions T lymphocytes to react to foreign cells |
|
|
Tonsils |
Mass of lymphatic tissue in the back of the oropharynx |
|
|
Toxin |
A poison |
|
|
Vaccination |
Exposure of an individual to a foreign protein (antigen) that provokes an immune response |
|
|
Vaccine |
Weakened or killed microorganisms, toxins, or other proteins (antigens) given to provoke an immune response |

