![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If the thyroid gland is enlarged bilaterally, what maneuver is appropriate?
|
listen for bruits over the thyroid lobes
|
|
|
It is normal to palpate a few lymph nodes in the neck of a healthy person. What are the characteristics of these nodes?
|
mobile, soft, and tender
|
|
|
The isthmus of the thyroid gland lies just below the:
|
cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
Normal cervical lymph nodes are:
|
smaller than 1 cm
|
|
|
Preauricular lymph nodes are located:
|
in front of the ear
|
|
|
Posterior auricular lymph nodes are located:
|
superficial to the mastoid process
|
|
|
Occipital lymph nodes are located:
|
at the base of the skull
|
|
|
Submental lymph nodes are located:
|
behind the tip of the mandible
|
|
|
Jugulodigastric lymph nodes are located:
|
under the angle of the mandilbe
|
|
|
Superficial cervical lymph nodes are located:
|
overlying the sternomastoid muscle
|
|
|
Deep cervical lymph nodes are located:
|
deep under the the sternomastoid muscle
|
|
|
Posterior cervical lymph nodes are located:
|
in the posterior triangle along the edge of the trapezius muscle
|
|
|
Supraclavicular lymph nodes are located:
|
above and behind the clavicle
|
|
|
hyperthyroidism
|
Most common sign-Tachycardia
symptoms of diarrhea, anxiety, fever, fatigue, weight loss, palpitations, rapid pulse, heat intolerance, fine, limp hair, diaphoresis, muscle weakness Grave's disease (goiter, bulging eyes) |
|
|
hypothyroidism
|
symptoms of fatigue, anorexia, cold intolerance, dry skin, brittle, coarse hair, menstrual irregularities, weight gain or difficulty losing weight, decreased libido
|
|
|
if lymphnodes are palpable describe the following
|
size, consistency, mobility, delimitation
|
|
|
require emergency investigation if
|
lymphatics larger than 1 cm, fixed, irregular, or hard or rubbery
hyperthyroidism with symptoms of hypermetabolosm in all systems |
|
|
malignant lumph nodes
|
non-tender, hard, fixed
|
|
|
lymphadenopathy
|
palpable nodes in 3 or more chain
|
|
|
indicator of thyroid problems
|
fatigue, weight problems, skin problems, difficulty sleeping, difficult temp regulations
|
|
|
if thyroid is englarged...
|
ascultate over each lobe for a bruit using the bell
|
|
|
normal lyphnode
|
non-palpable, "shotty" small <1 cm, mobile, non-tender
|
|
|
test of thyroid function
|
performed on patients of any age presenting signs or symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, usually TSh, T3, T4 are measured
|
|
|
Which direction do the head/neck lymph nodes drain
|
mostly in a generally inferior direction
|
|
|
What is the thyroid gland?
where is the thyroid gland? |
an endocrine gland that secretes hormones (T3 and T4) that control rates of metabolism.
straddles trachea in middle of neck |
|
|
If a lymph node is swollen what area should you explore?
|
area proximal (upstream) to that lymph node(s)
|
|
|
purpose of the lymph nodes
|
filter lymph and engulf pathogens, preventing harmful substances from entering circulation
|
|
|
signs that a lymph node is cancerous
|
unilateral, hard, , >3cm, nontender, matted and fixed
|
|
|
in chronic inflammation, lymph nodes are usually _______
|
clumped
|
|
|
Which lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in HIV?
|
occipital
|
|
|
Nodes are located throughout the body but only accessible for examination in what four areas?
|
head and neck
arms axillae groin |
|
|
where is the greatest supply of lymph nodes?
|
head and neck
|
|
|
Describe location of majority of the head/neck lymph nodes
|
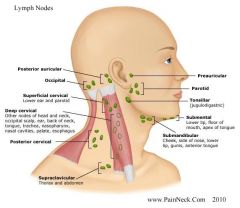
|
|
|
Pattern when examining lymph nodes
|
preauricular
posterior auricular occipital submental submandibulal tonsilar anterior cervical chain posterior cervial chain supraclavivular Use pads of 2nd, 3rd, 4th finger, gently palpate in circles |
|
|
Thyroid Hormone Levels
|

TSH, T3, T4
|

