![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a budget? |
A plan that is agreed in a advance |
|
|
What is the difference between a budget and a forecast? |
A prediction of what might happen whereas the budget is the planned outcome the firm hopes to achieve. |
|
|
What does the budget show? |
The money needed for spending and how it might be financed |
|
|
What is a budget based on? |
Business objectives |
|
|
What is a budget used to focus? |
Managers on planning ahead and improving co-ordination |
|
|
How long are most budgets set for? |
12 months |
|
|
What are the specific purposes of budgeting? |
Control and monitoring Planning Co-ordination Communication Effciency Motivation |
|
|
What is control and monitoring? |
- budgeting allows management to control the business. - it does this by setting objectives and targets - then theyre translated into budgets for a particular period - to find success compare budgets with actual results. - then any failure can be analysed and saved |
|
|
What is planning? |
- budgeting forces management to think ahead - budgeting plans for the future - it anticipates problems and their solutions. |
|
|
What is co-ordination? |
Budgeting is one way in which managers can co-ordinate and control activities of the many areas of business |
|
|
What is communication? |
- Planning allows the objectives of the business to be communicated to the workforce - managers (workers have a clear framework to operate with). - removes element of uncertainty - prioritys of business/costs are highlighted. |
|
|
What is effciency? |
Budgeting gives financial control to lower levels of management who are best able to make decisions at their point within the organisation. |
|
|
What is motivation? |
Provides targets and standards. Fear of failure to reach targets can be an incentive to the workforce. |
|
|
What are the two types of budgets? |
Sales budget The production cost budget |
|
|
What does it mean when budgets are prepared using historical figures? |
That the data used to prepare the budgets is based on data that the business has gathered in the past. Adjustments will have been made known for events in the future. |
|
|
What are some examples of budgets that use historical figures? |
- sales volume - sales revenue - production costs - overheads - total cost - marketing - R&D - profit - cash - master |
|
|
Describe sales volume budget? |
A key budget- shows planned sales levels |
|
|
Describe sales revenue budgets. |
Uses sales volume and prices to show planned revenue. |
|
|
Describe production cost budget. |
Based on sales volume and shows all planned production costs. |
|
|
Describe overhead budgeting. |
Shows all planned indirect costs such as insurance, rent and office wages. |
|
|
Describe total cost budgeting. |
Shows all planned business costs. |
|
|
Describe marketing budgeting |
Shows planned spending on, for example research, advetising, promotion and sales |
|
|
Describe R&D budgeting. |
Shows planned expenditure in research and development |
|
|
Describe profit budgeting. |
Shows planned revenue, costs and profit |
|
|
Describe cash budgeting. |
Shows planned cash inflows and outflows and cash balances |
|
|
Describe master budgets. |
Shows a summary of all budgets- including cost, revenue and profit |
|
|
What is zero based budgets (ZBB)? |
- usually budgets are based on historical data. - ZBB is when in some areas of the business its not easy to quantify costs. When costs cannot be justified no budget is allocated to them (ZBB) |
|
|
What would the manager do in the instance of ZBB? |
They must show that a particular item of spending will in the future generate an adequate amount of benefit to allow it to be allocated a budget. The concept of opportunity cost is used in this instance, so a business tries to minimise the opportunity cost and gets the best value for money for these types of activities. |
|
|
What are the advantages of ZBB? |
- the allocation of resources should be improved - a questioning attitude is developed which will help to reduce unneccesary costs and eliminate insuffcient practices. - staff motivation might improve because evaluation skills are practised and a greater knowledge of firms operations might develop. - it encourages manager to look for alternatives |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of ZBB? |
- time consuming as budegting involves collection and analysis so decisions can be made - skillful decision making is required and decisions could be subjective to opinion - threatens status quo and could affect motivation. - managers may not be perpared to justify spending on certain costs so may not be allocated effciently. |
|
|
What is budgetry control used for? |
To look into the future |
|
|
What are the stages in budgetry control? |
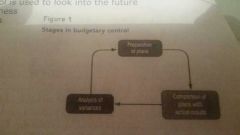
|
|
|
What is preparation of plan? |
All businesses have business objectives. Targets are usually set to see if they will meet these objectives. |
|
|
What is comparison of plans with actual results? |
- the financial period is diveded into quarters. - Each quarter will have a budget assigned to it. - at the end of a quarter a comparison is made of actual against the target set in the budget or control. - this determines the variance ( the difference between the actual and the budget) |
|
|
What is analysis of vairances? |
- The most important stage of the process. - this involves finding the reasons for the difference between the budget and the actual. - it can be the results of internal or external factors. - in future amendments to the budget will need to accomodate the reason for the variance |
|
|
What is a variance? |
- Is the difference between the figure that the business has budgeted for and actual. - usually calculated at the end of the budgetary period when the actual figure is known. |
|
|
What is formula for for variance? |
Actual - budget |
|
|
What can variances be? |
Favourable Adverse |
|
|
What is favourable variances? |
When the actual figures were better than budget . |
|
|
What is adverse variances? |
When the actual figures were worse than the budget. |
|
|
What is favourable income? |
When the monthly sales revenue actually made is higher than the budgeted sales revenue. |
|
|
What is favourable expenditures? |
When the monthly costs budgeted are lower than the actual costs |
|
|
What is adverse income? |
When the amount of sales revenue budgeted is less than the actual sales revenue made. |
|
|
What is adverse expenditure? |
When costs monthly budgeted for is lower than the actual costs. |
|
|
For wages, overheads and raw materials which should be bigger budget or cost? |
Budget |
|
|
For sales volume and labour hours, which should be bigger budget or actual? |
Actual |
|
|
For profit which should be bigger budget or actual? |
Actual |
|
|
What are the reasons for changes income variances? |
- the ability to charge higher prices - an increase in demand due to a marketing campaign - improvements in the quality of the products - an increase in consumer incomes - a change in consumers tastes in favour of bamboo and wicker furniture. |
|
|
What are the reasons for changes in expenditure variances? |
- Costs might be higher due to production being higher - suppliers may have raised prices - there may be some ineffciencies in production - wages may have been higher due to wages demands by workers. |

