![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is local anesthesia |
Technique used to render part of the body insensitive to pain without loss of consciousness as different from general anaesthesia where it causes loss of consciousness
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Local_anesthetics_general_structure.svg |
|
|
|
Modes of application of LA |
Topical, injection and infusion. It has a reversible effect |
|
|
|
Discovery of LA |
Albert Niemann isolated crystals from the cocoa shrub in 1860 that reversably numbed his tongue. He called it cocaine. |
|
|
|
First use in surgery |
Koller in 1884 used cocaine for eye surgery |
|
|
|
First synthetic LA |
1905 Alfred Einhorn produced the first Ester type LA Procaine |
|
|
|
First amide LA |
1943 Lidocaine by Nils Lofgren |
|
|
|
LA structure components |
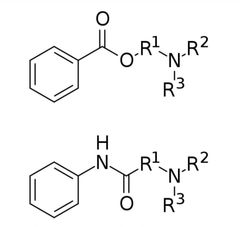
1.Aromatic ring ( usually substituted) , 2.a connecting group ( Esther - procaine or amide - lidocaine) 3.Ionisable amino group
|

|
|
|
2 important chemical properties of LA that determine activity |
Lipid solubility, ionisation constant |
|
|
|
Importance of lipid solubility in LA |
Determines potency, plasma protein binding and duration of action . More lipid soluble , more is potency , plasma binding and duration of action |
|
|
|
Importance of pK in LA |
Lower the pK , faster onset of action |
|
|
|
Why are sensory nerves more susceptible to LA than motor nerves? |
Because they are non myelinated |
|
|
|
Why are smaller nerves more susceptible to LA than larger nerves? |
Nerve conduction is through nodes of ranvier. At least 3 succeeding nodes need to be blocked to completely stop nerve conduction. In smaller nerves , the distance between nodes is shorter , hence less distance needed to be blocked compared to larger nerves |
|
|
|
Why are pain fibres more susceptible to LA |
Increased level of stimulation shows increased levels of LA blockade. As nerves transmitting pain have high rates of firing , they are blocked faster . |
|
|
|
Why are some types of nerves more susceptible to LA ? |
The longer the action potential, the more susceptible is the nerve fibre to LA . So cardiac muscle fibres are highly susceptible to LA coz of their long action potential |
|
|
|
Actions of LA on smooth muscle |
vasodilation , increased toxicity, hypotension |
|
|
|
What happens to action on smooth muscle by addition of vasoconstrictor to LA |
Vasoconstriction conteracts vasodilation of LA. Reduced toxicity. Decreased bleeding from surgical manipulation. |
|
|
|
vasoconstrictor used in LA |
Adrenaline at the concentration of one is to 200,000 ( means 1gm per 200,000 ml ) |
|
|
|
Effects of LA on heart |
Reduce myocardial excitability and pacemaker activity, prolong the refractory period of myocardial tissue. Collectively called the antiarrhythmic effects of LA on the heart Myocardial depression and anaesthetic induced vaso dilation can cause toxicity leading to cardiovascular collapse and death |
|
|
|
Effect on duration of action of Vasoconstrictor with LA and without LA |
2% LA Duration of action 10 minutes. 2% LA with adrenaline in 1:200,000 - duration of action 60 minutes |
|
|
|
Action of LA on Cns |
La in toxic doses can cause an initial excitatory phase with convulsions followed by a depression phase that can cause cardiovascular collapse plus death if not managed |
|
|
|
Uses of LA |
1. Block - injected near a nerve to block its distribution area and cause regional anaesthesia. ( for dental and minor surgery) 2. Topical - to skin for analgesia and mucous membranes for diagnosis 3. Spinal - injection into csf for major surgery like abdomen or childbirth 4. Local injection- to produce long lasting analgesia and reduce need for narcotics 5. iv infusion Eg. lidocaine for cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
|
What is ionization constant? |
Its a constant that depends upon the equilibrium between the ions and the molecules that are not ionized in a solution or liquid —symbol K |
|
|
|
What is the theory of ionisation? |
An electrolyte ( acid, base or salt) when dissolved in water breaks up into positive and negative particles called ions |
|
|
|
Importance of the aromatic ring structure in LA properties |
The aromatic ring, improves lipid solubility of the compound. Substitutions at the R site enhances lipid solubility. Greater lipid solubility enhances diffusion through nerve sheaths, as well as the neural membranes of individual axons comprising a nerve trunk. This property correlates with potency because a greater portion of an administered dose can enter neurons. |
|
|
|
Importance of the terminal Amine in aromatic ring |
The terminal amine may exist in a tertiary form (3 bonds) that is lipid soluble or as a quaternary form (4 bonds) that is positively charged and renders the molecule water soluble. It is thus an on off switch for ionization. |
|
|
|
What is the LA ph at storage? |
LA is a weak base. But it is, converted to a weak acid by formulating it as a hydrochloride salt which gives it better stability for storage. The vasoconstrictor also increases its acidity. |
|
|
|
What is the time of onset of LA depending on? |
The LA is a weak base and therefore doesn't penentrate the neuron on injection as it contains more of water soluble quarternary amine. When exposed to physiological pH of 7.4 of the body fluids, the quartenerary structure of the terminal Amine converts to the tertiary lipid soluble structure that can penetrate the neuron. The speed at which this happens is based on the pka constant or ionisation constant of the local anaesthesia. |
|
|
|
How does the inflamed tissue prevent local anaesthesia from diffusing into the neurons? |
Local anaesthesia is a weak base. inflamed tissue is slightly acidic it causes the ionization of local anaesthesia before it can penetrate the neuron. Once ionised, it cannot cross the lipid barrier into the neuron. thus preventing or delaying or reducing local anaesthetic effects |
|
|
|
Due to the acidic nature of inflamed tissues which is the best local anaesthesia that can be effective |
Bupivacaine at pka 8.1 would be the least effective while mepivacaine at pka 7.6 would be the most effective. Lower the pka constant, higher the ratio of tertiary lipid soluble amines at acidic ph, therefore, they cross the lipid barrier faster |
|
|
|
Examples of potency of local anaesthesia |
Bupivacaine has higher lipid solubility and therefore higher potency therefore it is packaged at 0.5% concentration (5mg/ml) than lidocaine at 2% concentration (20mg/ml) |
|
|
|
Order of blocking nerve fibers |
B, C, A delta, A alpha, beta, gamma |
|
|
|
Why is tachyphylaxis seen in epidural anesthesia |
? |
|
|
|
Esther LA causes allergic reactions because of |
Antibody production |
|
|
|
Types of LA |
Amides and esters |
|
|
|
Metabolism difference between amide and ester LA |
Amides are metabolised in the liver. Esters are metabolised by pseudo choline esterase in the blood plasma. |
|
|
|
Examples of amides |
Lidocaine bupivacaine mepivacaine articaine prilocaine |
|
|
|
Examples of esters |
Procaine cocaine tetracaine benzocaine |
|
|
|
Examples of esters |
Procaine cocaine tetracaine benzocaine |
|
|
|
LA safest for children |
Lidocaine |
|
|
|
LA not safe in children |
Bupivacaine |
|
|
|
LA that causes least vaso dilation |
Mepivacaine |
|
|
|
LA metabolised in both liver and blood plasma |
Articaine because it contains one ester chain |
|
|
|
LA that is most likely to cause methemglobinemia |
Prilocaine |
|
|
|
LA that is safest to use without a vasoconstrictor |
Mepivacaine because it causes the least vaso dilation |
|
|
|
Where does the LA act on the neuron for blocking impulse? |
Sodium channel blocker (from inside the neuron) |
|
|
|
Why should we check blood pressure before giving a dosage of local anesthesia |
Local anesthesia causes myocardial depression and vaso dilation which can cause fall in blood pressure. that is why we're supposed to check the blood pressure before giving an LA Administration |
|
|
|
Action of puffer fish toxin on the body |
Tetrodotoxin or TTX is the toxin secreted by the puffer fish. this causes a block of the sodium channels from the outside preventing an action potential from developing in the nerve |
|
|
|
Why does LA convert to ionised form in the neurons? |
Because it is slightly acidic inside the neuron cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Why is cocaine not administered along with adrenaline? |
Both are vaso constrictors. so they cannot be administered together |
|
|
|
Which is only local anesthetic that has vasoconstrictor action? |
Cocaine |
|
|
|
Which is only local anesthetic that has Cns excitatory effect? |
Cocaine. All others depress the Cns, after an initial excitation |
|
|
|
Which is the only esther local anesthetic that is not metabolised by pseudo choline esterase in the blood |
Cocaine |
|
|
|
Why are amide local anesthetics not recommended to be used in liver dysfunction cases |
Because they are metabolised in the liver |
|

