![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many sets of incisors do goats and sheep have? |
4 sets |
|
|
Goats under a year of will have what general feature to their lower incisors? |
All incisors will generally be the same size. |
|
|
When will you expect a goat to have all permanent incisors? |
4 years of age
|
|
|
What do you look for when aging permanent goat or sheep teeth? |
Wear and spacing between the teeth
|
|
|
Why do we age goats? |
To estimate how long they will be useful on pasture (or otherwise easily) |
|
|
Baby teeth have two other names. |
Milk teeth or deciduous teeth |
|
|
Central permanent incisors on goat erupt when? |
About 1 year of age |
|
|
2nd set of permanent incisors erupt in goats when? |
About 2 years of age |
|
|
3rd set of permanent incisors erupts in goats when? |
3 years of age |
|
|
A mouth full of adult incisors in a goat is also termed? How old are they? |
4-5-year-old and are called "a full mouth"
|
|
|
As a goat ages, what happens to the incisors? |
They appear to elongate: neck thins allowing feed material to get stuck in between |
|
|
A goat missing some incisors is termed what? |
A broken mouth goat |
|
|
Eruption of incisors on a cow versus sheep? |
Cows are generally a year ahead with the same eruption scheme |
|
|
Cattle or sheep showing popcorn teeth? |
Cows 8+, Sheep 5+ Sand shortens teeth life |
|
|
How many molars do sheep have? |
24 |
|
|
Are sheep born with baby teeth? |
No |
|
|
By what age are baby incisors erupt? |
2 weeks |
|
|
A 2-tooth means what? Sheep. |
1 year old roughly.
|
|
|
Are their teeth variation when it comes to maturity between breeds? |
Yes. British breeds mature faster than Merinos meaning their teeth erupt at an earlier age. |
|
|
How does feed effect teeth wear? |
Long soft feed: teeth grow long from lack of wear but remain in good condition Short feed: brings the teeth closer to the dirt, allowing for more wear |
|
|
The most reliable indicator of age in cows, sheep and goats is what? |
eruption of teeth and less from wear. |
|
|
What heart irregularity is relatively common in cattle? Particularly under what disease processes? |
Atrial fibrillation. Commonly encountered secondary to GI disease |
|
|
What is a springer heifer? |
A heifer that is coming up to calving |
|
|
3 diseases or pathogens that can cause early embryonic death? |
BVD, Tritricomonas, Campylobacter-vibrio |
|
|
cwt means what? |
per 100 lbs. |
|
|
When are typical beef calves weaned? |
6-9 months |
|
|
How much of a herd as a percentage is replaced every year in a beef herd? |
15-20% |
|
|
What is the average age of heifers in a beef herd? |
5 years of age |
|
|
How much of adult weight as a percentage do cattlemen typically look for prior to breeding heifers? |
60-65% of adult weight |
|
|
By what age are most beef heifers cycling? |
1 year of age |
|
|
How long do beef cattlemen typically wait before preg checking? |
at least 45 days |
|
|
White fat compared to yellow fat. What does this tell you about the cow? |
White fat: more grain fed Yellow: grass fed |
|
|
What are the calving seasons for most beef herds? |
Spring, alternatively in the fall |
|
|
How old is a cow before it generates income? |
30 months |
|
|
What is the best desired scheme for the schedule of calf births? |
70% of them born within 30 day of eachother |
|
|
What is the body fat percentage difference between 5-6 on the beef scale? |
7-8% |
|
|
What is the BCS scale for beef? |
1-9 |
|
|
Name 3 pathogens that are responsible for early embryonic death? |
Tritricomonas, Campylobacter vibrio, and BVD |
|
|
How long after calving are bulls usually put out with the cows? |
80 days |
|
|
At what age does E coli present in a calf? |
1-7 days of age |
|
|
At what age does Rotavirus typically present in calves? |
Day 4-9 typically, up to 5 weeks |
|
|
Coronavirus typically presents when in calves? |
Day 5-9, up to 6 weeks |
|
|
Clostridium perfringens typically presents in calves at what age? |
Day 1-2 up to week 6 |
|
|
Cryptosporidium parvum typically presents at what age in calves? |
Day 7-10 up to 21d |
|
|
Salmonella spp typically present when in calves? |
Day 7-21, up to 4 months |
|
|
Coccidia typically presents in calves at what age? |
Day 21 and up |
|
|
What is the best change to implement when it comes to preventing scours in calves? |
typically management changes make the biggest difference |
|
|
Most calves are encouraged to grow how much per day? |
1-2 lbs |
|
|
What are minimum standards for semen motility and morphology? |
Motility: >31% is "fair" Morphology: >71% is considered normal |
|
|
How often are bulls considered unsatisfactory to Dr Ondrak? |
Not that often, but criteria might include a missing testicle |
|
|
When do spring calving cows have their highest energy and protein requirements? |
Spring (Mar-May) |
|
|
What is a good thermoneutral temp for cows? |
30-60F (Dr Ondra says 80F) |
|
|
British cattle are known for what? |
Being smaller, more docile and maturing sooner than other breeds |
|
|
Heterosis is defined as what? |
Crossbreeding cows with the intention of changing one trait |
|
|
Complementarity is defined as what? |
Crossbreeding with the intention of changing several traits |
|
|
What are some ddx for late term abortions in cows? |
BVD, Lepto, IBR, Fungal...idiopathic |
|
|
What happens to the Breakeven equation when percent calf crop drops? |
Changes the BE 8-10 times more than weaning weight changes |
|
|
What time of year would one expect to see foot rot?
|
Spring (wet) and summer (standing in water to get away from flies)
|
|
|
Three respiratory pathogens of cattle? |
Histophilus somni, Pasteurella, Menheimia |
|
|
Three metabolic diseases to think about in the late winter/spring for cows? |
Grass tetany, milk fever and ketosis |
|
|
5 diseases that occur in the late winter/spring in cows? |
Obstetrical issues, neonatal diarrhea, metabolic problems, umbilical hernia and mastitis |
|
|
What is the etiology of grass tetany in cows? |
magnesium deficiency |
|
|
Hypomagnesemia can present under what conditions? |
early spring grass, fertilized pastures |
|
|
Grass tetany cows present how generally? |
Down, agitated with minor convulsions |
|
|
How does one diagnose grass tetany? |
clinical signs, response to treatment, blood test, aqueous humor mg level |
|
|
Treatment for grass tetany? |
IV or oral magnesium |
|
|
What is the formulation for Mg2+ admin? |
CMPK: Ca2+, Mg2+, Phos, Potassium |
|
|
What is a good way to prevent grass tetany? |
focusing on quality of winter nutrition |
|
|
Milk fever is what? |
Hypocalcemia |
|
|
When does milk fever generally occur? |
Post-calving in response to increased energy requirements |
|
|
Ketosis is closely linked to what other condition? |
hepatic lipidosis |
|
|
What are some diseases of concern during summer months? |
BRDC - summer pneumonia Footrot |
|
|
What is the etiology behind footrot? |
Fusobacterium necrophorum |
|
|
What are certain situations that may promote footrot? |
Moist conditions or trauma |
|
|
How does footrot generally present? |
Lame, uniform swelling, foul odor, painful between claws. |
|
|
How does a hoof abscess compare to footrot? |
Abscesses generally involve one claw. Footrot involves both by being inbetween |
|
|
What is a concern for footrot cows? |
That deeper infection might ensure leading to septic arthritis or osteomyelitis |
|
|
How do we diagnose footrot? |
clinical signs and response to treatment |
|
|
How do we treat footrot? |
Antibiotic (oxytet), NSAIDs, topical astringents or surgery |
|
|
Prevention of footrot? |
management preventative antibiotic regimen... |
|
|
Summer worries in breeding and/or replacement heifers? |
Early pregnancy loss, Pink eye, mycoplasma, footrot |
|
|
4 potential causes for early pregnancy loss? |
Vibriosis, Trichomoniasis, BVDV, BTV |
|
|
BTV is what? |
Blue Tongue Virus |
|
|
Blue tongue tends to be a bigger deal in what species? |
sheep |
|
|
What is the etiology behind Vibrio? |
Campylobacter fetus venerealis |
|
|
How do cows with Vibrio present? |
Reproductive losses- reduced pregnancy rates, increased gestation length and calving seasons occasionally endometritis |
|
|
Diagnosing Vibrio? |
Challenging! Culture/PCR/ELISA - vaginal/preputial swab/semen |
|
|
Prevention of Vibrio? |
Vaccination (?), BSEs, Biosecurity, cull carriers |
|
|
What is the etiology behind Trichomonas? |
Protozoan: Trichomoniasis foetus |
|
|
How to Trich cows typically present? |
Early embryonic losses and infertility. extended calving season |
|
|
How does one go about diagnosing Trich? |
Prepucial or vaginal swab for culture or PCR |
|
|
Treatment for Trich? |
No medical treatment: Cull positive bulls, allow for female clearance |
|
|
What does one do with a + trich bull? Cow? |
Bull: report and cull Cow: allow for clearance, next time will breed normally |
|
|
How does one prevent Trich from entering the herd? |
testing bulls, biosecurity, BSEs |
|
|
BSEs stands for what? |
Breeding soundness exams
|
|
|
BVDV stands for what? |
Bovine Viral Diarrheal Virus
|
|
|
What is the etiology behind BVDV? |
Pestivirus |
|
|
What is the primary reason for BVDV spread? |
Persistantly infected shedding |
|
|
How do BVDV cows present? |
Reproductive losses, congenital defects, performance losses, immunosuppressive, mucosal disease can be subclinical too |
|
|
How does one diagnose BVDV in a herd? |
IHC (ear notch --> sent in for immunohistochemistry), ELISA, PCR |
|
|
How do we prevent BVDV? |
Vaccination, Testing and biosecurity |
|
|
What is the consequence of BVD infection during pregnancy between 0-45 days in gestation? |
Decreased conception, infertility |
|
|
What is the consequence of BVD infection during pregnancy between 45-125 days in gestation? |
Development of persistently infected calves |
|
|
What is the consequence of BVD infection during pregnancy between days 125-173 days in gestation? |
abortion, congenital defects, weak calves |
|
|
What is the consequence of BVD infection during pregnancy between days 175-term? |
calves are typically born normal, may result in weak calves and occasionally abortion |
|
|
What are some disease processes at higher incidences in summer? |
Early pregnancy losses, Pink eye (IBK), Mycoplasma, footrot |
|
|
What are the etiologies behind IBK? |
Morazella bovis or bovoculi Mycoplasma BHV-1 |
|
|
What does IBK stand for? |
Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis |
|
|
What are some risk factors associated with the development of IBK? |
Flies, dust, tall grass |
|
|
IBK typically presents in older or younger cows? |
Younger |
|
|
How might an eye injury present if it were active? |
tearing |
|
|
IBK looks like what? |
corneal opacity, conjunctivitis, ruptured cornea |
|
|
IBK diagnosis? |
Conjunctival swab-culture Staining |
|
|
Treatment options for IBK? |
Antibiotics, NSAIDs, patch, surgery |
|
|
Prevention for IBK? |
Fly control, environmental management, vaccination (iffy) |
|
|
Largely speaking what are some important things to remember about Mycoplasma infection? |
Difficult to diagnose and treat. |
|
|
Mycoplasma infection is often associated with what? |
a breach in biosecurity |
|
|
What are some diseases to keep in mind for bovine during the late summer and early fall months? |
Anaplasmosis BRDC Coccidiosis |
|
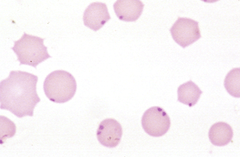
|
Anaplasma marginale |
|
|
Anaplasma marginale is what? |
a richettsial RBC parasite |
|
|
How does anaplasmosis present in bovine? |
Fever, Anemia, reproductive losses, performance losses, mortality |
|
|
Anaplasmosis is transmitted by what? |
Dermacentor and mechanical vector |
|

|
Dermacentor variabilis female |
|
|
Dermacentor spp are an example of what kind of tick? |
Hard tick |
|
|
Anaplasmosis is diagnosed how? |
Blood smear - microscope. PCR, ELISA |
|
|
Treatment for anaplasmosis? |
Antibiotics blood transfusion insecticides |
|
|
Anaplasmosis prevention? |
Tick control sanitation antibiotics carrier management |
|
|
What are 4 viral agents part of the BRDC? |
IBR - Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis PI3 - Parainfluenza BRSV - Bovine Respiratory Syncitial Virus BVDV - Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus |
|
|
What are 4 pathogenic agents part of BRDC? |
M. hemolytica P. multocida H. somnus Mycoplasma spp |
|
|
What are some disease risks to keep in mind for bovines in the fall/winter and even year round? |
Pregnancy loss Woody tongue Lumpy jaw Abscesses |
|
|
Woody tongue is caused by what etiologic agent? |
Actinobacillus lignieresii |
|
|
What is the inciting cause of Woody tongue? |
Introduction of the bacterium through a penetrating wound |
|
|
How does woody tongue present? |
hypersalivation difficulty eating/breathing firm enlarge tongue swollen surrounding tissue |
|
|
How does one diagnose woody tongue? |
PE: clinical signs Culture abscess material - histo: granulomatous abscess |
|
|
Treatment for Woody tongue? |
Antibiotics Sodium iodide Remove offending feed source Debulk mass |
|
|
How does one prevent Woody tongue? |
Ensure feed quality |
|

Differentials for this swollen jaw? |
Lumpy jaw or wooden tongue |
|
|
What is the typical etiologic agent for an abscess on a cow? |
Trueperella spp |
|
|
Why is it important to differentiate an abscess from a seroma or herniation? |
A seroma, if drained will come back because a walling off hasn't occurred yet. Rupturing one too soon can prolong recovery. |
|
|
What is the etiologic agent behind lumpy jaw? |
Actinomyces bovis |
|
|
What is the inciting cause of lumpy jaw?
|
traumatic introduction |
|
|
How does lumpy jaw typically present? |
a firm (boney) mass on face, +/- a draining tract/abscess |
|
|
Diagnosis of Lumpy jaw? |
radiographs culture clinical signs |
|
|
Treatment for Lumpy jaw? |
Sodium iodide Antibiotics |
|
|
Is Actinobacillus lignieresii a part of the normal flora? |
Yes |
|
|
Wooden tongue feel like what? |
Nodular, firm abscesses, lumpy on the tongue |
|
|
What is the percentage of cows at slaughter exhibiting Wooden tongue? |
.7-3.6% |
|
|
Late winter/spring pregnancy losses may be due to what disease processes? |
IBR=BHV1 BVDV BTV CVV - Cache Valley Virus Leptospirosis Brucellosis Listeriosis EBA - Enzootic Bovine Abortion Ureaplasma T. pyogenes Neospora Mycotic |
|
|
Antibiotic for cows...and horses with anaplasmosis? |
Oxytet (LA200) |
|
|
What is the difference when feeling lumpy jaw versus woody tongue? |
Lumpy Jaw is bone hard (haha) Woody tongue is soft tissue |
|
|
IBR is also known as? |
Red Nose |
|
|
Lumpy jaw is basically the development of: |
osteomyelitis |
|
|
Pine needle abortion is also what? |
Enxootic bovine abortion |
|
|
"Banged" means what? |
Brucellosis vaccinated |
|
|
Which strain of Brucella vaccine has more reactions? |
Strain 19 RB51 has few |

