![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PT and INR measure what pathway of the coagulation mechanism?
|
extrinsic pathway
|
|
|
aPTT assesses what pathway of the coagulation mechanism?
|
intrinsic pathway
|
|
|
PT evaluates the effectiveness of what drug therapy?
|
warfarin
|
|
|
aPTT evaluates the effectiveness of what drug therapy?
|
heparin
|
|
|
1 PRBC raises H/H by how much?
|
1 hgb and 3% hematocrit
|
|
|
angiotensin II is also known as
|
vasopressin
|
|
|
hypovolemic shock occurs after losing ___% of intravascular volume.
|
15%, or about 750ml
|
|
|
specialized macrophages located in the liver
|
kupffer cells
|
|
|
CVP
|
2-6 (our patients 8-10 common)
|
|
|
PAS
|
20-30
|
|
|
entecavir
|
hepatitis b, inhibits polymerase transcription. for PO do not mix with anything.
|
|
|
normal PAD
|
6-12
|
|
|
normal PAW
|
6-12
|
|
|
pentoxifylline
|
TNFa suppressor (high TNFa found to be predictive of poor survival), decreases incidence of hepatorenal syndrome.
Research also shows it is able to prevent the transition from a hyperdynamic response to hypodynamic response during sepsis, maintaining hemodynamic stability and preventing lethality from sepsis. |
|
|
piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn)
|
antibiotic, prophylaxis and treatment infection, sepsis, nosocomial pneumonia, peritonitis, PID.
|
|
|
Vancomycin
|
antibiotic. nephrotoxic, monitor peaks and troughs.
|
|
|
diflucan (Fluconazole)
|
antifungal, prophylaxis and treatment of fungal infections post OLT.
|
|
|
rifaximin
|
hepatic encephalopathy. low intestinal absorption antibiotic, ideal for killing bacteria that produce ammonia as a by-product with limited side effects.
|
|
|
PAD
|
6-12
|
|
|
PAW
|
6-12
|
|
|
Cardiac Output (CO)
|
4-8L
|
|
|
Cardiac Index (CI)
|
2.5-4.5L
|
|
|
SVR
|
800-1200 (in our patients <800 common)
|
|
|
PVR
|
<250
|
|
|
when CO goes up, SVR goes...
|
down; and vice versa
|
|
|
when calcium goes up, phosphorous goes...
|
down; and vice versa
|
|
|
upper limit temperature that requires intervention
|
38.5 (101.3)
|
|
|
Lactulose
|
1. acidification of gut lumen favors conversion of NH3 to NH4 which is less membrane-permeable
2. acidification also inhibits ammoniagenic coliform bacteria 3. increased transit time clears gut ammonia before it can be absorbed |
|
|
Sodium benzoate
|
conjugates with glycine, intermediary of ammonia, to form hippuric acid which can be excreted by kidneys. relies on good kidney function to be effective.
|
|
|
octreotide
|
treatment and prophylaxis of acute variceal bleeding. Also used in conjunction with midodrine to treat HRS.
|
|
|
TIPS
|
transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. creates new pathways for blood to flow.
|
|
|
PR interval
|
0.12-0.20
|
|
|
QRS duration
|
.04-.10
|
|
|
QT interval
|
0.36-0.44
|
|
|
piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn)
|
- antibiotic
- prophylaxis infection and sepsis post OLT - pneumonia, peritonitis |
|
|
aminocaproic acid (amicar)
|
treat severe bleeding secondary to problems with clotting system. promotes hemostasis.
|
|
|
tacrolimus (Prograf)
|
prophylaxis of LT rejection, immunosuppression via inhibition of T lymphocyte activation. hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, no grapefruit juice.
|
|
|
mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept)
|
prophylaxis of LT rejection, immunosuppression. Risk for skin malignancies.
|
|
|
methylprednisolone (Solu-medrol)
|
prophylaxis of LT rejection, graft vs host disease, prophylaxis of VAP. potent anti-inflammatory.
adverse effects of corticosteroids: · sodium and water retention · bone disease · diabetes (especially with concurrent use of calcineurin inhibitors) · hyperlipidemia |
|
|
ursodiol
|
chemodissolution/prophylaxis of bile duct stone and primary biliary cirrhosis.
|
|
|
sevelamer hydrochloride (Renagel)
|
hyperphosphatemia, ESRD
|
|
|
ganciclovir (Cytovene)
|
prophylaxis/treatment of cytomegalovirus infection post OLT
|
|
|
ciprofloxacin
|
broad spectrum antibiotic (fluoroquinolone), treats UTIs, pseudomonas in lower respiratory tract, intraabdominal infections.
|
|
|
colistimethate
|
aerobic gram-negative abx (enterobacter aerogenes, e coli, klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa)
|
|
|
ertapenem
|
broad spectrum abx, especially against anaerobic bacteria. not effective against MRSA, pseudomonas aeruginosa, or acinetobacters.
|
|
|
caspofungin
|
treatment of fungal infections including candidas
|
|
|
voriconazole
|
treatment of fungal infections, invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis, and emerging fungal infections. especially in immunocompromised patients.
|
|
|
tobramycin
|
binds bacterial ribosomes, inhibits mRNA translation. Effective against gram negatives, especially pseudomonas. better lung penetratiom than gentamicin.
|
|
|
fondaparinex
|
inhibits factor X, antithrombotic
|
|
|
loperamide
|
slows rhythm of digestion allowing more time for nutrient absorption in small intestines. Also used to reduce amount of stool in people who have an ileostomy.
|
|
|
levetiracetam (Keppra)
|
anticonvulsant, treatment/prophylaxis of seizures
|
|
|
norepinephrine (Levophed)
|
.1 - 1mcg/kg/min
8mg in 250ml D5W hypotension with low total peripheral resistance. beta 1 - positive inotropy beta 2 - minimal vasodilation alpha - peripheral, renal, and mesenteric vasoconstriction tissue necrosis, coronary artery vasoconstriction use after fluid resuscitation, dont mix with sodium bicarb, avoid extravasation |
|
|
vasopressin (Pitressin)
|
hypotension: 0.5 - 4 units/hr
VF/pulseless VT: 40 units IVP once 20 units in 100ml D5W low dose infusion of vasopressin for hypotensive patients also an alternative pressor to epinephrine in shock refractory |
|
|
amiodarone
|
loading:
150mg over 10 minutes 360mg over 6 hours 540mg over 18 hours maintenence: 0.5mg/min for VF/pulsless VT: 300mg IVP (in 20-30 D5W or NS) may repeat 150mg IVP in 5-10 minutes 300mg in 50ml D5W (syringe or buretrol) 6mg/ml max for central line 750mg in 500ml D5W (glass) 1.5mg/ml max for peripheral line treatment of prophylaxis of frequently recurring ventricular fibrillation or hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia. hypotension, nausea, arrhythmias, abnormal LFTs •multiple drug-drug interactions: digoxin, warfarin, quinidine, phenytoin, CSA, beta blockers. •USE IN LINE FILTER during administration •infusion over 2 hours must be in glass or polyolefin/buretrol ok |
|
|
dopamine (Intropin)
|
1 - 2 mcg/kg/min (delta)
2 - 10 mcg/kg/min (beta 1) 10 - 20 mcg/kg/min (alpha) 400mg in 250ml D5W 800mg in 250ml D5W (double strength) cardiogenic shock, septic shock, augmentation of renal perfusion •delta - dilation of renal and mesenteric blood vessels •beta 1 - positive inotropy, increase HR, increased cardiac output •alpha - peripheral vasoconstriction arrhythmias, increased HR, angina, tissue necrosis at higher doses use after fluid resuscitation, avoid extravasation, consider norepinephrine if dose exceeds 20mcg/kg/min, dont mix with sodium bicarb |
|
|
midodrine
|
alpha 1 receptor agonist, for orthostatic hypotension, weaning off pressors, and HRS 1 in conjunction with octreotide by constriction of splanchnic vessels and dilation of renal vasculature.
|
|
|
portopulmonary hypertension (PPH)
|
occurs in 4% of patients with cirrhosis. right heart dysfunction secondary to pulmonary hypertension.
by definition, mean PAP pressure >25 while PAW < 15. unlike HPS, patients with PPHTN develop orthopnea rather than platypnea. |
|
|
propanolol
|
beta blocker, also used for prophylaxis of esophageal varices
|
|
|
hepatic hydrothorax
|
occurs in 5% of patients with ESLD. leakage of ascitic fluid into thorax through tendious portion of diaphragm. can lead to compression atelectasis with resultant loss of lung volume for gas exchange.
|
|
|
hepatopulmonary syndrome
|
defect in oxygenation and intrapulmonary vascular dilation, leading to reduced gas exchange because of the increased distance oxygen must diffuse to reach the RBCs. results in significant V-Q mismatch. present in 10-20% of all patients with chronic liver disease.
•PaO2 less than 70mmHg in absence of cardiopulmonary disease has a high predictive value for HPS. •orthodeoxia is highly specific for HPS (5% or greater reduction in PaO2 when moving a patient from supine to upright position |
|
|
patients with a mean PAP of 50 mmHg have a ___% risk of mortality post transplant.
|
100%, patients with a mean PAP of 35 - 50 mmHg have a 50% risk of mortality.
PPHTN untreated and persistent is a contraindication to transplant because of high perioperative mortality. |
|
|
PPHTN vs. HPS
|
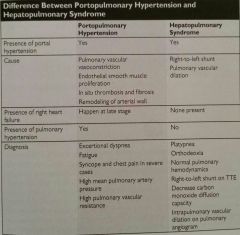
|
|
|
zinc sulfate
|
to correct zinc deficiency as a result of decreased absorption and use of diuretics which leads to urinary excretion of zinc.
zinc deficiency •poor wound healing •impaired protein metabolism •impaired immune system zinc deficiency also contributes to the lack of appetite found in patients with liver disease. |
|
|
causes of osteoporosis
|
• cholestatic liver disease impairs absorption of fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) vitamin D and calcium are vital to bones
• decreased hepatic glycogen reserves causes cirrhotic patients to mobilize amino acids from their bones when they are fasted even for short periods of time •prolonged bedrest of ICU patients |
|
|
how does protein deficiency contribute to hepatic encephalopathy?
|
protein deficiency causes an imbalance of brached chain amino acids (BCAAs) (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, methionine, and tyrosine). the expected ratio shifts from 3:5:1 to 1:1 in patients with ESLD. Simply, in ESLD, this ratio results in more tryptophan passing into the brain circulation which contributes to hepatic encephalopathy.
|
|
|
fulminant hepatic failure
|
Hepatic encephalopathy within 8 weeks of first symptoms of illness in the absence of pre-existing liver disease.
Goals: ICP < 20, sjO2 > 60, PCO2 28-32 (to constrict vessels to brain), MAP > 70 |
|
|
HBIG administration considerations
|
·Must premedicate with acetominophen and diphenhydramine
·Must run alone in central line over 6 hours ·Monitor for myalgia, SOB, fever, hypotension ·Draw trough before administering, titer should be > 500 iu/L |
|
|
enteral feeding considerations
|
·Residuals q 4 (hold if > 250ml)
·Flush q 4 peptamen 1.5 - 1.5kcal/ml, peptide based, calorically dense, high protein nepro - 1.8kcal/ml, concentrated fiber fortified, low in phosphorous, potassium, calcium, sodium |
|
|
IV medications that require in-line filters
|
amiodarone, anything with phosphate, calcium gluconate
|
|
|
erythromycin
|
antibiotic, also used as a prokinetic to reduce delayed gastric emptying
|
|
|
precedex
|
?
|
|
|
sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (Bactrim)
|
?
|
|
|
phenylephrine (Neosynephrine)
|
20-200mcg/kg
50mg in 250ml D5W hypotension with low total peripheral resistance alpha - peripheral, renal, and mesenteric vasoconstriction tissue necrosis, coronary artery vasoconstriction use after fluid resuscitation, avoid extravasation |
|
|
oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
|
less affinity (right shift) - e.g. muscles
•low pH •high temp •high pco2 •DPG higher affinity (left shift) - e.g. lungs •high pH •low temp •low pco2 •less DPG |
|
|
sevelamer hydrochloride
|
for hyperphosphatemia, hold if phosphorous <5.0
|
|
|
sensipar (cinacalcet)
|
for hypercalcemia
|

