![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical Lipoid Proteinosis/ Urbach-Wiethe disease;
Hyalinosis cutis et mucosae |
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Urbach-Wiether disease; Hyalinosis cutis et mucosae
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal recessive; extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) gene on 1 q21
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
DNA analysis in future
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Over 280 cases reported increased in South Africa; M=F
|
|
|
Age at Presentataion
|
Birth (hoarse cry) to first few years of life
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutation in ECMI correlated with phenotype; unknown cause
|
|
|
Clinical
|
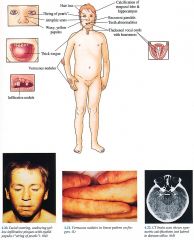
Skin
Early Bullae with residual atrophic scarring on face, neck and extremities Late Yellow papules, nodules on face, neck, extremities with eyelid "string of pearls”; Verrucous nodules of elbows, knees, and hands Hair Patchy alopecia in scalp, beard, eyelashes Mucous Membranes Infiltrative yellow papules and plaques on pharynx, lips, soft palate; with/without parotitis caused by stenotic parotid duct Ear Nose Throat Hoarse cry because of vocal cord infiltration Large, wooden tongue Central Nervous System Temporal and hippocampal calcification with/without seizures |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Amyloidosis; Erythropoietic protoporphyria (p. 224); Pseudoxanthorna elasticurn (p. 144); Xanthomas
|
|
|
Lab
|
Skin biopsy (PAS (+) hyaline material) Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
|
|
|
Management
|
Retinoids, oral dimethylsulphoxicle may be beneficial
Referral to ear nose throat special ist laser, surgical correction of vocal cords, tra¬cheostomy Referral to dermatologist diagnosis, dermabrasion, chemical peel Referral to neurologist if symptomatic |
|
|
Prognosis
|
May progress to involve internal organs; however, chronic and benign course with normal life span; laryngeal involvement may lead to respiratory difficulties in childhood
|

