![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What arethe major classes of fatty acids and lipids? |
fatty acids, waxes, fats, and oils |
|
|
Nonhydrolyzable |
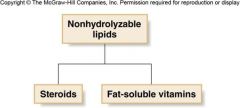
Lipidscannot be cleaved into smaller units by aqueous hydrolysis. |
|
|
waxes |
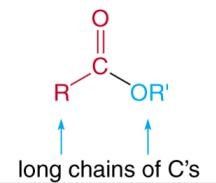
Waxes are esters (RCOOR’) formed from a fatty acid and a high molecular weight alcohol. |
|
|
wax hydrolysis |

inthe presence of acid or base to re-form thecarboxylic acid and alcohol theycame from |
|
|
fatty acids |
The naturally occurring fats and oils arearecomposed of long-chain carboxylic acids A long-chain carboxylic acid; those inanimal fats and vegetable oils often have 12–22 carbon atoms |
|
|
Triacylglycerols (triglycerides) |
are triesters- formed from glycerol and three molecules of- fatty acids.
carboxylic acid triestersof glycerol, a three-carbon trialcohol |
|
|
Oil |
Amixture of triacylglycerolsthat is liquid because it contains a high proportion of unsaturated fattyacids. |
|
|
Fat |
A mixture of triacylglycerolsthat is solid because it contains a high proportion of saturated fatty acids |
|
|
properties of fats and oils with double bonds |
Themore double bonds there are in a triacylglycerol, the harder it is for it tosolidify. |
|

|
Glycerol |
|

|
Triacylgylcerol (ester groups in red) |
|
|
cis-doublebonds to trans-double bonds not usually found in nature |
margerine,shortning,high fat baked goods |
|
|
saponification |
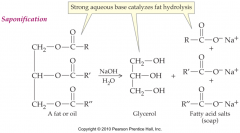
Hydrolysis of fats and oils carried outby strong aqueous bases to form soaps |
|
|
Micelle |
A spherical cluster formed by theaggregation of soap or detergent molecules so that their hydrophobic ends arein the center and their hydrophilic ends are on the surface |
|
|
simple lipids |
containjust two types of components (fatty acids and alcohols) |
|
|
complex lipids |
containmore than two types components (fatty acids, an alcohol, and other components) |
|
|
Phospholipid |
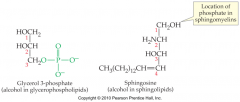
A lipid that has an ester link betweenphosphoric acid and an alcohol (either glycerol or sphingosine)and another alcohol (usually containing an amine |
|
|
Glycerophospholipid |

|

