![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are two major conditions that can occur with a patient that has untreated hyperlipidemia? |
Atherosclerosis (hypercholestermia) Liver Disease (Hypertriglycerrides) |
|
|
What are secondary causes of Lipid Disorders (7)? |
Increased Fat Intake Obesity Type II DM Advanced Age Hypothyroidism Obstructive Liver Disease Drug Induced (Propofol, DM Meds, Steroids) |
|
|
What are the types of Lipoproteins? |
Chylomicrons-Made from things you eat Very-Low Density (VLDL)-Transport to & From Liver Intermediate Density (IDL) Low Density (LDL)- Transport Into Liver High Density(HDL)- Assist Mostly into the Liver |
|
|
What is the relationship of Lipid to Protein for the types of Lipoproteins? |
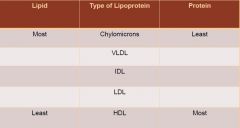
|
|
|
What are the optimal values of the lipoproteins? |
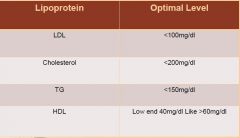
|
|
|
What are the three types of Lipoprotein Metabolism? |
Exogenous- Dietary fats, Cholesterol, and lipid soluble vitamins
Endogenous-Hepatic Cholesteol Synthesis Reverse Cholesterol Pathway |
|
|
What is the most effective drug in reducing LDL? |
Statins- reduce LDL 20-60%, Increase HDL-10% |
|
|
What four high risk groups are statins advocated in? |
Clinical Evidence of (ASCVD) Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease LDL>190 Age 40-70 with Diabetes and LDL 70-189 Age 40-75 without DM, LDL 70-189 and an estimated 10 risk of ASCVD |
|
|
What are the two mechanisms of action for Statins (HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors)? |
Inhibit Cholesterol Synthesis Competitively inhibit this enzyme causing increased Hepatic LDL-R |
|
|
What is the absolute contraindication for statins? |
Pregnancy |
|
|
What are prodrugs and what are two examples? |
Prodrugs need metabolism to become active. Lovastatin and simvastatin are examples Need hepatic P450 enzymes to be active |
|
|
What are the side effects of Statins? |
Skeletal Muscle issues Liver enzyme changes (increase Plasma Aminotransferase) Interacts with drugs especially ones that are metabolized by CP4503A4 GI Upset Fatigue Headache |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Bile Acid (anionic exchange) Resins?
Colesevelam, Cholestyramine, Colestipol |
Increases hepatic bile synthesis from cholesterol stores, increasing LDL-R and the uptake of LDL from the blood.
They are powders with no systemic absorption
Side Effect of constipation |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Niacin? High doses 1000 mg three times per day |
Inhibits synthesis of VLDL in the liver, inhibits the release of free fatty acid from adipose Increases the activity of lipoprotein lipase Lowers LDL and Triglycerides |
|
|
What are the side effects of Niacin? |
Flushing (histamine release), pruritis, GI Upset, hepatic dysfunction,Hyperglycemia, gout, and drug interactions |
|
|
What is the most effective drug at lowering Triglycerides? |
Fibrates- lowers by 50%, also increases HDL |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for Fibrates? What are the side effects? Gemfibrozil, Fenofibrate, Bezafibrate |
Increased activity of lipoprotein lipase GI upset, headache, gallstones, statin interactions (increases all bad effects), prolonged PTT |
|
|
What drug is used to potentiate the effects of Statins? What is its Mechanism of Action? |
Ezetimibe- a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption leading to secondary up-regulation of LDL-R Increase effects of Statins by 17% Used alone decreases LDL up to 22% |
|
|
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids (fish oil) used for? |
Decreases triglycerides Dose to effect unclear, not FDA regulated Long term safety not known |
|
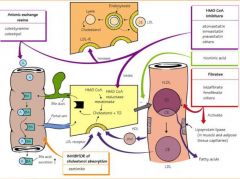
|
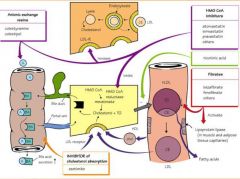
|

