![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
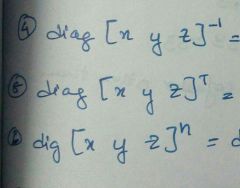
|
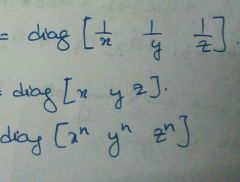
|
|
|
|
Formula for A inverse |

|
|
|
|
What happens if you multiply a row with Co factor of another row |
Results in zero |
|
|
|
Shortcut method for calculating determinant of a 3x3 matrix |
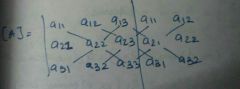
|
This method is applicable only for a 3x3 matrix |
|
|
Shortcut for calculating adjoint |

|
|
|
|
Orthogonal matrix |
If A(transpose) = A(inverse) then A is orthogonal matrix |
|
|
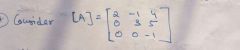
Find EV of A EV of A^3 EV of 4A EV of A(inverse) EV of adj(A) EV of A+3I EV of A(transpose) |
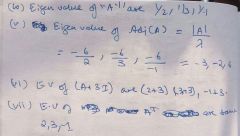
|
|
|
|
Can you swap two rows or columns while calculating determinant |
Yes you can. However determinant will be multiplied by -1 for each swap |
|
|
|
Eigen vectors corresponding to different Eigen values of a real symmetric matrix are ____________ Eigen vectors corresponding to same Eigen values of a real symmetric matrix are ____________ |
1. Orthogonal to each other. i.e their dot products is zero. 2. Maybe may not be orthogonal |
|
|
|
What are the conditions for diagonalization ? |
It must have distinct Eigen values |
|
|
|
What is the determinant of orthogonal matrix |
+- 1 |
|
|
|
If a non singular matrix A is symmetric, then is A inverse also symmetric |
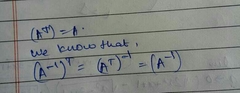
Yes |
|
|

Find the determinant of the matrix |
0 If the numbers are in sequential order the determinant is zero |
|
|
|
What are the diagonal elements of a skew symmetric matrix |
0 |
|
|
|
Find the minor and Cofactor of 1 1 2 2 3 4 4 7 -2 a21 |
Minor = -16 Cofactor = -1 * -16 = 16 |
|
|
|
A. Adj A = Adj A. A = ? |
Det (A) |
|
|
|
Derive Inverse (adj A) |
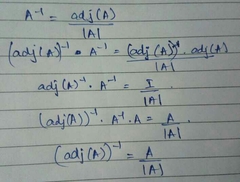
|
|
|
|
Determinant of odd order skew symmetric matrix |
0 |
|
|
|
Derive det ( adj A) |

|
|
|
|
Important properties regarding rank |

|
|
|
|
The rank of 5x6 matrix Q is 4, then how many LI rows or columns are there |
4 LI rows 4 LI columns |
|
|
|
How to confirm if a given set of vectors are linearly independent |
Arrange in a matrix and then calculate determinant If determinant = 0, then the vectors are not linearly independent |
|
|
|
Define dimension, basis and nullity of the matrix |
Dimension It is defined as the number of LI vectors. Dimension = No of non zero rows Basis Set of LI vectors Basis : Express the non zero rows in set form Nullity of a matrix : difference between order of matrix and rank of matrix |
|
|
|
Determinant of adj (adj A) |
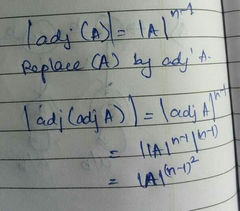
|
|
|
|
Det(AB) |
DetA. DetB |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
How many Eigen vectors are possible for an Eigen value |

|
|
|
|
Normalized Eigen vector |

|
|
|
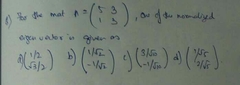
|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|
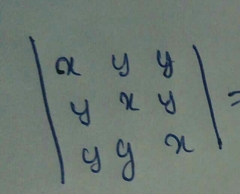
|
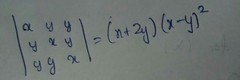
|
|
|
|
Define idempotent, involutory and nilpotent matrix |

|
|
|
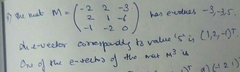
|
The Eigen vector will be the same for A^m |
|
|
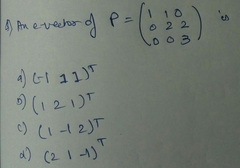
|
B |
|
|
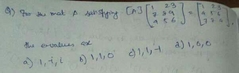
|

|
|
|

|
A |
|
|
|
Direct formula of 2x2 matrix |
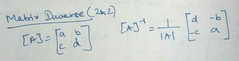
|
|
|
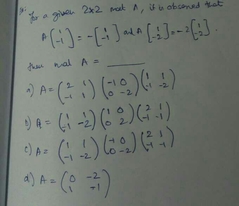
|
C |
|
|

Also solve the system of equations for B = ( 4 -6 7 ) |
Refer notebook |
|
|
|
When is a matrix diagonalizable |

|
|
|
|
Solution for a non homogeneous set of equations |
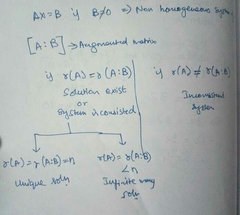
|
|
|
|
Solution for a homogeneous set of equations |
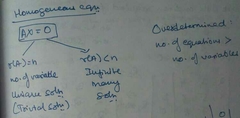
|
|
|
|
Revise all properties of Eigen values and Eigen vectors |
Refer notebook |
|
|
|
If a matrix has a rank r, what does it represent |
It means that the no of linearly independent vectors is r It also means the no of linearly independent solutions is n - r |
|
|
|
What is the span of vectors |
If you find the linear combination of the vectors what does it trace out to. In case the set of vectors are linearly independent it may trace out a plane6 |
|
|
|
Basis of a vector space |
A subset of a vector space Vf is said to be a basis of Vf if 1. S consists of linearly independent vectors 2. S generates Vf (1,0) (0,1) is a basis of V2 (1,0,0) (0,1,0) (0,0,1) is a basis of V3 |
|
|
|
What is (A + B) Transpose |
transpose (A ) + transpose (B) |
|
|
|
1.E-values of an idempotent matrix are 2.E-values of an involutory matrix are 3.E-values of nilpotent matrix are |
1. 0 or 1 2. 1 or -1 3. All zero Remember for nilpotent A^n = 0, This means A^n is null matrix |
|
|
|
If sum of all entries of each column in a matrix And is equal to S, then |
S is an Eigen value of A |
|

