![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the different types of light rays? |

|
|
|
What are the two law of reflection |

i=r Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie on the same plane |
|
|
Is light only reflected by smooth and shiny surfaces like mirrors? What about rough and dull surfaces like roads? Do they reflect light? |
All surfaces reflect light. However the type of surface affect how light is reflected off it. When light strike smooth surface, the reflection is regular. When it strikes a rough surface, the reflection is diffused |
|
|
Characteristic of a regular reflection |
-Occurs at smooth surfaces -Law of reflection holds true for each individual rays i=r -Parallel incident rays are reflected in the same direction because surface is even -All rays have the same angles of incidence and reflection -The normal at all points of incidence are parallel to each other |
|
|
Characteristic of diffuse reflection |
-Occurs at rough surface -Law of reflection holds true for each individual rays i=r -Parallel incident rays are reflected in different direction because the surface is uneven -The angle of incidence and angle of reflection of one ray are different from those of another ray -The normal at all points of incidence are not parallel to one another |
|
|
Characteristic of plane mirror image |
-Distance from mirror is equal to the distance of the object from the mirror -Upright -Virtual -Laterally inverted -Same size as the object |
|
|
Ray diagram for plane mirrors for a point object |

|
|
|
Ray diagram for an extended object |
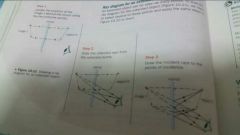
|
|
|
Uses of reflection |
Periscope Vision testing Mirror in an ammeter or voltmeter Blind corner mirrors |
|
|
Ray diagram for falling object |

|
|
|
Definition of refraction |
Refraction is the bending of light as light passes from one optical medium to another |
|
|
Speed of light in air |
3.0x10^8 |
|
|
Speed of light in glass |
2.0x10^8ms^-1 |
|
|
When is light fastest and when does it slows down |
Fastest in vacuum slows down in an optically denser medium such as glass and water |
|
|
When light ray travels from optically denser medium to optically less dense medium, what happens? |

Refracted away from medium |
|
|
When light ray travels from optically less denser medium to optically denser medium, what happens? |

Refracted towards the normal |
|
|
What are the laws of refraction |
-For two given media, the ratio of the Sine of the angle of incidence to the Sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. Sin i/Sin r=constant -The normal the refracted ray and the incident ray all lie in the same plane |
|
|
What is the definition of refractive index and the two formula |
The ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium ri=speed in vac/speed in medium OR speed in air/speed in medium ri=sin i/Sin r (for light travelling from vacuum to an optical mdcium) |
|
|
Density of glass in ascending order |
Air, ice, water, perspex, glass, diamond |
|
|
Daily phenomena and applications of refraction |
Refraction cause object in water to appear higher and the water to appear shallower |
|
|
When can total internal reflection only occur |

When light passes from an optically denser to a less dense medium Angle of incidence in the optically denser medium is higher than critical angle |
|
|
Definition and formula of critical angle |

The angle if incidence in the optically denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the optically less dense medium is 90 sin critical angle=1/refractive index |
|
|
Definition of total internal reflection |
The complete reflection of a light ray inside an optically denser medium at its boundary with an optically dense medium |
|
|
Application of total internal reflection |
Prism in periscope and binoculars Single lens reflex camera Optical fibres |
|
|
What are diverging lens |

Light rays are brought to diverge from a point |
|
|
What are converging lens |

Light rays are brought to converge to a point |
|
|
What is focal length |
The distance between the optical centre and the focal point |
|
|
How to construct ray diagram |
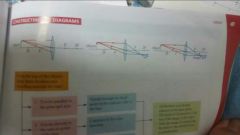
|
|
|
Image type of object at infinite object more than 2f object at 2f image at f image more than f below 2f image at 2f Application? |

|
|
|
Image type of object more than f and below 2f object at f object below f image more than 2f image at infinite image same side of lens behind the object |

|
|
|
Application of converging lens |
Magnifying glass LCD projector Film camera Visual correction for long sightedness
|

