![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the building block most organisms are made up of? |
Cells |
|
|
What are cells made up of? |
They are made up of molecules, mainly proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and water. |
|
|
What instrument is used to observe cells? |
A compound microscope. |
|
|
What is a another name for a compound microscope? |
Light microscope. |
|
|
When and Where was the first microscope invented? |
It was invented in Europe in the 1600s |
|
|
Who made the first microscope? |
Anton van Leeuwenhoek made the first microscope. |
|
|
Who invented the first microscope with 2 lenses? |
Robert Hooke was the person who made the first microscope with 2 lenses. |
|
|
How did the compound microscope help to progress science? |
It was used to make the discovery that yeast is a living fungus. It was used to discover the bacteria that causes tuberculosis and cholera. It was also helped the scientists in various branches such as agriculture veterinary science and geology to make many new discoveries. |
|
|
What are the two kinds of electron microscopes? |
Transmission electron microscope and Scanning electron microscope. |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of an electron microscope? |
Is very expensive. Is difficult to use. Is difficult to prepare specimens for observation and the preparation takes a long time. Cannot be used to observe live specimens because the preparation and staining kill the cells. |
|
|
What does the cell theory state? |
All known living organisms are made of cells so the cell is the unit of structure of all living organisms. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division; they never just appear. Cells contain hereditary* material, which passes from cell to cell during cell division. The cells of all living organisms have similar chemistry. All the chemistry of life happens inside cells. |
|
|
Name all the parts of the Light Miroscope. |
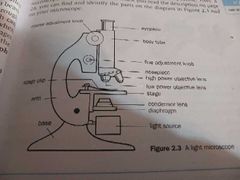
|
|
|
What is the formula for total magnifying? |
Power of eyepiece x power of objective = total magnifying power |
|
|
Label the plant cell. |
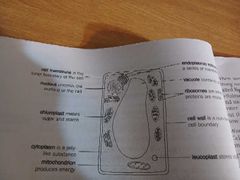
|
|
|
What is the cell wall? |
The outermost boundary of plant cells is the cell wall. The cell wall a tough bu flexible structure that gives the cell support. |
|
|
What are the strands of the cell wall made up of. |
Carbohydrates and Cellulose. |
|
|
What is the cell membrane? |
It forms a boundary that surrounds the cytoplasm, it keeps all the parts of the cell together. |
|
|
The cell membrane consists of: |
three main types of molecules called phospholod, protein and carbohydrates. |
|
|
What does Hydrophobic? |
It means that water is being repelled. |
|
|
What does Hydrophilic? |
It means attracted to water. |
|
|
What is it called when molecules use energy provided by the cell to move across the cell membrane? |
This is called active transport. |
|
|
What are the processes that kinetic energy move by called? |
Diffusion and Osmosis. |
|
|
Define diffusion. |
It is the random movement of one type of molecules from a region of a high concentration to a region of low concentration. |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane that separates two solutions of different strength. |
|
|
The cell membrane has 2 different kinds of proteins that actively transport substances. |
Channel proteins and Transport proteins. |
|
|
What are the examples of active transport in living organisms? |
Plants taking minerals from the soil. The movement of sodium and potassium ions. |
|
|
Label the nucleus |

|
|
|
What is DNA? |
Is an organic compound that contains genes. |
|
|
What is the cytoplasm? |
The whole of the inside of the cell except the nucleus. |
|
|
What is cytosol? |
Is the watery matrix of the cytoplasm. |
|
|
What is the constant movement of cytoplasm called? |
It's called cyclosis. |
|
|
What is the mitochondria? |
They change the energy in organic compounds such as glucose into a form of energy that cells can use. |
|
|
What makes the molecules of ATP. |
The Cristae |
|
|
What is ATP used for. |
It holds energy obtained from glucose during a process called cellular respiration. |
|
|
What are ribosomes? |
They are very small structures in the cell. |
|
|
What are ribosomes made up from. |
Ribosomal RNA. |
|
|
Some ribosomes are found in the: |
In the cytosol. Attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Inside the mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
|
|
Name the three types of plastids. |
Leucoplasts, Chloroplasts and Chromoplasts. |
|
|
Describe a Leucoplast. |
Have no colour and store starch. |
|
|
Describe Chloroplasts. |
Are green plastids that contain the pigment chlorophyll. |
|
|
Describe Chromoplasts. |
Are plastids that contain orange or red pigments. |
|
|
Label the Chloroplast. |

|
|
|
Label the Chromoplasts. |
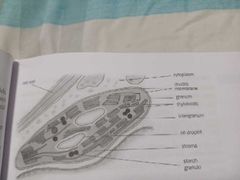
|

