![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are cohorts?
|
Cohort can be defined as a group of individuals that share a common demographic, experience, or exposure over a particular time span (people born in Africa between 1950 and 1960, or the college class of 2006). A cohort is often made of individuals within a similar age group to control for the effects of age on the research findings
|
|
|
What are normative age-graded influences?
|
A social influence: Influences within the life course that are correlated with chronological age. For example, puberty, marriage and retirement.
|
|
|
What are non-normative life events?
|
Unique turning points at which people change some direction in their lives (such as divorce, winning the lottery, or being severely injured in an accident)
|
|
|
Explain the nature vs nurture argument.
|
Nature involves the traits, abilities and capacities that are genetically inherited from parents (ex. not being able to focus- ADHD being genetically triggered)
Nurture involves the environment in which one is a part of that influences behavior (ex. toxins, economic status, peer pressure) |
|
|
What is Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory and what are the three parts?
|
Unconscious forces act on behavior and personality.
(1) ID: present from birth/ primitive and instinctive behavior (ex hunger-->need to eat) (2) Ego: reality and rationality (ex. weighing out the costs and benefits before making a decision) (3) Superego: right & wrong developed by parents and society |
|
|
What is the problem with Psychodynamic Perspective Theories?
|
They are good at describing the past but not at predicting the future. Difficult to back up with science.
|
|
|
What is the behavioral perspective?
|
Developmental patterns are a personal reflection of environmental stimuli. Rejects the idea that people pass through predictable stages of development.
|
|
|
What is classical conditioning?
|
Associations between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus. A situation which an organism learns to respond in a particular way to a neutral stimulus that normally doesnt bring about that response
|
|
|
What is operant conditioning?
|
A form of learning in which a voluntary response is strengthened or weakened by its association with positive or negative consequence.
|
|
|
What is Albert Bandura's Social Cognitive Learning?
|
Learning behavior by watching others perform the behavior and being motivated and deterred to replicate that behavior
|
|
|
What is the difference between classcial/operant conditioning and social cognitive learning?
|
Classical and Operant conditioning do not credit cognitive thought in any way.
|
|
|
What is Piaget's Cognitive Theory? Discuss scheme, assimilation and accommodation.
|
All humans pass through fixed 4 stages of cognitive development.
(a.) Scheme: organized patterns that represent ideas, behaviors, and actions that allow us to think about the world (b.) assimilation: new information from experience added to former scheme (c.) accommodation: process that changes existing ways of thinking in response to new stimuli |
|
|
What is the information processing approach to development?
|
Looking for ways individuals take, use and store information. Growth is more quantitative than qualitative.
|
|
|
What is the evolutionary perspective?
|
Involves behavioral genetics: the effects of heredity on behavior and personality traits. How environment influences whether we display such traits.
|
|
|
What is a cross-sectional study of development?
|
When you compare people of different ages at the same point in time. A positive to this is that it requires less money and time, you can see the differences between development at different age groups. Negatives include: cohort effects which are differences due to cohort membership, not age. Selective dropout which is some ages are more likely to leave the study. And unable to see changes over time
|
|
|
What is a longitudinal study of development?
|
Behavior of one or more individuals is measured over time as subjects age. Positives: changes can be easily compared. Negatives: requires a lot of time, loss of subjects over time, money, people familiarized with the questions over time.
|
|
|
What is a gamete?
|
It is haploid, meaning that it contains only 1 complete set of chromosomes. A gamete has only 1 allele for each gene; one sperm, one ovum
|
|
|
What is a zygote?
|
A new cell composed of two gametes
|
|
|
What is mitosis?
|
When 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total) of a cell split and replicate to produce two identical sets of chromosomes after the cell divides. = 2 daughter cells with 46 chromosomes each (23 pairs)
|
|
|
What is meiosis?
|
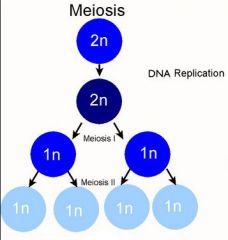
23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total) of a cell replicate and split, resulting splitting the number of chromosomes
|
|
|
What are monozygotic multiples?
|
Identical twins. Ovum divides after fertilization. *they are genetically the same and are the same sex*
|
|
|
What are dizygotic multiples?
|
Fraternal twins. Multiple eggs are fertilized by different sperm cells. They are no more genetically similar than siblings born at the same time and can be different sexes.
|
|
|
What pair chromosomes determine the sex of a baby is going to be a female?
|
Mom=XX, Dad XY--> XX
|
|
|
What set of chromosomes determines the sex?
|
the 23rd pair
|
|
|
What pair of chromosomes determines the sex of the baby will be a male?
|
Mom= XX, Dad=XY--->XY
|
|
|
What is a genotype?
|
Underlying combination of genetic material present (ex. Bb, bb, BB, etc)
|
|
|
What is phenotype?
|
The observable trait- what is seen physically. Ex. brown eyes
|
|
|
What is X-linked inheritance?
|
An x-linked genetic disorder where the recessive donated from the mother to the 23rd pair of chromosomes determines whether the child is free of symptoms, a carrier or exhibits the disorder. If a mother is heterozygous for the disorder: male is 50% likely to get the disorder, females are 50% likely to be a carrier and 50% likely to exhibit. Ex, Hemophilia, blood clotting
|
|
|
What is polygenic inheritance?
|
When one possesses extra chromosomes. Ex. Downs Syndrome means the person has an extra 21st chromosome. Other diseases include sickle cell anemia, Tay Sachs, Klinefelters
|
|
|
What is amniocentesis?
|
By examining a small amount of fetal cells drawn by needle from the amniotic fluid of the unborn child, one can determine whether some genetic disorders, etc are present
|
|
|
What is ultrasound sonography?
|
The process in which high frequency sound waves scan the mothers unborn child to produce an image that is used to access the size, shape and physical development
|
|
|
What is the first stage of labor?
|
It is 16- 24 hours long with contractions between 8-10 minutes. Toward the end there is a transition period where the contractions are the strongest and most frequent. By the end the cervix is completely open.
|
|
|
What is the second stage of labor?
|
It is the 90 minutes between the head starting to move through the cervix and birth canal and completely exiting the mothers body
|
|
|
What is the third stage of labor?
|
It is when the umbilical cord and placenta have been expelled. It only lasts a few minutes
|
|
|
What is oxytocin and what is it's significance?
|
It is a hormone released from the pituitary gland around 266 days after conception that causes the uterus to start having contactions
|
|
|
What is the Apgar scale?
|
The standard scale of measurement for good neonatal health. 5 qualities: appearance (color), pulse (heart rate), grimace (reflex irritability), activity (muscle reflex) and respiration. Each category is scored between 0-2 points for a total of 10 points. Most babies are 7 or greater. Less than 7 requires assistance to start breathing, less than 4 requires immediate life saving aid
|
|
|
Anoxia
|
Deprivation of oxygen during birthing stage. Brief periods of this will not cause any long lasting effects.
|
|
|
What is the mother minimum hospital stay after birth?
|
Legislation requires insurance to provide coverage for 48 hours after birth. American Academy of Pediatrics says no less than 48 hours
|
|
|
What are the causes of preterm and low birth weight?
|
Preterm is less than 38 weeks after conception, low birth weight is less than 5.5 lbs. Young age, pregnancies too close to one another, multiple babies at one time, health of mother, nutrition, medical care, economic support, environment
|
|
|
What is episiotomy?
|
A surgical incision made to enlarge the vaginal opening to help wit delivery. Imminent birth, head to large, baby in distress.
|
|
|
What is a Cesarean section?
|
Surgically removing the baby from the uterus due to fetal distress, breech position (feet first), transverse (horizontal position), baby's head being to large (usually post-term babies)
|
|
|
What has caused a soaring rate of Cesarean births?
|
The use of fetal monitors that monitor baby's heart rate. Often causing false results. These monitors are no longer standard procedure.
|
|
|
What are the consequences of Cesarean section?
|
Risk of infection, longer recovery, more stress on the baby
|
|
|
What are the reflexes of the new born?
|
Unlearned, organized involuntary responses that occur automatically. Sucking and swallowing are signs of hunger and eating. Rooting is turning in the direction of a light touch to the face or mouth (feeding). Others: coughing, sneezing, crying
|
|
|
What is the Lamaze birthing method?
|
Relaxation training with the help of a "coach" usually the cooperating soon to be father. Training to focus on a relaxing stimulus to positively deal with the pain.
|
|
|
What is the Leboyer birthing method?
|
Making the birth less stressful for the baby by creating an environment similar to the womb by dimming and softening the lights, allowing the baby to take several first breaths on the mothers stomach while still having the umbilical cord attached and then placing the baby in a warm bath afterward.
|
|
|
What is an infant related example of classical conditioning?
|
A hungry baby stops crying when her mother picks her up because she has learned to associate being picked up with subsequent feeding.
|
|
|
What is an infant example of operant conditioning?
|
An infant who learns that smiling at his or her parents brings positive attention so they may smile more often.
|
|
|
What is habituation?
|
The decrease in the response to stimulus that occurs after repeated presentations of the same stimulus.
|
|
|
What is an infant example of habituation?
|
A baby who showed interest and surprise at first seeing a novel toy may show no interest after seeing the toy several times.
|
|
|
What is the cephalocaudal principle?
|
Growth follows a pattern that begins at the head and upperbody and downward. During gestation and after birth developing our abilities. Head to toe.
|
|
|
What is the proximodistal principle?
|
development from the center of the body outward
|
|
|
What is plasticity?
|
the degree to which a developing structure or behavior is susceptible to experience. Ex. the cerebral cortex is not hard wired for life, this allows it to adapt to the environment it's in.
|
|
|
What are babies sleep schedules like?
|
Babies spend much more time asleep than in a wakeful state. They spend 20% of the time in REM sleep stage for the first several months due to autostimulation. Their body is developing rhythms- adjusting and organizing them
|
|
|
What did the SIDS rate decrease in the 1990s?
|
Guidelines for sleeping changed. The general rule of thumb is sleep on back and give them a pacifier during naps and bedtime.
|
|
|
What are general motor skills?
|
rolling over, grasping a rattle, walking, etc.
|
|
|
What are fine motor skills?
|
Nervous system and muscles interact on a trial and error basis as an infant. Effective movement cause the infant to create more synaptic contacts.
|
|
|
What is the Brazelton Neonatal Behavior Assessment?
|
Determine an infants neurological and behavioral responses to their environment as compared to norms gotten from testing these responses in many infants. Can substitute the Apgar Test
|
|
|
What is marasmus?
|
a disease caused by severe deficiencies in protein and calories during the first year of life: cessation of growth and physical wasting causing death.
|
|
|
Kwashiorkor
|
a disease in which a childs stomach, limbs and face swell due to malnutrition- older babies/children
|
|
|
What does the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend in regards to breast feeding?
|
It is best for the first 12 months of life, providing over 65 percent reduction in infection. Breast milk is more easily digested and has all the essential nutrients a child needs.
|
|
|
What was Robert Franz's research of infant visual preferences?
|
Idont know yet
|
|
|
Describe a newborn infants hearing abilities.
|
idk yet
|
|
|
Rolling over
|
3.2 months
|
|
|
Graspting rattle
|
3.3 months
|
|
|
Sitting without support
|
5.9 months
|
|
|
Standing while holding on
|
7.2 months
|
|
|
Grasping with thumb and finger.
|
8.2 months
|
|
|
Standing alone well
|
11.5 months
|
|
|
Walking well
|
12.3 months
|
|
|
Building a tower of two cubes
|
14.8 months
|
|
|
Walking up steps
|
16.6 months
|
|
|
Jumping in place
|
23.8 months
|
|
|
What is the percent that babies perform the specific tasks at the specific month in the milestones of motor development?
|
50%
|
|
|
What was Franz' research on infant visual preferences?
|
He built a chamber, had babies lie on their backs and view patters on the ceiling- he looked to see which patterns were reflecting on the infants eyes to see what they preferred.
Infants show preference for stimuli that have patterns or smaller stimuli. They prefer curved over straight, 3D over 2D, human face over non-human) |
|
|
What are newborns hearing abilities?
|
Infants hear before birth. They are more sensitive to high and low frequencies. They start to develop hearing that is more in the middle toward adult hearing after age 1.
|

