![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

CONGRESS OF VIENNA |
OBJECTIVES: Balance the power For Royal families to regain power Allience between monarchies Restablish peace in Europe |
|

FRENCH |
French liberals overthrew the Burbon Monarch Charles X and stablished a constitutional monarchy. This was a success |
|

BELGIUM |
Belgian nationalists rose up against Dutch control and created an independent state. This was a success |
|

POLAND |
Russian authorities crushed a nationalist uprising and blocked efforts to stablish an independent Poland. This uprising failed. |
|

ITALIAN |
Austrian troops put down nationalist revolts in various Italian States, the uprising failed. |
|

1848 FRANCE |
Bad situation or french people, so they overthrew the monarchy and settled for a Second Republic with a new Constitution. Charles Louis Napoleon Bonaparte was elected president. |
|

1848 GERMAN STATES |
The Congress of Vienna had recognized 38 German states with Austria and Prussia as the more powerful. German rulers promised a lot of good things. Frankfurt Assembly was held to prepare a constitution, to have the emperor with limited power and wit deputies elected. This failed. |
|

1848 AUSTRIAN EMPIRE |
Multinational empire, but revolutionary forces demanded a liberal constitution. This attempts failed, the goverment gave Hungary its own legislature. |
|

1848 ITALIAN STATES |
After the Congress of Vienna, italian people wanted a liberal constitution and a unified Italy. This was a failure, the old order prevailed. |
|

IMPERIALISM Causes |
CAUSES: -Industrial Revolution -New places to invest -Spread their religion -Global-dominance prestige -Show superiority -Seize markets |
|

IMPERIALISM (System) |
System: Direct rule- local elites are replace with officials from the mother country. Destroy traditional culture. (Assimilation) Indirect rule: Cooperation with local elites, respect for local culture. (Association) |
|
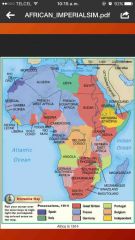
|
Belgium- Congo Portugal- Mozambique, Angola Germany- German SouthWest Africa, German East Africa, Cameroons, Togoland France- Morocco, Algeria, French West Africa, French Equatorial Africa, Madagascar. Great B- South Africa, Echuanaland, South and North Rnooesia, Uganda, Kenya, Sudan, Egypt, Somallia, Nigeria, Gold Coast, Sierra Leone, Gambia Italy- Guinea, Libya, Eritrea Spain- Rio Muni, Rio de Oro |
|

AFRICAN IMPERALISM Causes |
CAUSES: Christianity --- Commerce --- Civilization
Conference of Berlin 1884 Otto Von Bismarck set ground rules for future annexations of African territory to European nations. The free commerce in Congo was settled and also, new efforts to end the slave trade.
|
|
BRITISH RAJ Intro and pros |
After the Great Rebellion, the Queen Victoria sent a viceroy to rule in India. There was an increase in nationalism in India after the Sepoy's mutiny. There were some pros to the British control: Order and stabiliy, efficient government, school system, postal service, etc. |
|
BRITISH RAJ Cons and resolution |
The negative points for British rule: Economic cost, local industries destroyed, high taxes, damage in textile industry, starvation, among others.
The Indian Nationalist movement started with highly educated indians, One of the main characters is Mahatma Gandhi. Seeked reform not revolution. |
|

OPIUM WAR |
Northern India was groing opium under the sponsorship of British Companies, this was sent directly to Chineese markets. This wasn't good for China so (after asking it nicely and being ignored) war broke out. The British crushed the Chineese army but they got into an agreement (Treaty of NanJing) |
|
THE BOXER REBELLION |
-Members of the Society of Harmonius Fists -Disagreement with the foreign economic policies -"DESTROY THE FOREIGNER" -An allied army of western countries defeated the boxers and asked for indemnization. |
|
|
GERMAN UNIFICATION |
39 Weak states after the Congress of Vienna Austria and Prussia were the most powerful states Otto von Bismark led Prussia in the 7 WEEKS WAR against Austria.
|
|

GERMAN UNIFICATION |
39 Weak states after the Congress of Vienna Austria and Prussia were the most powerful states Otto von Bismark led Prussia in the 7 WEEKS WAR against Austria.
|
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Intro) |
-Japan isolation with Tokugawa Shogunate -Millard Filmore (U.S president) -> kanagawa Treaty: -End of Isolation -Japanese ports for trade -U.S Consulate in Japan |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Intro) |
-Japan isolation with Tokugawa Shogunate -Millard Filmore (U.S president) -> kanagawa Treaty: -End of Isolation -Japanese ports for trade -U.S Consulate in Japan |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Political transformation) |
Liberals vs. PROGRESSIVES
-Power shared between powers but executive has more control.
Democratic in form but authoritarian in practice. |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Intro) |
-Japan isolation with Tokugawa Shogunate -Millard Filmore (U.S president) -> kanagawa Treaty: -End of Isolation -Japanese ports for trade -U.S Consulate in Japan |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Political transformation) |
Liberals vs. PROGRESSIVES
-Power shared between powers but executive has more control.
Democratic in form but authoritarian in practice. |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Economic transformation) |
-Lands as private property (with tax) -Improvement in transportation and communication -Weapons and shipbuilding as main industries -Subsidies |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Intro) |
-Japan isolation with Tokugawa Shogunate -Millard Filmore (U.S president) -> kanagawa Treaty: -End of Isolation -Japanese ports for trade -U.S Consulate in Japan |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Political transformation) |
Liberals vs. PROGRESSIVES
-Power shared between powers but executive has more control.
Democratic in form but authoritarian in practice. |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Economic transformation) |
-Lands as private property (with tax) -Improvement in transportation and communication -Weapons and shipbuilding as main industries -Subsidies |
|
|
IMPERIALIST JAPAN (Social transformation) |
-Universal education -New imperial army -Women 3 obedience: Child to father, wife to husband, widow to son. -Western fashion culture. |
|
|
QING DYNASTY'S DECLINE Factors |
-External pressure form westernization. -Government corruption and incompetence -Peasant riots -A lot of population -Deficit in British commercial balance -Opium war |
|
|
PING REBELLION (Main cause and objectives) |
Sparked by the leadership of Hong Xiuquan.
Objectives: -Solve economic Problems -Land for them -Destroy Quing Dynasty -Stablish the Taiping Tianguo (Heavenly Kingdom of Great Harmony) |
|
|
PING REBELLION (Main cause and objectives) |
Sparked by the leadership of Hong Xiuquan.
Objectives: -Solve economic Problems -Land for them -Destroy Quing Dynasty -Stablish the Taiping Tianguo (Heavenly Kingdom of Great Harmony) |
|
|
TAIPING REBELLION (Beliefs) |
-Common property -Land Reform -Equality for women -Abstinence from Opium -Calendar reform -Literary reform -A new Political-Militsry organization |
|
|
PING REBELLION (Main cause and objectives) |
Sparked by the leadership of Hong Xiuquan.
Objectives: -Solve economic Problems -Land for them -Destroy Quing Dynasty -Stablish the Taiping Tianguo (Heavenly Kingdom of Great Harmony) |
|
|
TAIPING REBELLION (Beliefs) |
-Common property -Land Reform -Equality for women -Abstinence from Opium -Calendar reform -Literary reform -A new Political-Militsry organization |
|
|
ONE HUNDRED DAYS REFORM |
-Emperor Guang Xu -Political, administrative, education reforms -Modernization following western image
|

