![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Conditions patients usually complain about |
● Pain ● Swelling ● Esthetics ● Difficulty in mastication ● Difficulty in swallowing |
|
|
imbued with the responsibility of taking care of the oral health of people |
dentists |
|
|
two morbid states that often present several diagnostic dilemmas to the dentist |
Inflammation and Infection |
|
|
presence of a reproducing pathogen (bacteria, viruses etc.) in the body. |
infection |
|
|
can happen without any inflammation |
tetanus infection |
|
|
a common response by the body to infection or general disturbance. |
inflammation |
|
|
A localized protective response elicited by injury or destruction of tissues, which serves to destroy, dilute or wall off the injurious agent and the injured tissue. |
inflammation |
|
|
Cardinal signs of Inflammation: |
Calor (heat; hyperemia) ● Dolor (pain; nerve chemical mediators ● Functio laesa (loss of function; pain) ● Rubor (redness; hyperemia) ● Tumor (swelling; exudation) |
|
|
Mechanism of Inflammation |
Vasodilation ● Exudation ● Emigration ● Chemotaxis |
|
|
Excessive swelling causes congestion of the tissues ● Congestion may cause compression of vital tissues |
swelling |
|
|
Probably the single most important reason why patients see dentists ● Discomfort may interfere with a patient's activities. |
pain |
|
|
Managing pain and swelling begins with |
identifying the cause |
|
|
Signs of infection: |
Fever ● Lymphadenopathy ● Abscess ● Cellulitis ● Inflammation ● Trismus |
|
|
The invasion of a host organism's bodily tissues by disease causing organisms, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce |
infection |
|
|
Always caused by microbial invasion |
infection |
|
|
Not always caused by an infections |
inflammation |
|
|
Managed with antibiotics |
infection |
|
|
Managed by NSAIDs or other inflammatory measures |
inflammation |
|
|
Thorough examination: |
● Dental caries ● Periodontitis ● Ulcerations ● Traumatic occlusion ● Areas of erythema ● Percussion ● Absence of visible causes ● Radiographic evaluation ● Palpation |
|
|
S.O.C.R.A.T.E.S. |
Site - ● Onset - sudden or gradual? ● Character - ● Radiation - ● Associations - ● Time course - ● Exacerbating/Relieving Factors - ● Severity |
|
|
greater than that of paracetamol and is comparable to that of weak opioids |
analgesics of nsaids |
|
|
weak opiods |
(codeine, tramadol, |
|
|
required to achieve anti inflammatory than analgesic effects |
higher doses |
|
|
Optimum duration of treatment for analgesic purposes |
3 days |
|
|
Patients benefit from receiving optimal NSAID doses given at regular, ‘‘___ ’’ time interva |
clock based |
|
|
It is recommended to give NSAIDs before surgery. |
Pre-operative analgesia |
|
|
less effective as an analgesic when compared with ibuprofen and naproxen. |
celecoxib |
|
|
Combination therapy of NSAIDs andParacetamol NON OPIODS DRUG |
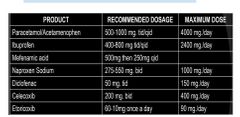
|
|
|
analgesic effect of acetaminophen is considered ____ when combined with NSAIDs |
synergistic |
|
|
A commercially available combination product containing ______ may be an option and is easy to prescribe. |
opioid and acetaminophen |
|
|
Commonly prescribed opioid for dental use |
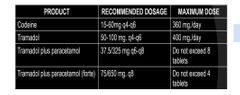
|
|
|
also known as narcotic analgesics. They have the potential for addiction and require a prescript |
opioid drugs |
|
|
are indicated for prevention of inflammatory manifestations (edema and trismus) (professional agreement) |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
Use of steroid as an |
anti inflammatory |
|
|
duration of steroid use |
The optimum duration of treatment is 3 days, with a maximum of 5 days (professional agreement); since this |
|
|
The invasion of a host organism's bodily tissues by disease causing organisms, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce |
infection |
|
|
Most odontogenic infections due to |
mixed flora |
|
|
Most Odontogenic Infections Are Compose |
Aerobic – 5% ○ Anaerobic – 35% ○ Mixed – 60% |
|
|
stages of infection |
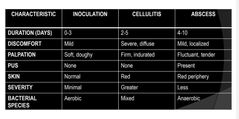
|
|
|
cellulitis |
A painful swelling of the soft tissue of the mouth and face resulting from a diffuse spreading of purulent exudate along the fascial planes that separate the muscle |
|
|
abscess |
- Well defined localized borders● Pus accumulation in tissues● Fluctuant to palpation● Considered a chronic state |
|
|
Inflammatory causes of oral pain● Pulpal |
Reversible Pulpitis○ Irreversible Pulpitis○ Periapical Periodontitis○ Localized dentoalveolar abscess○ Facial cellulitis |
|
|
Inflammatory causes of oral pain peeiodontal |
Lateral periodontal abscess○ Pericoronitis○ Dry socket○ Plaque induced gingivitis○ Chronic periodontitis |
|
|
A considerable percentage of dental pain originates from acute and chronic infections of pulpal origin |
operative intervention |
|
|
should only be used in acute periodontal conditions where drainage or debridement is impossible, |
systemic antimictobials |
|
|
Factor Influencing Post-operative Infections |
-Size of bacterial inoculum ● Duration of surgery ● Presence of foreign body/implants ● State of host resistance |
|
|
Cardiac Conditions Considered for Antibiotic Prophylaxis |
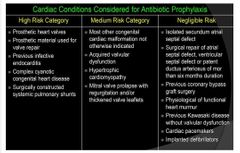
|
|
|
Common procedures done in the dental office |
-Extractions (single or multiple) ○ Frenectomies ○ Torus removal ○ Chronic apical infections |
|
|
Antibiotics must be in place prior to start of surgery |
Oral – 1 hour prior to surgery ■ Parenteral – less than 1 hour |
|
|
timing : Prolonged surgeries |
penicillin and clindamycin give every 3 hou |
|
|
timing : “Post operative prophylaxis” |
Evidence indicates increased infection if started after 2 hours |
|
|
Antibiotics are indicated in severe infections ● Signs Of Severety |
Fever ○ Dehydration ○ Rapid progression of swelling ○ Trismus ○ Quality and/or location of swelling ○ Marked pain ○ Elevation of tongue ○ Difficulty with speech and swallowing |
|
|
limited number of localized oral lesions that are indicated for antibiotic |
Periodontal abscess ○ Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis ○ Pericoronitis. |
|
|
Organism causing infection is not seen ● Prescription is not based on luck ● Experience in previous treatments are the main basis ● Also based on our knowledge of the most common organisms involved in odontogenic infection ● Based on knowledge of antibiotic sensitivity of the suspected organism |
Empirical antibiotic prescription |
|
|
Commonly prescribed antibiotics in dental practice |
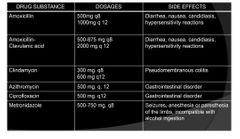
|
|
|
Empiric therapy based on predictable organisms |
antibiotic therapy |
|
|
antibiotic of choice |
amoxicillin |
|
|
limited action on anaerobic |
Cephalosporin |
|
|
broad spectrum, less effective than penicillin. Largely replaced by Azithromycin |
erythromycin |
|
|
effective only against anaerobes |
metronidazole |
|
|
such as ciprofloxacin for established osteomyelitis |
quinolones |
|
|
is the shortest time that will prevent both clinical and microbiological relapse. |
ideal antibiotic duration |
|
|
usually mentioned in the known resources for antibiotic prescribing, |
frequency of prescribing |
|
|
most commonly based on expert opinion. |
whereas duration of treatment recommended in therapeutic guidelines |
|
|
most patients with acute dentoalveolar infections can safely be 2-3 days, provided that drainage has been establishe |
duration of antibiotic therapy |

