![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Flow-inflating bags _______ work without a compressed gas source.
a. will b. will not |
b. will not |
|
|
A baby is born apneic and cyanotic. You clear her airway and stimulate her. Thirty seconds after birth, she has not improved. The next step is to
a. stimulation b. begin positive-pressure ventilation |
b. begin PPV |
|
|
The single most important and most effective step in neonatal resuscitation is
a. stimulation b. ventilating the lungs |
b. ventilating the lungs |
|
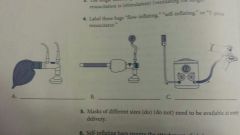
Label these
|
a. flow-inflating
b.self-inflating c. T-piece resuscitator |
|
|
Masks of different sizes ______ need to be available at every delivery.
a. do b. do not |
a. do
|
|
|
Self-inflating bags require the attachment of a ___________ to deliver a high concentration of oxygen.
|
oxygen reservior
|
|
|
T-piece resuscitators ________ work without a compressed gas source.
a. will b. will not |
b. will not
|
|
|
Neonatal ventilation bags are ____________ as adult ventilation bags.
a. much smaller than b. the same size as |
a. much smaller than
|
|
|
List the principal safety feature for each of the following devices:
Self-inflating bag _______ and______ Flow-inflating bag ______ and______ T-piece resuscitator ____ and______ |
Self - Pop-off valve and pressure gauge
Flow - Pressure gauge T-piece - Maximum pressure relief control and pressure gauge |
|
|
Free-flow oxygen can be delivered reliably through the mask attached to a
a. flow-inflating bag b. self-inflating bag c. T-piece resuscitator |
a. and c. but not through a self-inflating
|
|
|
When giving free-flow oxygen, place the mask ________ on the baby's face to allow some gas to escape around the edges of the mask.
a. securely b. loosely |
b. loosely
|
|
|
Before an anticipated resuscitation, the ventilation device should be connected to a(n) ___________, which enables you to provide oxygen in any concentration, from room air up to 100% oxygen.
|
blender
|
|
|
Resuscitation of the term newborn may begin with _______% oxygen. The inspired oxygen concentration used during resuscitation is guided by the use of a(n) ________, which measures oxygen saturation.
|
21%
oximeter |
|

|
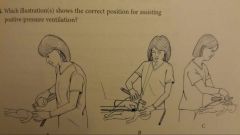
baby "A" is in the sniffing position
|
|
|
position A and B are both correct
|
|
|
You must hold the resuscitation device so that you can see the newborn's ________ and ________.
|
chest and abdomen
|
|
|
An anatomically shaped mask should be positioned with the __________ end over the newborn's nose.
a. pointed b. rounded |
a. pointed
|
|
|
When ventilating a baby, you should provide positive-pressure ventilation at a rate of _________ to_________ breaths per minute.
|
40 to 60
|
|
|
If you notice that the baby's chest looks as if he is taking deep breaths, you are __________ the lungs, and it is possible that a pneumothorax may occur.
a. overinflating b. underinflating |
a. overinflating
|
|
|
Begin positive-pressure ventilation with an initial inspiratory pressure of _____cm H2O
|
20
|
|
|
"MR SOPA" stands for:
|
M = Mask adjustment
R = Reposition airway S = Suction mouth and nose O = Open mouth P = Pressure increase A = Airway alternative |
|
|
Your assistant assesses effectiveness of positive-pressure ventilation by first assessing the _______ and _______ along with listening for _______ _______. If these signs are not acceptable, you should look for_______ movement.
|
heart rate and oximetry
breath sounds chest |
|
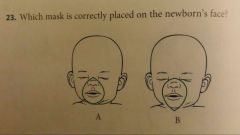
|
mask A
|
|
|
You have started positive`pressure ventilation on an apneic newborn. The heart rate is not rising, oxygen sateration is not improving, and your assistant does not hear bilateral breath sounds.
List 3 possibilities of what may be wrong. |
There may be an inadequate seal of the mask on the face.
The head may need to be repositioned to open the airway. Secretions may need to be suctioned. |
|
|
If, after performing the ventilation corrective sequence and making appropriate adjustments, you are unable to obtain a rising heart rate or bilateral breath sounds or see chest movement with positive-pressure ventilation, you usually will have to insert a(n) __________ or a(n)__________.
|
endotracheal
laryngeal mask airway |
|
|
You have administered positive-pressure ventilation (with bilateral breath sounds and chest movement) for 30 seconds. What do you do if the baby's heart rate is now
Below 60 bpm?____________________ More than 60 bpm and less than 100 bpm but steadily improving with effective positive-pressure ventilation?_________________________ More than 60 bpm and less than 100 bpm and not improving with effective positive-pressure ventilation?_________________________ |
Begin chest compressions and consider intubation
Adjust oxygen, gradually decrease pressure as heart rate improves, insert orogastric tube, continue monitoring Repeat MR SOPA and consider intubation. |
|
|
Assisted ventilation may be discontinued when
1._______________________ 2._______________________ |
heart rate is above 100 breaths per minute
baby is breathing |
|
|
If you must continue positive-pressure ventilation with a mask for more than several minutes, a(n) ______________ should be inserted to act as a vent for the gas in the stomach during the remainder of the resuscitation.
|
orogastric tube
|
|
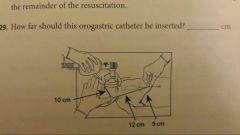
|
22 cm (10cm + 12cm)
|

