![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
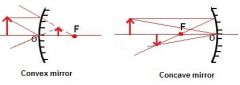
What is the difference between concave and convex mirrors? |
|
|
|
|
What is the relation of focal, center of curvature, and the mirror? |
Focal point is 1/2 distance between mirror and center of curvature. |
|
|
|
Relate center of curvature and radius |
Center of curvature is the radius of the circle. |
|
|
|
Relate focal length, object distance, and image distance |
1/f = 1/o + 1/i |
Randy Foi. |
|
|
relate radius of curvature to the optics equation |
1/f = 1/o + 1/i = 2/r |
foier! |
|
|
Concave pnemonic? |
Look into the cave |
|
|
|
For a mirror where is the positive focal point? |
We want the light rays to converge on the same side as incoming light. |
|
|
|
How can you define a real image? |
If the central ray and parallel ray converge |
|
|
|
Define a virual image |
Eye extrapolates a image (light rays don't actually converge) |
|
|
|
For mirrors when do lights ray diverge and when do they converge? |
diverge in convex mirror. converge in concave mirror. |
|
|
|
What is the equation for magnification? |
(-i)/o |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a parallel ray and a central ray? |
parallel goes from object to mirror in a line parallel to central axis then through focal point. central ray goes from object to mirror on a diagonal then through focal point. |
|
|
|
What is true of all real images? |
They are inverted. |
Think about how images are formed on the retina. |
|
|
For concave mirror if rays converge on same side incoming light? |
Real. Converge at Positive Focal Point. |
|
|
|
For concave mirror, if rays converge on other side of mirror of incoming light? |
Virtual, converge at negative Focal point. |
|
|
|
For concave mirror, object behind focal point. |
Real Inverted Magnified |
Behind the R.I.M. |
|
|
For concave mirror, object on top of the focal point |
no image. rays never converge. |
|
|
|
Object in front of the focal point |
Magnified Upright Virtual. Light rays converge behind the mirror. virtual. |
MUV in front. |
|
|
What is true of all convex mirrors? |
Light rays diverge |
|
|
|
For all converging mirrors, what is the focal point of the image going to show? |
Negative focal length |
|
|
|
No matter where the object is what is the image going to show? |
Upright Reduced Virtual |
U Really Vex me. |
|
|
For Lenses, convex lenses are always? |
Converging. |
|
|
|
Where do we want the light rays to converge for lens in general? |
Opposite side of mirror. This will be the + focal point. |
Opposed to mirrors. |
|
|
For lenses, concave lenses are always? |
Diverging. |
|
|
|
For convex lenses object behind the focal point? |
Real Inverted Magnified |
Behind the R.I.M. |
|
|
For convex lenses object at the focal point, |
no image. rays never converge |
|
|
|
For convex lenses, object in front of the focal point? |
Magnified Upright Virtual converge on the same side as incoming light. |
MUV in front |
|
|
The rules of a convex lenses = |
Rules of a concave mirror |
Both converging. |
|
|
rules of a concave lens = |
rules of a convex mirror. |
|
|
|
For a concave lens |
reduced virtual upright |
same as convex mirror. |

