![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
When owner of goods , delivers (delivery aka bailment) goods to bank, to get loan secured, its called |
Pledge |
|
|
|
Pledge is defined under |
Sec 172 of indian contract act 1871 |
|
|
|
Actual (with bank ) / contructive delivery |
Cd = financing of warehousing receipts |
|
|
|
Pledge can be created by |
1. Owner of goods 2. Merchantile agent 3. Seller of goods who is still in possession of goods |
|
|
|
Borrower is callled pawnor/ pledger/ bailor |
Bank is called pawnee / pledger / bailee |
|
|
|
In pledge ownership n possession |
With borrowr With bank Ex gold loan |
|
|
|
Und sec 176 |
Notice will be given bfre selling goods |
|
|
|
Rights of bank wrt pledge |

|
|
|
|
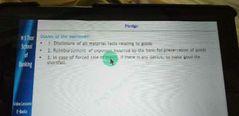
Duties of borrower wrt pledge |
|
|
|
|
Case law in SC WRT pledge |

Accretion is increase in value of security |
|
|
|
Hypothecation def und |
Under sec 2 of SARFAESI Act 2002 |

|
|
|
Hypothecation other points |

|
|
|
|
In case of default in hypothecation |
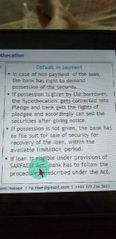
Notice is given under sec176 after filing suit |
|
|
|
Diff btwn pledge, hypo n mortgage |
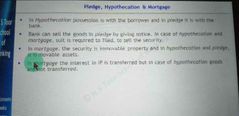
|
|
|
|
On railway receipts what type of charge is created |
Since its goods, pledge is created |
|
|
|
Mortgage is called equitable charge t or f |
F! Hypothecation is equitable charge |
|
|
|
Interest in propety is trf in case of |
Mortgages |
|
|
|
Bill of exchange are drawn to cover legally.. |
Payment arising out of sale or purchase of goods n serviced by people or firms |
|
|
|
Bill of exch is under |
Sec 5 of ni act |
|
|
|
Boe is unconditional order of drawer (seller/suresh )to drawee (david) |
True |
|
|
|
Firm who signs boe is called |
Drawer |
|
|
|
Firms who r odered to pay are called |
Drawee |
Sometimes payee could be drawer himself |
|
|
A. Holder (sec___ of ni act) B. Holder in due course (sec ___) C. Payment in due course (sec... D. Negotiation (sec.. E. Endorsement (sec... F. Liability of drawer(sec... G. Liability of acceptor(sec.. H.. Liability of endorser (sec... I. Int rate( if specicied under sec 79 of 18% as per sec .... |
A. 8 B. 9 C. 10 D. 14 E. 15 F. 30 G. 32 H. 35 I. 80 |
ALL ARE OF NI ACT 1991 B. Shld have boe in possession, boe shld be obtained for considerstion. |
|
|
Inland bills Foreign bills Demand bills |
Sec 11 Sec 12 Sec 19 |
Demand bills r payable on denand. Usance bills r payable on maturity not demand. |
|
|
Clean bills |
Not supported by documents of title goods |
Documentary bills r accompanied by documents of title to goods |
|
|
Clean bills r drawn when goods r directly sent to buyer |
T |
|
|
|
Different types of bill financing 3 |
Bills purchasing Bills discounting (usance bills) Advance against collection of bills |
|
|
|
More than 1 parties ( drawer n drawee ) are liable on boe |
T |
|
|
|
Bills are easily transferable |
T |
|
|
|
Document in which the ownership can be transferred by endorsement n delivery is called |
Document of title to goods |
|
|
|
Co acceptance scheme of boe |
Bank gives co acceptance on the bills accepted by the drawee |
|
|
|
Under drawee bills scheme |
Bank agrees to pay the drawer of the bills drawn on its borrowers (buyer) on presentation n recover on due date |
|
|
|
How many parties are involved in case of dishonor of usance bill |
2 |
|
|
|
Holder of boe is a person sho obtains its possession for value and is in actual possession of boe |
True |
|
|
|
What is legal status of a bank when boe is purchased by bank |
Bank becomes holder for value |
|
|
|
Usance bills are.. demand bills are... |
Discounted / accepted Purchased |
|

