![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
207 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SS category? |
The SS category encourages strategies that minimize the impacts on ecosystems & water resources |
|
|
EA category? |
The EA category promotes better building energy performance & ozone protection through energy optimization, refrigerant management, renewable energy, and commissioning strategies. |
|
|
What is the 40/60 rule? |

|
|
|
What are the 3 MPRs? |
1- Must be in a Permanent location on existing land 2- Must use reasonable LEED boundaries 3- Must comply with project size requirement (for LEED BD+C a minimum of 1000 sq ft gross floor area) |
|
|
With a photo explain different types of boundaries? |
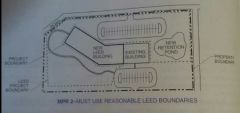
|
|
|
What are the steps in LEED certification Process? |
1- Register project 2- Prepare application 3- Submit application - preliminary design review - Final design review (optional) - Preliminary construction review - Final construction review(optional) 4- Receive certification |
|
|
What are the 11 recommended steps of a LEED work plan? |

|
|
|
What are the application of certification Paths? |
For the certification of multiple buildings |
|
|
What are the 2 certification paths that are applicable to LEED BD+C? |
- LEED Volume Program - LEED Campus Program |
|
|
What is LEED Volume Program? |
If the project owner is planning multiple similar buildings in different locations, the LEED Volume Program may allow the owner to streamline certification through the use of prototype standards. |
|
|
What is LEED Campus Program? |
The LEED Campus Program is commonly used for multiple projects that are on a shared site under the control of a single entity seeking individual certification for each building. |
|
|
What are the 2 approaches under campus program? |
- the group approach allows buildings that are substantially similar and are in a single location to certify as one project that shares a single certification. - the campus approach allows buildings that share a single location and site attributes to achieve separate LEED certification for each project, building space, or group on the master site. |
|
|
What are CIRs? |
- The purpose of Credit Interpretation Rulings or Credit Interpretation Requests is clarification of a single issue on one credit or prerequisite. - CIRs must request guidance on only one MPR, credit, or prerequisities and generally contain one or multiple related questions. - Because CIRs are project specific, a CIR cannot apply to another project |
|
|
What are LEED interpretations? |
- LEED interpretations are official answers to formal technical inquiries about implementing LEED on a project. - They are similar to CIRs but they can be applied to other projects. - LEED interpretations are published in a searchable database found on USGBC website. |
|
|
How we can define Homes, Midrise, or New Construction? |
|
|
|
What are the differences between project CIR & LEED Interpretation? |

|
|
|
What are addenda? |
Addenda incorporate changes & improvements to LEED rating systems and reference guides to help clarify, correct, interpret or provide alternative language. Addenda are subject to USGBC committee review and are published quarterly. Project teams must follow addenda published prior to their project's registration date. |
|
|
What are ACPs? |
- Alternative Compliance Paths are developed by USGBC to recognize environmental & climate differences in conditions, codes, laws, and standards based on different locations (to cover the projects outside the US). - ACPs for LEED credits provide additional options that address unique circumstances. - Some ACPs are available only for projects outside the US, however the others can be used regardless of location. |
|
|
What is the LEED Pilot Credits? |
The LEED Pilot Credit Library is like a database designed to test new and revised LEED credit language & ACPs. The library is a feedback loop for both testing & comments. - It's like a forum. project teams can see all the comments to increase their information & USGBC can collect comments to refine credits. |
|
|
How many types of special project situations are there & what are them? |
1- Mixed-Use Projects 2- Multitenant Complexes 3- Incomplete Spaces 4- Projects With Several Physically Distinct Structures |
|
|
What is a development footprint? |
A development footprint is the total land area of a project site covered by buildings, streets, parkings area, and other impermeable surfaces constructed as part of the project. Surfaces paved with permeable pavement (at least 50% permeable) are excluded from development footprint. |
|
|
How is the residential building occupancy calculated? |
The number of bedrooms plus one for each unit. |
|
|
life-cycle costing (LCC)? |
An analytic tool used to determine the most cost-effective option among competing alternatives based on the costs of the options throughout their life cycles. |
|
|
hard costs? |
Initial costs associated directly with the construction of a project, such as materials and labor. |
|
|
FTE? |
full-time equivalency is a designation for a building occupant, or full-time-equivalent employee, who spends 40 hours per week in the project building. |
|
|
soft costs? |
Initial costs that cover expenditures such as design fees, commissioning agents fees, and energy modeling fees. |
|
|
previously developed site? |
A site that, prior to the project, consisted of at least 75% previously developed land. |
|
|
What are the Phases of integrative process? |
1- Discovery Phase 2- Design & Construction phase (implementation) 3- Occupancy, operations, and performance feedback phase |
|
|
How long should be the charrette to comply with IP Prequisite-Integrative Project Planning & Design for Healthcare project? |
A minimum of 4-hour integrative design charrette |
|
|
How many people should be involved in an integrated project team as part of IP-prerequisite? |
As many of design & construction professoinals involved in the project as feasible (Minimum of four), in addition to the owner or owner's representative. |
|
|
What is a water budget? |
A project-specific method of calculating the amount of water required by the building and associated grounds. The budget takes into account indoor, outdoor, process, and makeup water demands and any on-site supply, including estimated rainfall. |
|
|
What is an OPR? |
owners project requirements (OPR) is a written document that details the ideas, concepts, and criteria determined by the owner to be important to the success of the project. |
|
|
iterative process? |
A process used in design that involves conducting research, sharing data, receiving feedback, and refining the design repeatedly until all of a projects sustainable goals are met. |
|
|
What is simple box energy modeling analysis? |
A simple base-case energy analysis that informs the team about the buildings likely distribution of energy consumption and is used to evaluate potential project energy strategies. |
|
|
What is basis of design (BOD)? |
The information necessary to accomplish the owners project requirements (OPR), including system descriptions, indoor environmental quality criteria, design assumptions, and references to applicable codes, standards, regulations, and guidelines. |
|
|
How many prerequisites & credits does IP category have? What are them? |
1 prerequisite: Integrative project process & design, Applicable for Healthcare buildings 1 credit: integrative process |
|
|
How many prerequisites & credits does LT category have? What are them? |
No prerequisites. 8 credits: - LEED for Neighborhood Developmemt location - Sensitive Land Protection - High-Priority Site - Surrounding Density & Diverse Uses - Access to Quality Transit - Bicycle Facilities - Reduced Parking Footprint - Green Vehicles |
|
|
What type of parking spaces should not be included in total parking capacity? |
- on-street (parallel or pull-in) parking spaces on public right-of-way - parking spaces for fleet and inventory vehicles, unless these vehicles are regularly used by employees for commuting and business purposes - motorbike or bicycle spaces |
|
|
What are ineligible for LT credit-LEED for ND Location? |
- Prereviewed plans - Conditional approvals - any LEED ND Stage 1 projects |
|
|
What types of lands are listed as sensitive lands? |
- prime farmland - flood hazard areas - threatened or engangered species habitats - areas within 50 ft of wetlands - areas within 100 ft of water bodies |
|
|
What is the resource reference for prime farmlands? |
Prime farmlands are identified in the Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS) soil survey for the area or in a local equivalent for projects outside US. |
|
|
What is the resource reference for flood hazard areas? |
Flood hazard areas are identified in flood hazard maps by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and/or a local agency. Projects outside the US may use equivalent standards or determine the flood hazard area with a qualified peofessional. |
|
|
What is the resource reference for threatened or endagered species? |
Threatened or endangered species are identified under the US Endangered Species Act, listed by a state endangered species act, or classified by NatureServe as GH, G1, or G2. Outside the US local equivalents can be used. |
|
|
What is the resource reference for wetlands? |
Project located in the US can utilize the US Army Corps of Engineers' Wetland Delineation Manual for further guidance on wetlands. |
|
|
What is the definition of minor improvements? |
Any necessary improvement to enhance appreciation of the wetlands or water body and its buffer are considered minor and are allowed per the credit requirements. |
|
|
What are different types of minor improvement? |
- bicycle & pedestrian pathways no more than 12 ft wide (3.5), of which no more than 8 ft may be impervious - activities to maintain or restore native natural communities and/or natural hydrology - one single-story structure per 300 linear feet on average, not exceeding 500 sq ft - grade changes necessary to ensure public access - clearings, limited to one per 300 linear feet on average, not exceeding 500 sq ft each - brownfield remediation activities - removal of the following tree types: hazardous trees, up to 75% of dead trees; trees less than 6 in. diameter at breast height; up to 20% of trees more than 6 in. diameter at breast height with a condition rating of 40% or higher; trees under 40% condition rating (the condition rating must be based on an assessment by an arborist certified by the International Society of Arboriculture (ISA) using ISA standard measures) |
|
|
How much is 1 acre in sq ft? |
43560 sq ft |
|
|
In density calculations, what type of buildings should be excluded? |
-Project buildings & nonhabitable spaces, such as garages or public right-of-way, - and land that is excluded from development by law. |
|
|
What are the required distances for Density & Diverse uses? |
- average density with a 1/4 mile radius - diverse uses with in a 1/2 mile walking distance |
|
|
What are the eligible diverse use categories? |
1- Food retail (supermarket, grocery with produce section) 2- community-serving retail (convenience store, farmers market, pharmacy,....) 3- services (bank, hair care, restaurant, ....) 4- civic & community facilities (senior/child care, police or fire station, post office, public library, . . .) 5- Community anchor uses (Commercial office(100 or more full-time jobs), Housing (100 or more dwelling units)) |
|
|
What are different types of eligible transit vehicles? |
- bus - streetcar - bus rapid transit (BRT) - rail Or - Ferry |
|
|
How many minimum trips are required during weekdays? |
72 with multiple transit types & 24 with commuter rail or ferry service only |
|
|
How many minimum trips are required during weekends? |
40 with multiple transit types & 6 with commuter rail or ferry service only |
|
|
If transit service varies by weekdays, the .......... should be counted. If weekends counts are different, ........ should be used. |
- lowest number of trips - the average number |
|
|
What is the minimum percentage of students living in walking distance to get 1 credit for quality transit? |
%50 |
|
|
What is a Bicycle network? |
A bicycle network is a continuous network consisting of: 1- off street at least 8 ft wide for a two-way path & at least 5 ft wide for a one-way path 2- physically designated on street at least 5 ft wide 3- streets designed for a target speed of 25 mph or less |
|
|
How many short-term & long-term bicycle storage & shower facilities are required for residential buildings? |
- Short term= peak visitors x 0.025 - Long term= regular building occupants x 0.30 or the number of dwelling units, whichever is greater - additional shower are not required since they have access to showers in their units |
|
|
How many short-term & long-term bicycle storage & shower facilities are required for retail buildings? |
- Short term= 2 x [building floor area (sq ft)/5000] - Long term= regular building occupants x 0.05 - shower facilities 1 for the first 100 regular building occupants then for each 150 another 1 |
|
|
How long must the bicycle routes be? |
Any distance less than 3 miles |
|
|
What is the minimum number of short-term and long-term bicycle storage? |
At least 4 short-term & 4 long term except: - for schools, there is no need for short-term - for retails, at least 2 short-term & 2 long-term |
|
|
For reduced parking footprint, we have 2 cases; what are them? |
1- projects earning 1 or more points under either LT-surrounding density & Diverse uses or LT-Access to quality transit: ))) 40% reduction from base ratio 2- otherwise(no points under the 2 category): ))) 20% reduction from base ratio |
|
|
Under reduced parking footprint, what must the percentage of carpool parking be? |
5% after reduction are made |
|
|
How many parking spaces with fueling station are needed for LT-green vehicles? |
2% of total parking spaces |
|
|
What are the EVSE(Electeric Vehicle Supply Equipment) requirements? |
1- provide a level 2 charging capacity (208-240 V) or greater 2- comply with the relevant regional or local standards, such as the Society of Automative Engineers (SAE) surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772 3- Be networked or Internet addressable of participating in a demand response program or time-of-use pricing |
|
|
What is informal transit? |
A publicly available transit service that includes a fixed route service, fare structure, and regular operation. It does not consist of taxi, private shuttles, or seasonal, on-call, or on-demand transit. |
|
|
functional entry? |
A building opening designed to be used by pedestrians and open during regular business hours. A functional entry does not include any door exclusively designated as an emergency exit or a garage door not designed as a pedestrian entrance. |
|
|
employment center? |
A nonresidential area of at least 5 acres (2 hectares) with a job density of at least 50 employees per net acre (at least 125 employees per hectare net). |
|
|
brownfield? |
Real property or the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse of which may be complicated by the presence or possible presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant. |
|
|
long-term bicycle storage? |
Bicycle parking that is easily accessible to residents and employees and covered to protect bicycles from rain and snow. |
|
|
density? |
The ratio of building coverage on a given parcel of land to the size of that parcel. |
|
|
diverse use? |
A distinct business or organization that provides goods or services intended to meet daily needs and is publicly available. It does not include automated facilities such as ATMs, vending machines, and touchscreens. |
|
|
adjacent site? |
A site having at least a continuous 25% of its boundary bordering parcels that are previously developed sites. |
|
|
demand response (DR)? |
A change in electricity use by demand-side resources from their normal consumption patterns in response to changes in the price of electricity or to incentive payments designed to induce lower electricity use at times of high wholesale market prices or when system reliability is jeopardized. |
|
|
time-of-use pricing? |
An arrangement in which customers pay higher fees to use utilities during peak time periods and lower fees during off-peak time periods. |
|
|
intermodal facility? |
A venue for the movement of goods in a single loading unit or road vehicle that uses successively two or more modes of transportation without the need to handle the goods themselves. |
|
|
multitenant complex? |
A site that was master-planned for the development of stores, restaurants, and other businesses. Retailers may share some services and common areas. |
|
|
infill site? |
A site where at least 75% of the land area, exclusive of rights-of-way, within 1/2 mile (800 m) of the project boundary is previously developed. |
|
|
attendance boundary? |
The limits used by school districts to determine what school students attend based on where they live. |
|
|
preferred parking? |
The parking spots closest to the main entrance of a building (exclusive of spaces designated for handicapped persons). For employee parking, preferred parking refers to the spots that are closest to the entrance used by employees. |
|
|
What are the 7 site factors which will be included in site assessment? |
- topography - hydrology - climate - vegetation - soils - human use - human health effects |
|
|
The difference between SS Prerequisite-Environmental Site Assesment & SS Credit-site assesment? |
SS Prerequisite-Environmental Site Assesment concerns contaminants in site soils and/or ground water, and SS Credit-site assesment is about surveying site features to be utilized in design decisions for multiple credits & prerequisites. |
|
|
For SS-site develpoment- protect & restore habitat, there are 2 types of restoration, what are them? |
1- all projects must preserve and protect 40% of the greenfield area on site. 2- then, if they choose not to donate, they should use this formula: minimum restoration area=30% x Total previously developed site area |
|
|
For SS-site develpoment- protect & restore habitat, what is the donation formula? |
Min Financial contributiom=total site area (sq ft) x $0.40/sq ft |
|
|
For SS-open spaces, what are the formulas for required open spaces? |
Min open spaces=30% x total site area |
|
|
For SS-open spaces, what are the formulas for required vegetated spaces? |
Min vegetated spaces= 25% x open spaces |
|
|
For SS-open spaces, when does an accessible green roof count toward the vegetation requirement? |
If FAR is greater than 1.5 |
|
|
For SS-heat island reduction, what is the minimum percentage of covered parkings? |
75% |
|
|
How many lighting zone levels are there & what are them? |
There are 5 lighting zones range from natural environments with no artificial lighting(LZ0) to areas of very high ambient lighting, such as Times Square in NY city (LZ4). - LZ1(low)= single & multifamily residential communities, rural town centers, . . . - LZ2(Moderate)= multifamily & institutional uses, schools, hospitals, hotels,..... - LZ3(Moderately high)= town centers, commertial corridors, regional shopping malls, car dealership, . . . |
|
|
What are the important points regarding lighting boundary? |
- when the property line abuts a public area that includes, but is not limited to, a walkaway, bikeway, plaza, or parking lot, the lighting boundary may be moved to 5 ft (1.5 m) beyond the property line. - when the property abuts a public street, alley, or transit corridor, the lighting boundary may be moved to the center line of that street, alley, or corridor. - when there are additional properties owned by the same entity that are contiguous to the property (or properties) that the LEED project is within & have the same or higher MLO lighting zone designation as the LEED project, the lighting boundary may be expanded to include those properties. |
|
|
For light pollution, what are the maximum of calculation points & grade level? |
Calculation points may be no more than 5 ft apart and extend up from grade level to 33 ft above the height of the highest luminaire. |
|
|
solar reflectance index (SRI)? |
A measure of the constructed surfaces ability to stay cool in the sun by reflecting solar radiation and emitting thermal radiation. Standard black surface has an initial SRI of 0, and a standard white surface has an initial SRI of 100. |
|
|
light trespass? |
Obtrusive illumination that is unwanted because of quantitative, directional, or spectral attributes. Light trespass can cause annoyance, discomfort, distraction, or loss of visibility. |
|
|
solar reflectance (SR)? |
The fraction of solar energy that is reflected by a surface on a scale of 0 to 1. Black paint has a solar reflectance of 0; white paint has a solar reflectance of 1. |
|
|
site assessment? |
An evaluation of an areas above ground and subsurface characteristics, including its structures, geology, and hydrology. |
|
|
construction general permit (CGP)? |
A permit that requires compliance with effluent limits and construction stormwater discharge requirements where the EPA is the permitting authority. |
|
|
zero lot line project? |
A plot whose building footprint typically aligns or nearly aligns with the site limits. |
|
|
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) soils delineation? |
A U.S.-based soil survey that shows the boundaries of different soil types and special soil features on the site. |
|
|
three-year aged SR or SRI value? |
A solar reflectance or solar reflectance index rating that is measured after three years of weather exposure. |
|
|
place of respite? |
An area that connects healthcare patients, visitors, and staff to health benefits of the natural environment. |
|
|
inpatient? |
An individual admitted to a medical, surgical, maternity, specialty, or intensive-care unit for a length of stay exceeding 23 hours. |
|
|
master plan boundary? |
The limits of a site master plan, which includes the project area, may include all associated buildings and sites outside of the LEED project boundary, and considers future sustainable use, expansion, and contraction. The limits of a site master plan, which includes the project area, may include all associated buildings and sites outside of the LEED project boundary, and considers future sustainable use, expansion, and contraction. |
|
|
outpatient? |
A patient who is not hospitalized for 24 hours or more but who visits a hospital, clinic, or associated healthcare facility for diagnosis or treatment. |
|
|
thermal emittance? |
The ratio of the radiant heat flux emitted by a specimen to that emitted by a blackbody radiator at the same temperature. |
|
|
floor-area ratio (FAR)? |
The density of nonresidential land use, exclusive of parking, measured as the total nonresidential building floor area divided by the total buildable land area available for nonresidential structures. |
|
|
low-impact development (LID)? |
An approach to managing rainwater runoff that emphasizes on-site natural features to protect water quality, by replicating the natural land cover hydrologic regime of watersheds, and addressing runoff close to its source. |
|
|
open-grid pavement system? |
Pavements that consist of loose substrates supported by a grid of a more structurally sound grid or webbing. |
|
|
National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES)? |
A U.S. program that regulates stormwater discharges from construction activities that disturb 1 acre (0.4 hectare) or more and applies to smaller sites that are part of a larger development or sale. |
|
|
net usable program area? |
The sum of all interior areas in the project available to house the projects program, excluding areas for building equipment, vertical circulation, or structural components. |
|
|
multitenant complex? |
A site that was master-planned for the development of stores, restaurants, and other businesses. Retailers may share some services and common areas. |
|
|
site master plan? |
An overall design or development concept for the project and associated (or potentially associated) buildings and sites. The plan considers future sustainable use, expansion, and contraction. |
|
|
previously disturbed area? |
A defined area that has been graded, compacted, cleared, previously developed, or disturbed in any way. |
|
|
green infrastructure (GI)? |
A soil- and vegetation-based approach to wet weather management that is cost-effective, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. GI management approaches and technologies infiltrate, evapotranspire, capture, and reuse stormwater to maintain or restore natural hydrologies. |
|
|
What is LWR & what does it include? |
The landscape water requirement (LWR) is the amount of water that the site landscape area requires for the site's peak watering month. The factors used to calculate LWR are plant type, plant density, and the irrigation needs. |
|
|
What are the baseline water consumption of fixtures? |
- toilet=1.6 gpf - urinal=1.0 gpf - public restroom faucet= 0.5 gpm @ 60 psi - private restroom faucet= 2.2 gpm @ 60 psi - kitchen faucet= 2.2 gpm @ 60 psi -showerhead=2.5 gpm @ 80 psi |
|
|
What is the required information for USGBC Indoor Water Use Calculator? |
- Project occupancy (number of FTEs, visitors,....) - Gender ratio - Days of operation - Project fixture types |
|
|
What are private fixtures? |
Private fixtures are those fixtures in residential-type bathrooms, hotel guest rooms, dormitory resident bathrooms, prisoners bathrooms, or private rooms in healthcare projects. |
|
|
Regarding WE prerequisite, What is the maximum flow rate for a watersense aerator? |
1.5 gpm @ 60 psi |
|
|
Regarding WE prerequisite, What are the requirements for cooling tower & evaporative condensers? |
Cooling towers & evaporative condensers must have: - makeup water meters - conductivity controllers & overflow alarms - efficient drift eliminators |
|
|
What are the eligible alternatives to potable water? |
- municipally supplied reclaimed water ("purple pipe" water) - graywater - rainwater - stormwater - treated seawater condensate - foundation dewatering water - used process water - reverse-osmosis reject water |
|
|
Which type of water consumption is not included in WE credit-water metering? |
Cooling Towers |
|
|
For WE-Water Metering, what are the only 2 types of the consumption that need to be metered at 100%? |
- Boiler water - Reclaimed water |
|
|
process water? |
Water that is used for industrial processes and building systems, such as cooling towers, boilers, and chillers. It can also refer to water used in operational processes, such as dish washing, clothes washing, and ice making. |
|
|
reference evapotranspiration rate? |
The amount of water lost from a specific vegetated surface with no moisture limitation. Turf grass with height of 120 mm is the reference vegetation. |
|
|
conductivity? |
The measurement of the level of dissolved solids in water, using the ability of an electric current to pass through water. Because it is affected by temperature, conductivity is measured at 25°C for standardization. |
|
|
landscape water requirement (LWR)? |
The amount of water that the site landscape area(s) requires for the sites peak watering month. |
|
|
graywater? |
Untreated household wastewater which has not come into contact with toilet waste. Some states and local authorities allow kitchen sink wastewater to be included in graywater. |
|
|
WaterSense? |
A voluntary partnership and labeling program launched by the EPA in 2006 as a simple way for consumers to identify products that use 20% less water and perform well. |
|
|
hardscape? |
The inanimate elements of the building landscaping, including pavement, roadways, stone walls, wood and synthetic decking, concrete paths and sidewalks, and concrete, brick, and tile patios. |
|
|
evapotranspiration? |
The combination of evaporation and plant transpiration into the atmosphere. Evaporation occurs when liquid water from soil, plant surfaces, or water bodies becomes vapor. Transpiration is the movement of water through a plant and the subsequent loss of water vapor. |
|
|
cooling tower blowdown? |
The water discharged from a cooling tower typically because increased salinity or alkalinity has caused scaling. Cooling tower blowdown may be too saline for use in landscape irrigation. |
|
|
metering control? |
A regulator that limits the flow time of water, generally a manual-on and automatic-off device, most commonly installed on lavatory faucets and showers. |
|
|
external meter? |
A device installed on the outside of a water pipe to record the volume of water passing through it. Also known as a clamp-on meter. |
|
|
wet meter? |
A device installed inside a water pipe to record the volume of passing water. |
|
|
landscape water budget? |
A method used to calculate the amount of water a landscape needs, taking into account the inputs and outputs of water to and from the root zone. |
|
|
alternative water source? |
Nonpotable water from other than public utilities, on-site surface sources, and subsurface natural freshwater sources. Examples include graywater, on-site reclaimed water, collected rainwater, captured condensate, and rejected water from reverse-osmosis systems. |
|
|
What are the Commissioning(Cx) activities of the Commissioning Authority (CxA)? |
The CxA must perform the following Cx activities: - Review the OPR, BOD, and project design - Develop & implement a Cx plan - Confirm incorporation of Cx requirements into the construction documents - Develop construction checklists and a system test procedure. - Verify system test execution - Maintain a log of issues and benefits throughout the Cx process - Prepare a final Cx process report - Document all findings and recomendations and report directly to the owner |
|
|
The CxA should be engaged by the end of ........... phase as a requirement of EA Prerequisite-fundamental commisioning and verufication. |
Design Development |
|
|
What is Exceptional Calculation Method (ECP)? |
Exceptional Calculation Method (ECP) is a term used in ASHRAE 90.1 (energy efficiency). For the purpose of LEED, an ECM covers any savings claimed for an unregulated load. |
|
|
Regarding EA Prerequisite-Min Energy Performance, what is the minimum savings of energy & what is the percentage for power & cooling infrastructure? |
It requires 5% minimum savings which must include at least 2% coming from building power & cooling infrastructure. |
|
|
Regarding EA-optimize energy performance, What are the minimum saving percentages? |
- for New Constructions = %6 - for Major Renovation = 4% - for Core & Shell = 3% |
|
|
Regarding EA-Advanced energy metering, what type of appliances must be submetered? |
All end uses that contribute at least 10% of the total building energy use must be submetered. |
|
|
EA-Advanced Energy Metering requires that the meter must be capable of ....... |
- Storing data for 36 months - Reporting daily, hourly, monthly, and annual usage |
|
|
Qualified resources for EA-Green Power and Carbon Offsets must have come online since which date? |
Jan 1st, 2005 |
|
|
demand response (DR) event? |
A specific period of time when the utility or independent service operator calls for a change in the pattern or level of use in grid-based electricity from its program participants. Also known as a curtailment event. |
|
|
solar garden? |
A shared solar array or other renewable energy system with grid-connected subscribers who receive credit for the use of renewables using virtual net metering. Also known as a community renewable energy system. |
|
|
upstream equipment? |
A heating or cooling system or control associated with the district energy system (DES) but not part of the thermal connection or interface with the DES. |
|
|
Scope 1 emissions? |
Direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from sources owned or controlled by the entity, such as emissions from fossil fuels burned on site. |
|
|
global warming potential (GWP)? |
The ratio of the warming caused by a substance to the warming caused by a similar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2). |
|
|
district energy system (DES)? |
A central energy conversion plant and transmission and distribution system that provides thermal energy to a group of buildings (such as a central cooling plant on a university campus). It does not include central energy systems that provide only electricity. |
|
|
commissioning (Cx)? |
The process of verifying and documenting that a building and all of its systems and assemblies are planned, designed, installed, tested, operated, and maintained to meet the owners project requirements (OPR). |
|
|
Scope 2 emissions? |
Indirect greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with the generation of purchased electricity, heating/cooling, or steam off site, through a utility provider for the entitys consumption. |
|
|
natural refrigerant? |
A compound that is not manmade and is used for cooling. Such substances generally have much lower potential for atmospheric damage than manufactured chemical refrigerants. Examples include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and ammonia. |
|
|
commissioning authority (CxA)? |
The individual designated to organize, lead, and review the completion of commissioning (Cx) process activities. The CxA facilitates communication among the owner, designer, and contractor to ensure that complex systems are installed and function in accordance with the owners project requirements (OPR). |
|
|
downstream equipment? |
The heating and cooling systems, equipment, and controls located in the project building or on the project site and associated with transporting the thermal energy of the district energy system (DES) into heated and cooled spaces. |
|
|
carbon offset? |
A unit of carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent that is reduced, avoided, or sequestered to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere. |
|
|
ozone depletion potential (ODP)? |
The ozone depletion potential (ODP) is the ratio of the impact on ozone of a chemical compared to the impact of a similar mass of CFC-11, a commonly used refrigerant. |
|
|
combined heat and power? |
An integrated system that captures the heat, otherwise unused, generated by a single fuel source in the production of electrical power. Also known as cogeneration. |
|
|
recycled content? |
The proportion, by mass, of recycled material in a product or packaging as defined in accordance with the ISO 14021, Environmental Labels and Declarations, Self-Declared Environmental Claims (Type II Environmental Labeling). |
|
|
Health Product Declaration (HPD)? |
An open standard for reporting product ingredients and their associated health hazards. |
|
|
product (permanently installed building product)? |
An item that arrives on the project site either as a finished element ready for installation or as a component to another item assembled on site. |
|
|
source separated? |
Construction or demolition waste materials that are sorted into separate bins on the project site. This waste strategy often isolates waste materials targeted for reuse, donation, or recycling programs. Typically, sorted materials on site include metals, wood, ceiling tiles, furniture, and concrete. |
|
|
life-cycle inventory? |
A database that defines the environmental effects (inputs and outputs) for each step in a materials or assemblys life cycle. The database is specific to countries and regions within countries. |
|
|
universal waste? |
Hazardous items that are easily purchased and commonly used. Examples include batteries, pesticides, mercury-containing equipment, and light bulbs. |
|
|
enclosure? |
The exterior plus semi-exterior portions of the building. |
|
|
departmental gross area (DGA)? |
The floor area of a diagnostic and treatment of clinical department, calculated from the centerline of the walls separating the department from adjacent spaces. |
|
|
extended producer responsibility? |
Measures undertaken by the maker of a product to accept its own and sometimes other manufacturers products as postconsumer waste at the end of the products useful life. Producers recover and recycle the materials for use in new products of the same type. |
|
|
shell space? |
An area designed to be fitted out for future expansion. It is enclosed by the building envelope and left unfinished inside. |
|
|
chain of custody (CoC)? |
A procedure that tracks a product from the point of harvest or extraction to its end use, including all successive stages of processing, transformation, manufacturing, and distribution. |
|
|
embodied energy? |
The total energy consumed by the extraction of raw materials, the processing of the materials, and the manufacturing and delivery of a product. |
|
|
clean waste? |
Nonhazardous materials left over from construction and demolition. Clean waste excludes lead and asbestos. |
|
|
land-clearing debris and soil? |
Materials that are natural (such as rock, soil, stone, and vegetation). Materials that are manmade (such as concrete, brick, and cement) are considered construction waste even if they were on site. |
|
|
persistent bioaccumulative toxic chemical (PBT)? |
A substance that poses a long-term risk to both humans and the environment because it remains in the environment for long periods, increases in concentration as it moves up the food chain, and can travel far from the source of contamination. |
|
|
alternative daily cover (ADC)? |
Material other than earthen material placed on the surface of the active face of a municipal solid waste landfill at the end of each operating day to control vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and scavenging. |
|
|
interstitial space? |
An intermediate space located between floors with a walk-on deck, often used to run the majority of the utility distribution and terminal equipment. |
|
|
environmental product declaration (EPD)? |
A standardized, internationally recognized, comprehensive tool for providing information on a products environmental impact based on an ISO-compliant life-cycle assessment (LCA) and can be verified by a third party. |
|
|
biobased material? |
Commercial or industrial products (other than food or feed) that are composed in whole, or in significant part, of biological products, renewable agricultural materials (including plant, animal, and marine materials), or forestry materials. For the purposes of LEED, this excludes leather and other animal hides. |
|
|
life-cycle assessment (LCA)? |
An evaluation of the environmental effects of a product from cradle to grave, as defined by ISO 140402006 and ISO 140442006. |
|
|
soft space? |
An area whose functions can be easily changed. |
|
|
Total waste per area is only required for ......... of MR-Construction & Demolition Waste Management. |
Option 2 |
|
|
For MR-Construction & Demolition Waste Management, what is the percentage of waste diversion? |
At least 50% waste diversion |
|
|
What are source reduction strategies for option 2 of MR-Construction & Demolition Waste Management? |
- Prefabrication for wall assemblies - Modular design for bathrooms - Designs for standard material lengths for drywall & studs |
|
|
For MR-PBT Source Reduction-Mercury for a Healthcare, what Types of lamps are prohibited? |
- Flurescent lamps because of contamination - Probe-start metal halide lamps because of short life |
|
|
What is the difference between MR-Building Life-Cycle Impact Reduction & MR-Building Product Disclosure and Optimization-Sourcing of Raw Materials? |
Building and material reuse for MR-Building Life-Cycle Impact Reduction is measured in surface area. This is different from measurement of material reuse for MR-Building Product Disclosure and Optimization-Sourcing of Raw Materials where reuse is measured by cost or replacement value. |
|
|
Which type of Analysis for LCA? |
Cradle to Grave |
|
|
Which type of Analysis for EPD? |
Cradle to gate |
|
|
For MR-Building Disclosure and Optimization-Sourcing of Raw Materials, what are the important factors? |
- The product report must be current for the product at the time of installation. - Reports published within one year of the project's LEED registration date are acceptable - A compliant report must be issued by either the manufacturer or the raw material supplier. |
|
|
For MR-Material Ingredients, Cradle to Cradle(C2C) V3 Gold-certified products ....... |
Are valued at 150% of their cost |
|
|
The calculations for ventilation are run for the worst conditions, which typically occur when ........ |
the ventilation system in the heating mode and supply airflows are the lowest or supply air temprature is the highest. |
|
|
shared multioccupant space? |
A place of congregation, or where occupants pursue overlapping or collaborative tasks. |
|
|
view factor? |
A measure of the amount and quality of views within a 90° cone of vision from an individual workstation. View factor is rated from 0 (poor quality) to 5 (high quality). |
|
|
reverberation time (RT)? |
A measure of the amount of reverberation in a space and equal to the time required for the level of a steady sound to decay by 60 dB after the sound has stopped. |
|
|
color rendering index? |
A measurement from 0 to 100 that indicates how accurately an artificial light source, as compared with an incandescent light, displays hues. The higher the index number, the more accurately the light is rendering colors. |
|
|
regularly occupied space? |
An area where one or more individuals normally spend time (more than continuous one hour per person per day on average) seated or standing as they work, study, or perform other focused activities inside a building. |
|
|
densely occupied space? |
An area with a design occupant density of 25 people or more per 1000 ft2 (93 m2). |
|
|
pilot credit? |
A LEED rating system credit that is designed to test new and revised LEED credit language, alternative compliance paths, and new or innovative green building technologies and concepts. |
|
|
.......... is only applicable to healthcare projects for EQ-Acoustic Performance |
Speech Privacy |
|
|
............ is a good strategy to increase ventilation. |
Heat Recovery |
|
|
To achieve option 2 for naturally ventilated spaces the project can choose one of these sterategies: |
- Exterior contamination prevention - Additional source control and monitoring - Natural ventilation room-by-room calculations |
|
|
What documentations are acceptable for documenting low-emitting products? |
- Material Safety data sheets (MSDSs) - Testing Reports - Third-party certifications |
|
|
What are the categories included in the SMACNA Guidelines? |
- HVAC protection - pathway interruption - source control - scheduling - housekeeping |
|
|
If occupancy is desired before the flush-out is completed, the space may be occupied only after delivery of a minimum of ............. |
3500 ft3 of outdoor air/ft2 |
|
|
For indoor air quality, once a space is occupied, it must be ventilated at ...... |
Minimum rate of 0.3 cfm/ft2 |
|
|
How many points can a project achieve for IN-Innovation? |
Projects can earn an maximum of 5 points, but only 2 points of those can be earned through exemplary performance. |
|
|
Who identifies the regional priority credits? |
USGBC chapters and the LEED International Roundtable |
|
|
How many RP credit points may a project earn? |
4 |
|
|
What is the best time for IP-Integrative process? |
It should be addressed before the schematic design phase. |
|
|
What is the important point regarding water-related systems for IP-Integrative Process? |
It should be demonstrated how at least one nonpotable water supply source was used to offset at least two water demand components. (Indoor, outdoor, and process water) |

